|
Bayfordbury Observatory
Bayfordbury Observatory is the University of Hertfordshire's astronomical and atmospheric physics remote sensing observatory, and one of the largest teaching observatories in the UK. It is located in the relatively dark countryside of Bayfordbury, Hertfordshire, 6 miles from the main university campus in Hatfield. The first telescope was built in 1969, and since then has been used as a teaching observatory for undergraduate students, staff and student research as well as for public outreach activities. History The first telescope, a 16-inch Newtonian/ Cassegrain telescope, was built on the site in 1969, one year after astronomy was first taught at the Hatfield Polytechnic. In 1970 the observatory was formally opened by Richard van der Riet Woolley, then Astronomer Royal. Over the years the number of telescopes has increased along with the size of astronomy department. On the 30th anniversary in 2000, the observatory underwent a large renovation. Three new telescope domes a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Hertfordshire
The University of Hertfordshire (UH) is a public university in Hertfordshire, United Kingdom. The university is based largely in Hatfield, Hertfordshire, Hatfield, Hertfordshire. Its antecedent institution, Hatfield Technical College, was founded in 1948 and was identified as one of 25 Colleges of Technology in the United Kingdom in 1959. In 1992, Hatfield Polytechnic was granted university status by the British government and subsequently renamed University of Hertfordshire. It is one of the post-1992 universities. Hertfordshire is mainly based at two campuses - College Lane and de Havilland. As of 2021, it has over 25,130 students, including more than 5,200 international students that together represent 100 countries. The university is one of Hertfordshire's largest employers with over 2,700 staff, 812 of whom are academic members of staff. It has a turnover of more than £235 million. The university has 9 schools: Hertfordshire Business School, Computer Science, Creative Arts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Telescopes
An optical telescope is a telescope that gathers and focuses light mainly from the visible part of the electromagnetic spectrum, to create a magnified image for direct visual inspection, to make a photograph, or to collect data through electronic image sensors. There are three primary types of optical telescope: * Refracting telescopes, which use lenses and less commonly also prisms ( dioptrics) * Reflecting telescopes, which use mirrors ( catoptrics) * Catadioptric telescopes, which combine lenses and mirrors An optical telescope's ability to resolve small details is directly related to the diameter (or aperture) of its objective (the primary lens or mirror that collects and focuses the light), and its light-gathering power is related to the area of the objective. The larger the objective, the more light the telescope collects and the finer detail it resolves. People use optical telescopes (including monoculars and binoculars) for outdoor activities such as observation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomical Interferometer
An astronomical interferometer or telescope array is a set of separate telescopes, mirror segments, or radio telescope antenna (radio), antennas that work together as a single telescope to provide higher resolution images of astronomical objects such as stars, nebulas and galaxy, galaxies by means of interferometry. The advantage of this technique is that it can theoretically produce images with the angular resolution of a huge telescope with an aperture equal to the separation between the component telescopes. The main drawback is that it does not collect as much light as the complete instrument's mirror. Thus it is mainly useful for fine resolution of more luminous astronomical objects, such as close binary stars. Another drawback is that the maximum angular size of a detectable emission source is limited by the minimum gap between detectors in the collector array. Interferometry is most widely used in radio astronomy, in which signals from separate radio telescopes are combi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Line
The hydrogen line, 21 centimeter line, or H I line is the electromagnetic radiation spectral line that is created by a change in the energy state of neutral hydrogen atoms. This electromagnetic radiation has a precise frequency of , which is equivalent to the vacuum wavelength of in free space. This frequency falls below the microwave region of the electromagnetic spectrum, which begins at 3.0 GHz (10 cm wavelength), and it is observed frequently in radio astronomy because those radio waves can penetrate the large clouds of interstellar cosmic dust that are opaque to visible light. This line is also the theoretical basis of the hydrogen maser. The microwaves of the hydrogen line come from the atomic transition of an electron between the two hyperfine levels of the hydrogen 1 s ground state that have an energy difference of []. It is called the ''spin-flip transition''. The frequency, , of the quantum, quanta that are emitted by this transition bet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radio Telescope
A radio telescope is a specialized antenna and radio receiver used to detect radio waves from astronomical radio sources in the sky. Radio telescopes are the main observing instrument used in radio astronomy, which studies the radio frequency portion of the electromagnetic spectrum emitted by astronomical objects, just as optical telescopes are the main observing instrument used in traditional optical astronomy which studies the light wave portion of the spectrum coming from astronomical objects. Unlike optical telescopes, radio telescopes can be used in the daytime as well as at night. Since astronomical radio sources such as planets, stars, nebulas and galaxies are very far away, the radio waves coming from them are extremely weak, so radio telescopes require very large antennas to collect enough radio energy to study them, and extremely sensitive receiving equipment. Radio telescopes are typically large parabolic ("dish") antennas similar to those employed in trackin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radio Astronomy
Radio astronomy is a subfield of astronomy that studies celestial objects at radio frequencies. The first detection of radio waves from an astronomical object was in 1933, when Karl Jansky at Bell Telephone Laboratories reported radiation coming from the Milky Way. Subsequent observations have identified a number of different sources of radio emission. These include stars and galaxies, as well as entirely new classes of objects, such as radio galaxies, quasars, pulsars, and masers. The discovery of the cosmic microwave background radiation, regarded as evidence for the Big Bang theory, was made through radio astronomy. Radio astronomy is conducted using large radio antennas referred to as radio telescopes, that are either used singularly, or with multiple linked telescopes utilizing the techniques of radio interferometry and aperture synthesis. The use of interferometry allows radio astronomy to achieve high angular resolution, as the resolving power of an interferom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
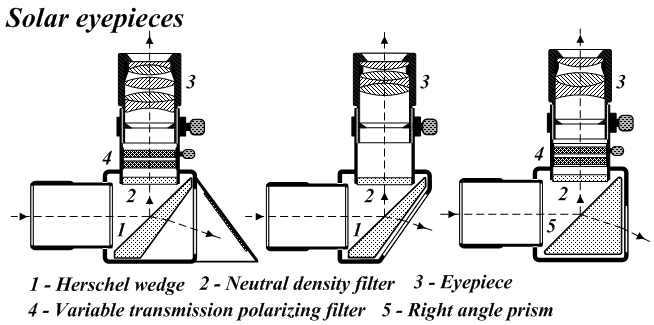
Solar Telescope
A solar telescope is a special purpose telescope used to observe the Sun. Solar telescopes usually detect light with wavelengths in, or not far outside, the visible spectrum. Obsolete names for Sun telescopes include heliograph and photoheliograph. Professional solar telescopes Solar telescopes need optics large enough to achieve the best possible diffraction limit but less so for the associated light-collecting power of other astronomical telescopes. However, recently newer narrower filters and higher framerates have also driven solar telescopes towards photon-starved operations. Both the Daniel K. Inouye Solar Telescope as well as the proposed European Solar Telescope (EST) have larger apertures not only to increase the resolution, but also to increase the light-collecting power. Because solar telescopes operate during the day, seeing is generally worse than for night-time telescopes, because the ground around the telescope is heated which causes turbulence and degrades ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
H-alpha
H-alpha (Hα) is a specific deep-red visible spectral line in the Balmer series with a wavelength of 656.28 nm in air and 656.46 nm in vacuum; it occurs when a hydrogen electron falls from its third to second lowest energy level. H-alpha light is the brightest hydrogen line in the visible spectral range. It is important to astronomers as it is emitted by many emission nebulae and can be used to observe features in the Sun's atmosphere, including solar prominences and the chromosphere. Balmer series According to the Bohr model of the atom, electrons exist in quantized energy levels surrounding the atom's nucleus. These energy levels are described by the principal quantum number ''n'' = 1, 2, 3, ... . Electrons may only exist in these states, and may only transit between these states. The set of transitions from ''n'' ≥ 3 to ''n'' = 2 is called the Balmer series and its members are named sequentially by Greek letters: *''n'' = 3 to ''n'' = 2 is called Balmer-alp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autoguider
An autoguider is an automatic electronic guidance tool used in astronomy to keep a telescope pointed precisely at an object being observed. This prevents the object from drifting across the field of view during long-exposures which would create a blurred or elongated image. Usage Imaging of dim celestial targets, usually deep sky objects, requires exposure times of many minutes, particularly when narrowband images are being taken. In order for the resulting image to maintain usable clarity and sharpness during these exposures, the target must be held at the same position within the telescope's field of view during the whole exposure; any apparent motion would cause point sources of light (such as stars) to appear as streaks, or the object being photographed to appear blurry. Even computer-tracked mounts and GoTo telescopes do not eliminate the need for tracking adjustments for exposures beyond a few minutes, as astrophotography demands an extremely high level of precision that the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Video Astronomy
Video astronomy ''(aka - Camera Assisted Astronomy, aka electronically-assisted astronomy or "EAA")'' is a branch of astronomy for near real-time observing of relatively faint astronomical objects using very sensitive CCD or CMOS cameras. Unlike lucky imaging, video astronomy does not discard unwanted frames, and image corrections such as dark subtraction are often not applied, however, the gathered data may be retained and processed in more traditional ways.. Although the field has a long history reaching back to 1928 with the inception of live television broadcasting of the planet Mars, it has largely been developed more recently by amateur enthusiasts and is characterized by the use of relatively inexpensive equipment, such as easily available sensitive security cameras, in contrast to the equipment used for advanced astrophotography. By using either method of rapid internally stacked images, or very short exposure times, and using a TV monitor (for analog cameras) or a compute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectrograph
An optical spectrometer (spectrophotometer, spectrograph or spectroscope) is an instrument used to measure properties of light over a specific portion of the electromagnetic spectrum, typically used in spectroscopic analysis to identify materials. The variable measured is most often the light's intensity but could also, for instance, be the polarization state. The independent variable is usually the wavelength of the light or a unit directly proportional to the photon energy, such as reciprocal centimeters or electron volts, which has a reciprocal relationship to wavelength. A spectrometer is used in spectroscopy for producing spectral lines and measuring their wavelengths and intensities. Spectrometers may operate over a wide range of non-optical wavelengths, from gamma rays and X-rays into the far infrared. If the instrument is designed to measure the spectrum on an absolute scale rather than a relative one, then it is typically called a spectrophotometer. The majori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Active-pixel Sensor
An active-pixel sensor (APS) is an image sensor where each pixel sensor unit cell has a photodetector (typically a pinned photodiode) and one or more active transistors. In a metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) active-pixel sensor, MOS field-effect transistors (MOSFETs) are used as amplifiers. There are different types of APS, including the early NMOS APS and the now much more common complementary MOS (CMOS) APS, also known as the CMOS sensor. CMOS sensors are used in digital camera technologies such as cell phone cameras, web cameras, most modern digital pocket cameras, most digital single-lens reflex cameras (DSLRs), and mirrorless interchangeable-lens cameras (MILCs). CMOS sensors emerged as an alternative to charge-coupled device (CCD) image sensors and eventually outsold them by the mid-2000s decade. The term ''active pixel sensor'' is also used to refer to the individual pixel sensor itself, as opposed to the image sensor. In this case, the image sensor is sometim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)





.jpg)

