|
Beacon Hill Formation
The Beacon Hill Formation is a geologic formation in Leicestershire, and lies within the wider Beacon Hill area. It preserves fossils dating back to the Lower Ediacaran period. Paleobiota The Beacon Hill Formation contains the oldest best preserved fossils within the Charnian Supergroup, most of which can be found in the Outwoods Member, with some found in the overlying and underlying members. Petalonamae ''incertae sedis'' Ivesheadiomorph See also * List of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in the United Kingdom *List of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in England See also * Lists of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in Europe * Lists of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in the United Kingdom References * {{DEFAULTSORT:Fossiliferous stratigraphi ... References * {{cite web, title= Fossilworks: Gateway to the Paleobiology Database, author= ((Various Contributors to the Paleobiology Database)), url= https://www.fossilworks.org, access-date= 17 De ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formation (geology)
A geological formation, or simply formation, is a body of rock having a consistent set of physical characteristics ( lithology) that distinguishes it from adjacent bodies of rock, and which occupies a particular position in the layers of rock exposed in a geographical region (the stratigraphic column). It is the fundamental unit of lithostratigraphy, the study of strata or rock layers. A formation must be large enough that it can be mapped at the surface or traced in the subsurface. Formations are otherwise not defined by the thickness of their rock strata, which can vary widely. They are usually, but not universally, tabular in form. They may consist of a single lithology (rock type), or of alternating beds of two or more lithologies, or even a heterogeneous mixture of lithologies, so long as this distinguishes them from adjacent bodies of rock. The concept of a geologic formation goes back to the beginnings of modern scientific geology. The term was used by Abraham Gottlob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Period (geology)
The geologic time scale or geological time scale (GTS) is a representation of time based on the rock record of Earth. It is a system of chronological dating that uses chronostratigraphy (the process of relating strata to time) and geochronology (a scientific branch of geology that aims to determine the age of rocks). It is used primarily by Earth scientists (including geologists, paleontologists, geophysicists, geochemists, and paleoclimatologists) to describe the timing and relationships of events in geologic history. The time scale has been developed through the study of rock layers and the observation of their relationships and identifying features such as lithologies, paleomagnetic properties, and fossils. The definition of standardised international units of geological time is the responsibility of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS), a constituent body of the International Union of Geological Sciences (IUGS), whose primary objective is to precisely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Fossiliferous Stratigraphic Units In The United Kingdom
*List of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in England See also * Lists of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in Europe * Lists of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in the United Kingdom References * {{DEFAULTSORT:Fossiliferous stratigraphic units in England England England is a Countr ... * List of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in Wales * List of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in Scotland * List of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in Northern Ireland {{DEFAULTSORT:Fossiliferous stratigraphic units in the United Kingdom * * United Kingdom geology-related lists United Kingdom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudovendia Charnwoodensis
The "ivesheadiomorphs" are a group of fossilised structures known from Ediacaran localities in England and Newfoundland. They are considered to be taphomorphs, representing the poorly preserved biological remains of various contemporary taxa such as ''Charnia'', '' Charniodiscus'', ''Bradgatia'', '' Primocandelabrum'', ''Pectinifrons'' and others, that were effaced by partial decay by micro-organisms following death on the seafloor before burial by sediment. Ivesheadiomorph structures were previously described as distinct organisms, namely ''Ivesheadia lobata'' ("pizza disk"), ''Blackbrookia oaksi'', ''Shepshedia palmata'' and ''Pseudovendia charnwoodensis''. However, all of these fossils have since been rejected as valid taxa. See also * List of Ediacaran genera The existence of life, especially that of animals, before the Cambrian had long been the subject of debate in paleontology. The apparent suddenness of the Cambrian explosion had no firm explanation, and Charles Darwin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hiemalora Stellaris
''Hiemalora'' is a fossil of the Ediacaran biota, reaching around 3 cm in diameter, which superficially resembles a sea anemone. The genus has a sack-like body with faint radiating lines originally interpreted as tentacles, but discovery of a frond-like structure seemingly attached to some ''Heimalora'' has added weight to a competing interpretation: that it represents the holdfast of a larger organism. In 2020, a new study was published that described nine different specimens from the Indreelva member, Digermulen Peninsula, Finnmark (Arctic Norway). The specimens described in the paper have high degrees of variation between morphologies and within the specimens that are thought to be of the same species. Some of the representative fossils from that paper either show multiple Aspidella-like structures on the same specimen, or a Primocandelabrum-like cone visible in one of the fossils. All of the examples of fossils in the publication were determined to most likely represen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclomedusa
''Cyclomedusa'' is a circular fossil of the Ediacaran biota; it has a circular bump in the middle and as many as five circular growth ridges around it. Many specimens are small, but specimens in excess of 20 cm are known. The concentric disks are not necessarily circular, especially when adjacent individuals interfere with each other's growth. Many radial segment lines — somewhat pineapple-like — extend across the outer disks. A few specimens show what might be a stem extending from the center in some direction or other. ''Cyclomedusa'' is widely distributed in Ediacaran strata, with a number of species described. It has also been found in sediments dating to the Tonian (~). ''Cyclomedusa'' was originally thought to be a jellyfish but some specimens seem to be distorted to accommodate adjacent specimens on the substrate, apparently indicating a benthic (bottom-dwelling) creature. The markings do not match the musculature pattern of modern jellyfish. The fossils have b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
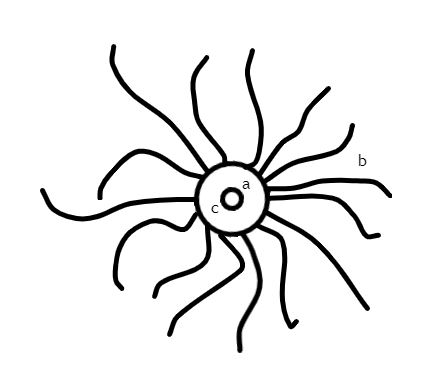
Aspidella Surface
:Aspidella'' is also a homonym for the mushroom genus ''Saproamanita. ''Aspidella'' is an Ediacaran disk-shaped fossil of uncertain affinity. It is known from the single species ''A. terranovica''. Morphology ''Aspidella'' consists of disk-shaped fossils, with concentric rings and/or centripetal rays. The diameter of circular ''Aspidella'' varies from 1 to 180 mm.Peterson. P. 131 Most individuals are between 4 and 10 mm, but smaller individuals would presumably have decayed before they could fossilize. Other ''Aspidella'' take the form of ellipses, 3–8 cm long and 1–4 cm wide. Most have a central pimple. The rim of all specimens is made up by ridge-edged rays and/or concentric rings. Ecology The rarity of large individuals probably indicates that ''Aspidella'' were R/K selection theory, r-strategists, producing numerous offspring of which most died young. It is most common in deep-water sediments, but is a constituent of most Ediacaran fossil assemb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aspidella
:Aspidella'' is also a homonym for the mushroom genus '' Saproamanita. ''Aspidella'' is an Ediacaran disk-shaped fossil of uncertain affinity. It is known from the single species ''A. terranovica''. Morphology ''Aspidella'' consists of disk-shaped fossils, with concentric rings and/or centripetal rays. The diameter of circular ''Aspidella'' varies from 1 to 180 mm.Peterson. P. 131 Most individuals are between 4 and 10 mm, but smaller individuals would presumably have decayed before they could fossilize. Other ''Aspidella'' take the form of ellipses, 3–8 cm long and 1–4 cm wide. Most have a central pimple. The rim of all specimens is made up by ridge-edged rays and/or concentric rings. Ecology The rarity of large individuals probably indicates that ''Aspidella'' were r-strategists, producing numerous offspring of which most died young. It is most common in deep-water sediments, but is a constituent of most Ediacaran fossil assemblages, including tho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charnia
''Charnia'' is an extinct genus of frond-like lifeforms belonging to the Ediacaran biota with segmented, leaf-like ridges branching alternately to the right and left from a zig-zag medial suture (thus exhibiting glide reflection, or opposite isometry). The genus ''Charnia'' was named after Charnwood Forest in Leicestershire, England, where the first fossilised specimen was found; the species was named after Roger Mason, a schoolboy who was believed to have initially discovered it. ''Charnia'' is significant because it was the first Precambrian fossil to be recognized as such. The living organism grew on the sea floor, 570 to 550 million years ago, and is believed to have fed on nutrients in the water. Despite ''Charnia'' fern-like appearance, it is not a photosynthetic plant or alga because the nature of the fossil beds where specimens have been found implies that it originally lived in deep water, well below the photic zone where photosynthesis can occur. Diversity Severa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charnian Supergroup
The Charnian Supergroup is a geologic supergroup in the United Kingdom, and is a part of the wider Charnwood terrane. It preserves fossils dating back to the Ediacaran and through into the Cambrian period, with suggestions that the Brand Group and Maplewell Groups have a major hiatus in-between. It mainly contains volcaniclastics, but is interrupted by and succeeded by greywackes, and is interbedded with pelites, tuffs. Due to the thickness of the Supergroup, it spans over , with a possible lower date of and a maximum upper date of . This also means that it spans across two Ediacaran assemblages, with the Blackbrook Group and part of the lower Maplewell Group sitting within the Avalon assemblage, whilst the rest of the Maplewell Group sits within the White Sea assemblage. The Brand Group was originally a part of the supergroup, until the discovery of several ichnogenera, like '' Teichichnus'', which helped to date it to the Lower Cambrian, and was subsequently taken out of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |