|
Bayeke People
The Garanganze, Yeke or Bayeke are a people of Katanga, in the Democratic Republic of Congo. They established the Yeke Kingdom under the warrior-king Msiri, who dominated the southern part of Central Africa from 1850 to 1891 and controlled the trade route between Angola and Zanzibar from his capital, at Bunkeya. Msiri and his people were originally Nyamwezi traders from around Tabora who migrated to Katanga to reach the source of copper, ivory and slaves to trade. They took over and merged with a Wasanga chieftainship and established a powerful base by conquering neighbouring tribes. In 1891, Msiri was killed by the Stairs Expedition sent by King Leopold II of Belgium to take possession of Katanga for his Congo Free State. Many of the Yeke dispersed, with some settling in the Luapula Valley and the western shores of Lake Mweru around the Garanganze Missions of the Plymouth Brethren, led by Dan Crawford. Others who had been regarded as the Yeke were reabsorbed into the W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Katanga Province
Katanga was one of the four large provinces created in the Belgian Congo in 1914. It was one of the eleven provinces of the Democratic Republic of the Congo between 1966 and 2015, when it was split into the Tanganyika Province, Tanganyika, Haut-Lomami, Lualaba Province, Lualaba, and Haut-Katanga provinces. Between 1971 and 1997 (during the rule of Mobutu Sese Seko when Congo was known as Zaire), its official name was Shaba Province. Katanga's area encompassed . Farming and ranching are carried out on the Katanga Plateau. The eastern part of the province is a rich mining region which supplies cobalt, copper, tin, radium, uranium, and diamonds. The region's former capital, Lubumbashi, is the second-largest city in the Congo. History Copper mining in Katanga dates back over 1,000 years, and mines in the region were producing standard-sized ingots of copper for international transport by the end of the 10th century CE. In the 1890s, the province was beleaguered from the south by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congo Free State
The Congo Free State, also known as the Independent State of the Congo (), was a large Sovereign state, state and absolute monarchy in Central Africa from 1885 to 1908. It was privately owned by Leopold II of Belgium, King Leopold II, the constitutional monarch of the Kingdom of Belgium. In legal terms, the two separate countries were in a personal union. The Congo Free State was not a part of, nor did it belong to, Belgium. Leopold was able to Colonization of the Congo Basin, seize the region by convincing other European states at the Berlin Conference on Africa that he was involved in humanitarian and philanthropic work and would not tax trade. Via the International Association of the Congo, he was able to lay claim to most of the Congo Basin. On 29 May 1885, after the closure of the Berlin Conference, the king announced that he planned to name his possessions "the Congo Free State", an appellation which was not yet used at the Berlin Conference and which officially replaced "I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People From Katanga Province
The term "the people" refers to the public or common mass of people of a polity. As such it is a concept of human rights law, international law as well as constitutional law, particularly used for claims of popular sovereignty. In contrast, a people is any plurality of persons considered as a whole. Used in politics and law, the term "a people" refers to the collective or community of an ethnic group or nation. Concepts Legal Chapter One, Article One of the Charter of the United Nations states that "peoples" have the right to self-determination. Though the mere status as peoples and the right to self-determination, as for example in the case of Indigenous peoples (''peoples'', as in all groups of indigenous people, not merely all indigenous persons as in ''indigenous people''), does not automatically provide for independent sovereignty and therefore secession. Indeed, judge Ivor Jennings identified the inherent problems in the right of "peoples" to self-determination, as i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethnic Groups In The Democratic Republic Of The Congo
demography, Demographic features of the population of the Democratic Republic of the Congo include Ethnic group, ethnicity, education level, health, Socioeconomic status, economic status, Religion in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, religious affiliations and other aspects of the population. As many as 250 ethnic groups have been distinguished and named. The most numerous people are the Luba people, Luba, Mongo people, Mongo, and Bakongo, Kongo. Although 700 local languages and dialects are spoken, the linguistic variety is bridged both by the use of French language, French, and the intermediary languages Kituba language, Kikongo ya leta, Luba-Kasai language, Tshiluba, Swahili language, Swahili, and Lingala language, Lingala. Population The The World Factbook, CIA World Factbook estimated the population to be over 105 million as of 2022 (the exact number being 108,407,721), now exceeding that of Vietnam (with 98,721,275 inhabitants as of 2020) and ascending the country to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mobutu
Mobutu Sese Seko Kuku Ngbendu wa za Banga ( ; born Joseph-Désiré Mobutu; 14 October 1930 – 7 September 1997), often shortened to Mobutu Sese Seko or Mobutu and also known by his initials MSS, was a Congolese politician and military officer who was the first and only president of Zaire from 1971 to 1997. Previously, Mobutu served as the second president of the Democratic Republic of the Congo from 1965 to 1971. He also served as the fifth chairperson of the Organisation of African Unity from 1967 to 1968. During the Congo Crisis, Mobutu, serving as Chief of Staff of the Army and supported by Belgium and the United States, deposed the democratically elected government of left-wing nationalist Patrice Lumumba in 1960. Mobutu installed a government that arranged for Lumumba's execution in 1961, and continued to lead the country's armed forces until he took power directly in a second coup in 1965. To consolidate his power, he established the Popular Movement of the Revolution ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Godefroid Munongo
Godefroid Munongo Mwenda M'Siri (20 November 1925 – 28 May 1992) was a Congolese politician. He was a minister and briefly interim president, in 1961. It has been claimed he was involved in ethnic cleansing and in the assassination of Prime Minister Patrice Lumumba, during the Congo Crisis. Early life Munongo was born on 20 November 1925 in Bunkeya (now in Lualaba Province). He was a descendant of King Msiri Msiri (c. 1830 – December 20, 1891) founded and ruled the Yeke Kingdom (also called the Garanganze or Garenganze kingdom) in south-east Katanga (now in DR Congo) from about 1856 to 1891. His name is sometimes spelled 'M'Siri' in articles in F ... of the Nyamwezi, who founded the State of Garenganze in the latter half of the 19th century.Patrick Munongo , his son, accessed February 2009 He entered the major seminary in [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tribal Chief
A tribal chief, chieftain, or headman is a leader of a tribe, tribal society or chiefdom. Tribal societies There is no definition for "tribe". The concept of tribe is a broadly applied concept, based on tribal concepts of societies of western Afroeurasia. Tribal societies are sometimes categorized as an intermediate stage between the band society of the Paleolithic stage and civilization with centralized, super-regional government based in Cities of the Ancient Near East, cities. Anthropologist Elman Service distinguishes two stages of tribal societies: simple societies organized by limited instances of social rank and prestige, and more stratified society, stratified societies led by chieftains or tribal kings (chiefdoms). Stratified tribal societies led by tribal kings are thought to have flourished from the Neolithic stage into the Iron Age, albeit in competition with Urban area, urban civilisations and empires beginning in the Bronze Age. In the case of tribal societies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swahili Language
Swahili, also known as as it is referred to endonym and exonym, in the Swahili language, is a Bantu languages, Bantu language originally spoken by the Swahili people, who are found primarily in Tanzania, Kenya, and Mozambique (along the East African coast and adjacent littoral islands). Estimates of the number of Swahili speakers, including both native and second-language speakers, vary widely. They generally range from 150 million to 200 million; with most of its native speakers residing in Tanzania and Kenya. Swahili has a significant number of loanwords from other languages, mainly Arabic, as well as from Portuguese language, Portuguese, English language, English and German language, German. Around 40% of Swahili vocabulary consists of Arabic loanwords, including the name of the language ( , a plural adjectival form of an Arabic word meaning 'of the coasts'). The loanwords date from the era of contact between Arab slave trade, Arab traders and the Northeast Bantu languages, B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dan Crawford (missionary)
Daniel Crawford (7 December 1869 – 3 June 1926), also known as 'Konga Vantu', was a Scottish missionary of the Plymouth Brethren in central-southern Africa. He was born in Gourock, son of a Clyde boat captain. He was influenced to go to Africa by meeting Frederick Arnot in 1888, a missionary who had just returned from two years at Bunkeya, capital of the Garenganze King, Msiri, where he had founded the Plymouth Brethren's Garenganze Evangelical Mission. Crawford arrived at Bunkeya in 1890 to join two Plymouth Brethren already at the mission. He was therefore a junior observer rather than a player in the dramatic events of late 1891 when British and Belgian expeditions competed to take Msiri's kingdom into their respective colonies, and Msiri was killed by Lieutenant Bodson of the Belgian expedition, In the aftermath of the killing and a massacre of Msiri's men, the 10,000-strong population of Bunkeya fled into the bush, and Crawford moved to the western shore of Lak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plymouth Brethren
The Plymouth Brethren or Assemblies of Brethren are a low church and Nonconformist (Protestantism), Nonconformist Christian movement whose history can be traced back to Dublin, Ireland, in the mid to late 1820s, where it originated from Anglicanism. The group emphasizes ''sola scriptura'', the belief that the Bible is the only authority for church doctrine and practice. Plymouth Brethren generally see themselves as a network of like-minded free churches, not as a Christian denomination. History Origins in Ireland The Plymouth Brethren movement began in Dublin, Ireland, where several groups of Christians met informally to celebrate the Eucharist together, the first meeting being in 1825. The central figures were Anthony Norris Groves, a dentist studying theology at Trinity College; Edward Cronin (homeopath), Edward Cronin, studying medicine, John Nelson Darby, a curate in County Wicklow; and John Gifford Bellett, a lawyer who brought them together. They did not have any liturgy, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
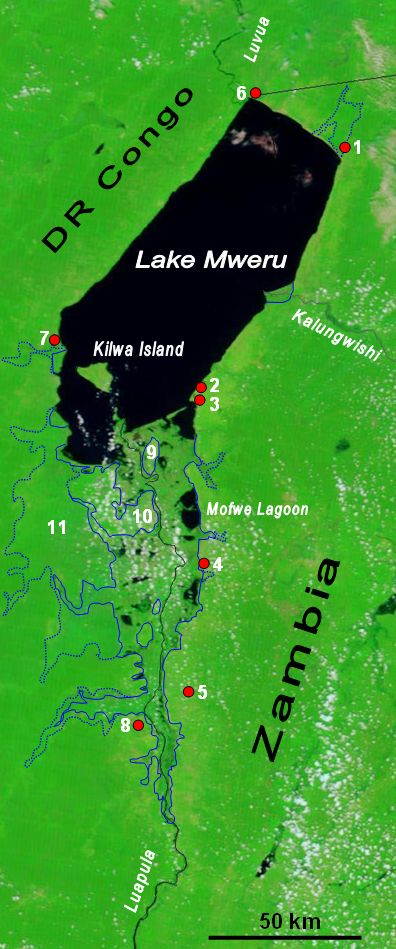
Lake Mweru
Lake Mweru (also spelled ''Mwelu'', ''Mwero'') (, ) is a freshwater lake on the longest arm of Africa's second-longest river, the Congo. Located on the border between Zambia and Democratic Republic of the Congo, it makes up of the total length of the Congo, lying between its Luapula River (upstream) and Luvua River (downstream) segments.Google Earth accessed 29 March 2007. When in flood Lake Bangweulu and its swamps may temporarily have a larger area, but not a larger volume. Mweru means 'lake' in a number of Bantu languages, so it is often referred to as just 'Mweru'.The '' Northern Rhodesia Journal'' online at NZRAM.org: J B W Anderson: "Kilwa Island and the Luapula." Vol II, No. 3 pp87–88 (1954) Physical geography Mweru is mainly fed by the Luapula River, which comes in through swamps from the south, and the Kalungwishi River from the east. At its north end the lake is drained by the Luvua River, which flows in a northwesterly direction to join the Lualaba River and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |