|
Battle Of Magetobriga
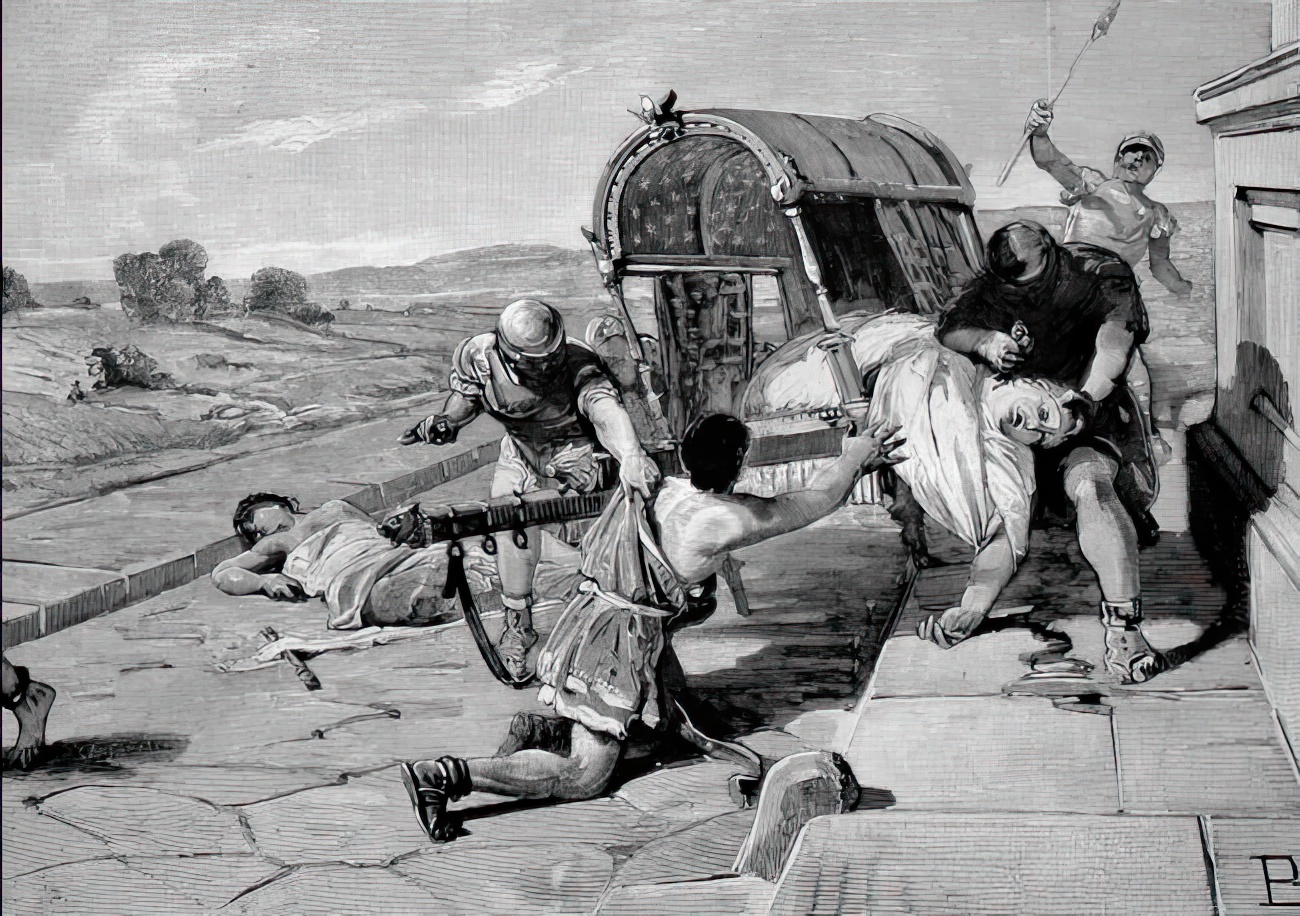
The Battle of Magetobriga (Amagetobria, Magetobria, Mageto'Bria, Admageto'Bria) was fought in 63 BC between rival tribes in Gaul. The Aedui tribe was defeated and massacred by the combined forces of their hereditary rivals, the Sequani and Arverni tribes. To secure their victory, the Sequani and Arverni enlisted the aid of the Germanic Suebi tribe led by its king Ariovistus, who would subsequently make increasingly imposing demands upon his Gallic allies. Following their defeat, the Aedui sent envoys to the Roman Senate, their traditional ally, seeking aid. The Roman general Julius Caesar would use the Aedui’s entreaties and Ariovistus’ oppression as pretexts for launching his conquest of Gaul. Background The cause of the conflict between the Aedui and Sequani was commercial. The Arar (Saône) River formed part of the border between the hereditary rivals. Each tribe claimed the Arar and the tolls on trade along it.Kahn, ''The Education of Julius Caesar'', 220 Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallic Wars
The Gallic Wars were waged between 58 and 50 BC by the Roman general Julius Caesar against the peoples of Gaul (present-day France, Belgium, and Switzerland). Gauls, Gallic, Germanic peoples, Germanic, and Celtic Britons, Brittonic tribes fought to defend their homelands against an aggressive Roman Military campaign, campaign. The Wars culminated in the decisive Battle of Alesia in 52 BC, in which a complete Roman victory resulted in the expansion of the Roman Republic over the whole of Gaul. Though the collective Gallic armies were as strong as the Roman forces, the Gallic tribes' internal divisions eased victory for Caesar. Gallic chieftain Vercingetorix's attempt to unite the Gauls under a single banner came too late. Caesar portrayed the invasion as being a preemptive and defensive action, but historians agree that he fought the wars primarily to boost his political career and to pay off his debts. Still, Gaul was of significant military importance to the Romans. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
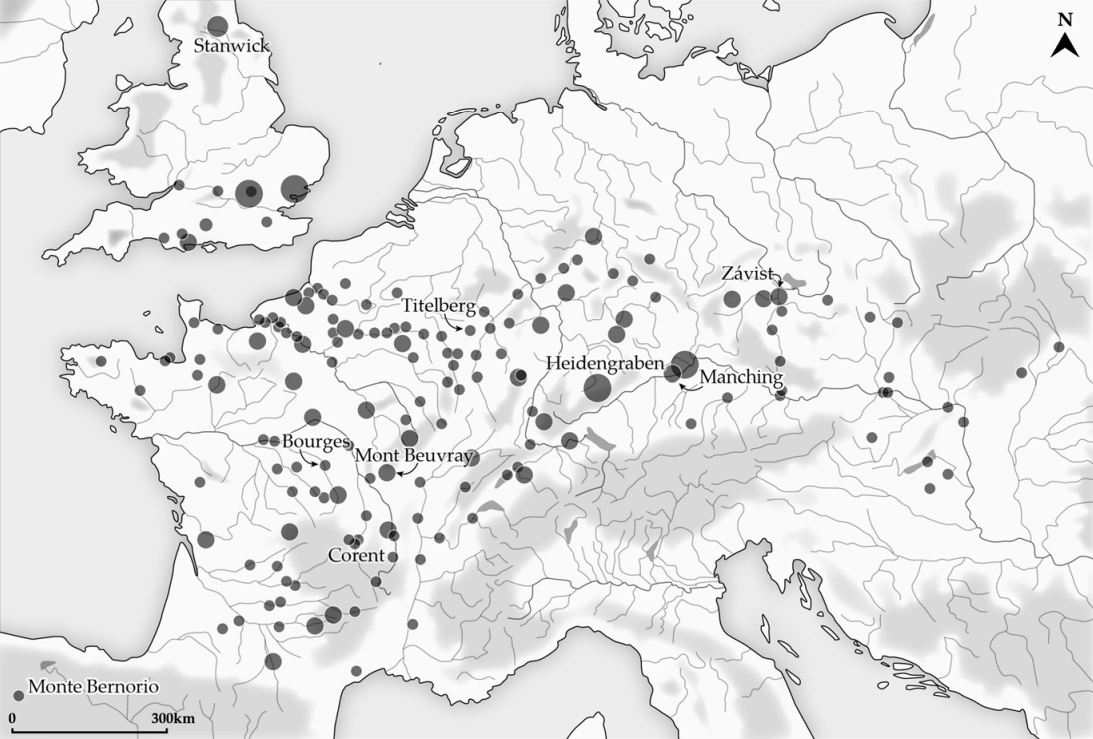
Oppidum
An ''oppidum'' (: ''oppida'') is a large fortified Iron Age Europe, Iron Age settlement or town. ''Oppida'' are primarily associated with the Celts, Celtic late La Tène culture, emerging during the 2nd and 1st centuries BC, spread across Europe, stretching from British Iron Age, Britain and Iberia in the west to the edge of the Great Hungarian Plain, Hungarian Plain in the east. These settlements continued to be used until the Romans conquered Southern and Western Europe. Many subsequently became Roman-era towns and cities, whilst others were abandoned. In regions north of the rivers Danube and Rhine, such as most of Germania, where the populations remained independent from Rome, ''oppida'' continued to be used into the 1st century AD. Definition is a Latin word meaning 'defended (fortified) administrative centre or town', originally used in reference to non-Roman towns as well as provincial towns under Roman control. The word is derived from the earlier Latin , 'encl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helvetii
The Helvetii (, , Gaulish: *''Heluētī''), anglicized as Helvetians, were a Celtic tribe or tribal confederation occupying most of the Swiss plateau at the time of their contact with the Roman Republic in the 1st century BC. According to Julius Caesar, the Helvetians were divided into four subgroups or '' pagi.'' Of these, Caesar names only the Verbigeni and the Tigurini, while Posidonius mentions the Tigurini and the Tougeni (). They feature prominently in the '' Commentaries on the Gallic War,'' with their failed migration attempt to southwestern Gaul (58 BC) serving as a catalyst for Caesar's conquest of Gaul. The Helvetians were subjugated after 52 BC, and under Augustus, Celtic oppida, such as Vindonissa or Basilea, were re-purposed as garrisons. In AD 68, a Helvetian uprising was crushed by Aulus Caecina Alienus. The Swiss plateau was at first incorporated into the Roman province of Gallia Belgica (22 BC), later into Germania Superior (AD 83). The Helvetians ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harudes
The Charudes or Harudes were a Germanic group first mentioned by Julius Caesar as one of the tribes who had followed Ariovistus across the Rhine. While Tacitus' ''Germania'' makes no mention of them, Ptolemy's ''Geographia'' locates the Charudes (Χαροῦδες) on the east coast of the Cimbrian peninsula (see Hardsyssel). People of classical times Sometime before 60 BC, the "rex Germanorum" Ariovistus had been petitioned by the Celtic Sequani for assistance in their war against the Aedui. In return, Ariovistus was promised land grants in Gaul, although exactly where is not certain. Gathering forces from a wide area of Germany, Ariovistus crossed the Rhine with large numbers and defeated the Aedui at the Battle of Magetobriga. It is in the context of Ariovistus' subsequent land claims that the Harudes are first mentioned by Caesar: "But a worse thing had befallen the victorious Sequani than the vanquished Aedui, for Ariovistus, the king of the Germans, had settled in thei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classical Antiquity
Classical antiquity, also known as the classical era, classical period, classical age, or simply antiquity, is the period of cultural History of Europe, European history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD comprising the interwoven civilizations of ancient Greece and ancient Rome, Rome known together as the Greco-Roman world, centered on the Mediterranean Basin. It is the period during which ancient Greece and Rome flourished and had major influence throughout much of Europe, North Africa, and West Asia. Classical antiquity was succeeded by the period now known as late antiquity. Conventionally, it is often considered to begin with the earliest recorded Homeric Greek, Epic Greek poetry of Homer (8th–7th centuries BC) and end with the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476 AD. Such a wide span of history and territory covers many disparate cultures and periods. ''Classical antiquity'' may also refer to an idealized vision among later people of what was, in Ed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Senate
The Roman Senate () was the highest and constituting assembly of ancient Rome and its aristocracy. With different powers throughout its existence it lasted from the first days of the city of Rome (traditionally founded in 753 BC) as the Senate of the Roman Kingdom, to the Senate of the Roman Republic and Senate of the Roman Empire and eventually the Byzantine Senate of the Eastern Roman Empire, existing well into the post-classical era and Middle Ages. During the days of the Roman Kingdom, the Senate was generally little more than an advisory council to the king. However, as Rome was an electoral monarchy, the Senate also elected new Roman kings. The last king of Rome, Lucius Tarquinius Superbus, was overthrown following a coup d'état led by Lucius Junius Brutus, who founded the Roman Republic. During the early Republic, the Senate was politically weak, while the various executive Roman magistrates who appointed the senators for life (or until expulsion by Roma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Druid
A druid was a member of the high-ranking priestly class in ancient Celtic cultures. The druids were religious leaders as well as legal authorities, adjudicators, lorekeepers, medical professionals and political advisors. Druids left no written accounts. While they were reported to have been literate, they are believed to have been prevented by doctrine from recording their knowledge in written form. Their beliefs and practices are attested in some detail by their contemporaries from other cultures, such as the Romans and the Greeks. The earliest known references to the druids date to the 4th century BC. The oldest detailed description comes from Julius Caesar's ''Commentarii de Bello Gallico'' (50s BC). They were described by other Roman writers such as Cicero, Cicero (44) I.XVI.90. Tacitus, and Pliny the Elder. Following the Roman invasion of Gaul, the druid orders were suppressed by the Roman government under the 1st-century AD emperors Tiberius and Claudius, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Letters To Atticus/1
Letter, letters, or literature may refer to: Characters typeface * Letter (alphabet), a character representing one or more of the sounds used in speech or none in the case of a silent letter; any of the symbols of an alphabet * Letterform, the graphic form of a letter of the alphabet, either as written or in a particular type font * Rehearsal letter in an orchestral score Communication * Letter (message), a form of written communication ** Mail * Letters, the collected correspondence of a writer or historically significant person **Pauline epistles, addressed by St. Paul to various communities or congregations, such as "Letters to the Galatians" or "Letters to the Corinthians", and part of the canonical books of the Bible ** Maktubat (other), the Arabic word for collected letters * The letter as a form of second-person literature; see Epistle ** Epistulae (Pliny) ** Epistolary novel, a long-form fiction composed of letters (epistles) * Open letter, a public letter as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cicero
Marcus Tullius Cicero ( ; ; 3 January 106 BC – 7 December 43 BC) was a Roman statesman, lawyer, scholar, philosopher, orator, writer and Academic skeptic, who tried to uphold optimate principles during the political crises that led to the establishment of the Roman Empire. His extensive writings include treatises on rhetoric, philosophy and politics. He is considered one of Rome's greatest orators and prose stylists and the innovator of what became known as "Ciceronian rhetoric". Cicero was educated in Rome and in Greece. He came from a wealthy municipal family of the Roman equestrian order, and served as consul in 63 BC. He greatly influenced both ancient and modern reception of the Latin language. A substantial part of his work has survived, and he was admired by both ancient and modern authors alike. Cicero adapted the arguments of the chief schools of Hellenistic philosophy in Latin and coined a large portion of Latin philosophical vocabulary via ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amage, Haute-Saône
Amage () is a commune in the Haute-Saône department in the region of Bourgogne-Franche-Comté in eastern France. It is the site of the ancient Magetobria, known for the Battle of Magetobriga. See also * Communes of the Haute-Saône department The following is a list of the 536 communes in the French department of Haute-Saône. The communes cooperate in the following intercommunalities (as of 2025):Communes of Haute-Saône {{Lure-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Broye-Aubigney-Montseugny
Broye-Aubigney-Montseugny () is a Communes of France, commune in the Haute-Saône Departments of France, department in the Regions of France, region of Bourgogne-Franche-Comté in eastern France. History It was created in 1973 by the merger of three former communes: Broye-lès-Pesmes, Aubigney, and Montseugny. ''Journal officiel de la République française'' n° 0024, 28 January 1973, pp. 1114-1117. Broye-lès-Pesmes has been proposed as the location of Amagetobria, a major settlement of the Sequani tribe in the pre-Roman and Roman era. Up to the 19th century, the town was called Moigte-de-Broie, which was derived from its ancient name. Ga ...
|
Germanic People
The Germanic peoples were tribal groups who lived in Northern Europe in Classical antiquity and the Early Middle Ages. In modern scholarship, they typically include not only the Roman-era ''Germani'' who lived in both ''Germania'' and parts of the Roman Empire, but also all Germanic speaking peoples from this era, irrespective of where they lived, most notably the Goths. Another term, ancient Germans, is considered problematic by many scholars since it suggests identity with present-day Germans. Although the first Roman descriptions of ''Germani'' involved tribes west of the Rhine, their homeland of ''Germania'' was portrayed as stretching east of the Rhine, to southern Scandinavia and the Vistula in the east, and to the upper Danube in the south. Other Germanic speakers, such as the Bastarnae and Goths, lived further east in what is now Moldova and Ukraine. The term ''Germani ''is generally only used to refer to historical peoples from the 1st to 4th centuries CE. Different ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |