|
Bayer Process
The Bayer process is the principal industrial means of refining bauxite to produce alumina (aluminium oxide) and was developed by Carl Josef Bayer. Bauxite, the most important ore of aluminium, contains only 30–60% aluminium oxide (Al2O3), the rest being a mixture of silica, various iron oxides, and titanium dioxide. The aluminium oxide must be further purified before it can be refined into aluminium. The Bayer process is also the main source of gallium as a byproduct despite low extraction yields. Process Bauxite ore is a mixture of hydrated aluminium oxides and compounds of other elements such as iron. The aluminium compounds in the bauxite may be present as gibbsite (Al(OH)3), böhmite (γ-AlO(OH)) or diaspore (α-AlO(OH)); the different forms of the aluminium component and the impurities dictate the extraction conditions. Aluminium oxides and hydroxides are amphoteric, meaning that they are both acidic and basic. The solubility of Al(III) in water is very low but in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
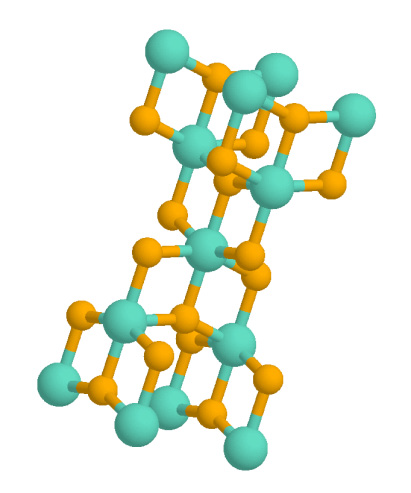
Bauxite
Bauxite () is a sedimentary rock with a relatively high aluminium content. It is the world's main source of aluminium and gallium. Bauxite consists mostly of the aluminium minerals gibbsite (), boehmite (γ-AlO(OH)), and diaspore (α-AlO(OH)), Mixture, mixed with the two iron oxides goethite (FeO(OH)) and haematite (), the aluminium Clay minerals, clay mineral kaolinite () and small amounts of anatase () and ilmenite ( or ). Bauxite appears dull in Lustre (mineralogy), luster and is reddish-brown, white, or tan. In 1821, the French people, French geologist Pierre Berthier discovered bauxite near the village of Les Baux-de-Provence, Les Baux in Provence, southern France. Formation Numerous classification schemes have been proposed for bauxite but, , there was no consensus. Vadász (1951) distinguished Laterite, lateritic bauxites (silicate bauxites) from karst bauxite ores (carbonate bauxites): * The carbonate bauxites occur predominantly in Europe, Guyana, Suriname, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seed Crystal
A seed crystal is a small piece of single crystal or polycrystal material from which a large crystal of typically the same material is grown in a laboratory. Used to replicate material, the use of seed crystal to promote growth avoids the otherwise slow randomness of natural crystal growth, and allows manufacture on a scale suitable for industry. Crystal enlargement The large crystal can be grown by dipping the seed into a supersaturated solution, into molten material that is then cooled, or by growth on the seed face by passing vapor of the material to be grown over it. Theory The theory behind this effect is thought to derive from the physical intermolecular interaction that occurs between compounds in a supersaturated solution (or possibly vapor). In solution, liberated (soluble) molecules (solute) are free to move about in random flow. This random flow permits for the possibility of two or more molecular compounds to interact. This interaction can potentiate intermolecular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aluminium Sulfate
Aluminium sulfate is a salt with the chemical formula, formula . It is soluble in water and is mainly used as a Coagulation (water treatment), coagulating agent (promoting particle collision by neutralizing charge) in the purification of drinking water and wastewater treatment plants, and also in paper manufacturing. The anhydrous form occurs naturally as a rare mineral millosevichite, found for example in volcanic environments and on burning coal-mining waste dumps. Aluminium sulfate is rarely, if ever, encountered as the anhydrous salt. It forms a number of different hydrates, of which the hexadecahydrate and octadecahydrate are the most common. The heptadecahydrate, whose formula can be written as , occurs naturally as the mineral alunogen. Aluminium sulfate is sometimes called alum or papermaker's alum in certain industries. However, the name "alum" is more commonly and properly used for any double sulfate salt with the generic formula , where ''X'' is a valence (chemistry) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Carbonate
Sodium carbonate (also known as washing soda, soda ash, sal soda, and soda crystals) is the inorganic compound with the formula and its various hydrates. All forms are white, odourless, water-soluble salts that yield alkaline solutions in water. Historically, it was extracted from the ashes of plants grown in sodium-rich soils, and because the ashes of these sodium-rich plants were noticeably different from ashes of wood (once used to produce potash), sodium carbonate became known as "soda ash". It is produced in large quantities from sodium chloride and limestone by the Solvay process, as well as by carbonating sodium hydroxide which is made using the chloralkali process. Hydrates Sodium carbonate is obtained as three hydrates and as the anhydrous salt: * sodium carbonate decahydrate ( natron), Na2CO3·10H2O, which readily effloresces to form the monohydrate. * sodium carbonate heptahydrate (not known in mineral form), Na2CO3·7H2O. * sodium carbonate monohydrate ( thermonatr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Precipitation (chemistry)
In an aqueous solution, precipitation is the "sedimentation of a solid material (a precipitate) from a liquid solution". The solid formed is called the precipitate. In case of an inorganic chemical reaction leading to precipitation, the chemical reagent causing the solid to form is called the precipitant. The clear liquid remaining above the precipitated or the centrifuged solid phase is also called the supernate or supernatant. The notion of precipitation can also be extended to other domains of chemistry (organic chemistry and biochemistry) and even be applied to the solid phases (e.g. metallurgy and alloys) when solid impurities segregation (materials science), segregate from a solid phase. Supersaturation The precipitation of a compound may occur when its concentration exceeds its solubility. This can be due to temperature changes, solvent evaporation, or by mixing solvents. Precipitation occurs more rapidly from a strongly supersaturated solution. The formation of a pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkali
In chemistry, an alkali (; from the Arabic word , ) is a basic salt of an alkali metal or an alkaline earth metal. An alkali can also be defined as a base that dissolves in water. A solution of a soluble base has a pH greater than 7.0. The adjective alkaline, and less often, alkalescent, is commonly used in English as a synonym for basic, especially for bases soluble in water. This broad use of the term is likely to have come about because alkalis were the first bases known to obey the Arrhenius definition of a base, and they are still among the most common bases. Etymology The word ''alkali'' is derived from Arabic ''al qalīy'' (or ''alkali''), meaning (see calcination), referring to the original source of alkaline substances. A water-extract of burned plant ashes, called potash and composed mostly of potassium carbonate, was mildly basic. After heating this substance with calcium hydroxide (''slaked lime''), a far more strongly basic substance known as ''caustic potash ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titanium Dioxide
Titanium dioxide, also known as titanium(IV) oxide or titania , is the inorganic compound derived from titanium with the chemical formula . When used as a pigment, it is called titanium white, Pigment White 6 (PW6), or Colour Index International, CI 77891. It is a white solid that is insoluble in water, although mineral forms can appear black. As a pigment, it has a wide range of applications, including paint, sunscreen, and food coloring. When used as a food coloring, it has E number E171. World production in 2014 exceeded 9 million tonnes. It has been estimated that titanium dioxide is used in two-thirds of all pigments, and pigments based on the oxide have been valued at a price of $13.2 billion. Structure In all three of its main dioxides, titanium exhibits Octahedral molecular geometry, octahedral geometry, being bonded to six oxide anions. The oxides in turn are bonded to three Ti centers. The overall crystal structures of rutile and anatase are tetragonal in symmetry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcia
Calcium oxide (formula: Ca O), commonly known as quicklime or burnt lime, is a widely used chemical compound. It is a white, caustic, alkaline, crystalline solid at room temperature. The broadly used term '' lime'' connotes calcium-containing inorganic compounds, in which carbonates, oxides, and hydroxides of calcium, silicon, magnesium, aluminium, and iron predominate. By contrast, ''quicklime'' specifically applies to the single compound calcium oxide. Calcium oxide that survives processing without reacting in building products, such as cement, is called free lime. Quicklime is relatively inexpensive. Both it and the chemical derivative calcium hydroxide (of which quicklime is the base anhydride) are important commodity chemicals. Preparation Calcium oxide is usually made by the thermal decomposition of materials, such as limestone or seashells, that contain calcium carbonate (CaCO3; mineral calcite) in a lime kiln. This is accomplished by heating the material to above ,Merc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron Oxides
An iron oxide is a chemical compound composed of iron and oxygen. Several iron oxides are recognized. Often they are nonstoichiometric, non-stoichiometric. Ferric oxyhydroxides are a related class of compounds, perhaps the best known of which is rust. Iron oxides and oxyhydroxides are widespread in nature and play an important role in many geological and biological processes. They are used as iron ores, pigments, Catalysis, catalysts, and in thermite, and occur in hemoglobin. Iron oxides are inexpensive and durable pigments in paints, coatings and colored concretes. Colors commonly available are in the "earth tone, earthy" end of the yellow/orange/red/brown/black range. When used as a food coloring, it has E number E172. Stoichiometries Iron oxides feature as ferrous (Iron(II), Fe(II)) or Iron(III), ferric (Iron(III), Fe(III)) or both. They adopt Octahedral molecular geometry, octahedral or Tetrahedral molecular geometry, tetrahedral coordination geometry. Only a few oxide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bauxite Tailings
Red mud, now more frequently termed bauxite residue, is an industrial waste generated during the processing of bauxite into alumina using the Bayer process. It is composed of various oxide compounds, including the iron oxides which give its red colour. Over 97% of the alumina produced globally is through the Bayer process; for every tonne () of alumina produced, approximately of red mud are also produced; the global average is 1.23. Annual production of alumina in 2023 was over resulting in the generation of approximately of red mud. Due to this high level of production and the material's high alkalinity, if not stored properly, it can pose a significant environmental hazard. As a result, significant effort is being invested in finding better methods for safe storage and dealing with it such as waste valorization in order to create useful materials for cement and concrete.Evans, K., "The History, Challenges and new developments in the management and use of Bauxite Residue", ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Starch
Starch or amylum is a polymeric carbohydrate consisting of numerous glucose units joined by glycosidic bonds. This polysaccharide is produced by most green plants for energy storage. Worldwide, it is the most common carbohydrate in human diets, and is contained in large amounts in staple foods such as wheat, potatoes, maize (corn), rice, and cassava (manioc). Pure starch is a white, tasteless and odorless powder that is insoluble in cold water or Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol. It consists of two types of molecules: the linear and helix, helical amylose and the branched amylopectin. Depending on the plant, starch generally contains 20 to 25% amylose and 75 to 80% amylopectin by weight. Glycogen, the energy reserve of animals, is a more highly branched version of amylopectin. In industry, starch is often converted into sugars, for example by malting. These sugars may be fermentation, fermented to produce ethanol in the manufacture of beer, whisky and biofuel. In addition, sugars ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |