|
Battle Of Yehuling
The Battle of Yehuling, also known as the Battle of Wild Fox Ridge, or the Battle of Badger Mouth took place in Jin China between August and October 1211 at Yehuling (野狐嶺; lit. "Wild Fox Ridge"). It was fought by the Mongol Empire and the Jurchen-led Jin dynasty during the first stage of the Mongol conquest of the Jin dynasty. The battle was fought in the northwest of present-day Wanquan District, Zhangjiakou, Hebei Province. It concluded in a Mongol victory over the northern part of the Jin, hastening the decline of the Jin dynasty. Background In 1206, Temüjin (previous name of Genghis Khan) had united all the tribes on the Mongolian Plateau under his rule and received the title "Genghis Khan". The Jurchen-led Jin dynasty in northern China became a major obstacle to the Mongol Empire's quest for world domination. In the past, the Jin dynasty had adopted a divide-and-rule strategy to break up the various Mongol tribes and keep them under control. Howeve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mongol Empire
The Mongol Empire was the List of largest empires, largest contiguous empire in human history, history. Originating in present-day Mongolia in East Asia, the Mongol Empire at its height stretched from the Sea of Japan to parts of Eastern Europe, extending northward into parts of the Arctic; eastward and southward into parts of the Indian subcontinent, mounting invasions of Southeast Asia, and conquering the Iranian plateau; and reaching westward as far as the Levant and the Carpathian Mountains. The Mongol Empire emerged from the unification of several nomad, nomadic tribes in the Mongol heartland under the leadership of Temüjin, known by the title of Genghis Khan (–1227), whom a council proclaimed as the ruler of all Mongols in 1206. The empire grew rapidly under his rule and that of his descendants, who sent out Mongol invasions, invading armies in every direction. The vast transcontinental empire connected the Eastern world, East with the Western world, West, and the Pac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crucifixion
Crucifixion is a method of capital punishment in which the condemned is tied or nailed to a large wooden cross, beam or stake and left to hang until eventual death. It was used as a punishment by the Achaemenid Empire, Persians, Ancient Carthage, Carthaginians, and Roman Empire, Romans, among others. Crucifixion has been used in some countries as recently as the 21st century. The crucifixion of Jesus is central to Christianity and the Christian cross, cross (in Catholic Church, Roman Catholicism usually crucifix, depicted with Jesus nailed to it) is Christianity's preeminent religious symbol. His death is the most prominent example of crucifixion in history, which in turn has led many cultures in the modern world to associate the execution method closely with Jesus and with Christian spirituality. Other figures in Christianity are traditionally believed to have undergone crucifixion as well, including Saint Peter, who was crucified upside-down, and Andrew the Apostle, Saint Andr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
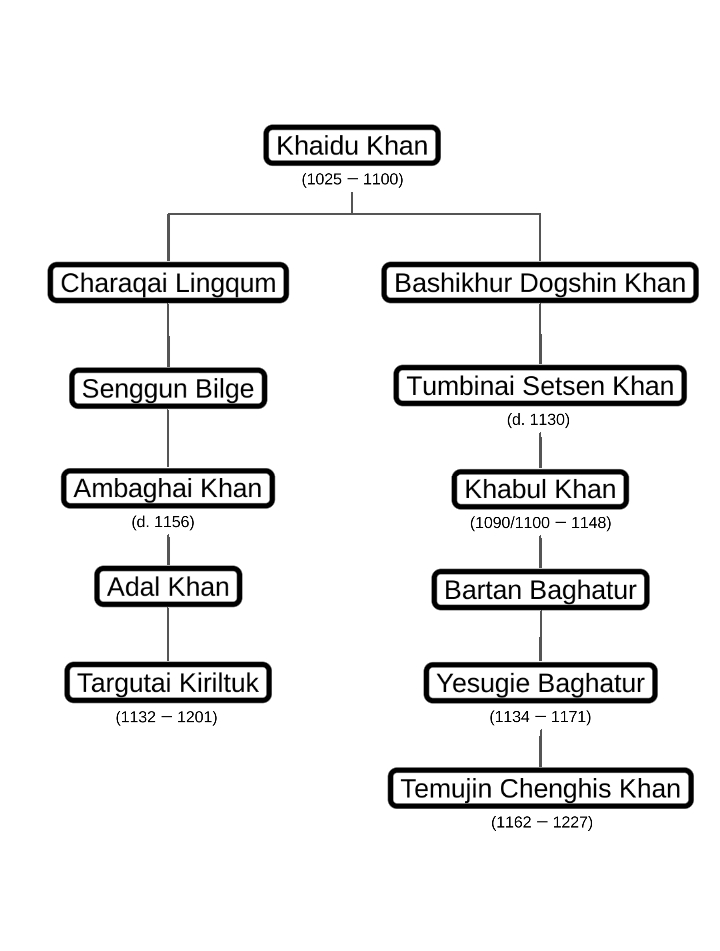
Ambaghai
Ambaghai () or Hambaqai Khan (? – died 1156) was a Khan of the Khamag Mongol, succeeding his cousin Khabul Khan. He was one of the great-grandsons of Khaidu Khan and the cousin and predecessor of Hotula Khan. He was the Leader of the Taichud clan, one of the sub-branches of the Borjigid, and also grandson and successor of Charaqai Lingqum. Life Ambaghai was born to Sorqaduqtu China, a son of Charaqai Lingqum who in turn was son of Khaidu Khan. His father is mentioned as Senggüm Bilge in ''The Secret History of the Mongols.'' A member of the cadet branch of Borjigin clan, he was ruler of the Taichuud tribe and later khan of Khamag Mongol. According to Rashidaddin, Ambaghai succeeded Khabul Khan, because he was senior most in the Borjigid line. Toward the end of his rule, he was captured alongside Khabul Khan's son Tödö'en Otchigin by the Tatars when he was on a trip to marry his son Qadaan Taishi to a daughter of the chief of the Airu'ut Tatars. In fact, this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kherlen River
Kherlen River (also known as Kerülen; ; ) is a 1,254 km river in Mongolia and China. It is also one of the two longest rivers in Mongolia, along with the Orkhon River. Course The river originates in the south slopes of the Khentii mountains, near the Burkhan Khaldun mountain in the Khan Khentii Strictly Protected Area, about northeast of Ulaanbaatar. This area constitutes the divide between the Arctic ( Tuul River) and Pacific (Kherlen, Onon) basins and is consequently named "Three River Basins". From there the Kherlen flows in a mostly eastern direction through the Khentii ''aimag''. Further downriver, it crosses the eastern Mongolian steppe past Ulaan Ereg and Choibalsan, entering China at and emptying into Hulun Nuur after another . The mean streamflow of Kherlen River has decreased by more than a half from 2000 to 2008 when compared with prior decades. Kherlen-Ergune-Amur In years with high precipitation, the normally exitless Hulun Lake may overflow at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tengri
Tengri (; Old Uyghur: ; Middle Turkic: ; ; ; ; ; ; ; Proto-Turkic: / ; Mongolian script: , ; , ; , ) is the all-encompassing God of Heaven in the traditional Turkic, Yeniseian, Mongolic, and various other nomadic religious beliefs. Some qualities associated with Tengri as the judge and source of life, and being eternal and supreme, led European and Muslim writers to identify Tengri as a deity of Turkic and Mongolic peoples. According to Mongolian belief, Tengri's will (''jayayan'') may break its own usual laws and intervene by sending a chosen person to earth. It is also one of the terms used for the primary chief deity of the early Turkic and Mongolic peoples. Worship surrounding Tengri is called ''Tengrism''. The core beings in Tengrism are the Sky Father (Tenger Etseg) and the Earth Mother ( Umay Ana). It involves ancestor worship, as Tengri was thought to have been the ancestral progenitor of mankind in Turkic regions and Mongolia, shamanism, animism, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yin Mountains
The Yin Mountains, also known by their Chinese name as the Yin Shan or Yinshan and by various romanizations as the Daqing Mountains, are mountains in the Eastern Gobi Desert steppe of the Inner Mongolian Autonomous Region of China. The Yellow River borders the mountains to the south. Geology The mountains are mainly composed of very old metamorphic rock Metamorphic rocks arise from the transformation of existing rock to new types of rock in a process called metamorphism. The original rock ( protolith) is subjected to temperatures greater than and, often, elevated pressure of or more, caus .... References Mountain ranges of China Mountain ranges of Inner Mongolia Mountains of Hebei Gobi Desert {{InnerMongolia-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ongud
The Ongud (also spelled Ongut or Öngüt; Mongolian: Онгуд, Онход; Chinese: 汪古, ''Wanggu''; from Old Turkic ''öng'' "desolate, uninhabited; desert" plus ''güt'' "class marker") were a Turkic tribe that later became Mongolized active in what is now Inner Mongolia in northern China around the time of Genghis Khan (1162–1227).Roux, p.40 Many Ongud were members of the Church of the East. They lived in an area lining the Great Wall in the northern part of the Ordos Plateau and territories to the northeast of it. They appear to have had two capitals, a northern one at the ruin known as Olon Süme and another a bit to the south at a place called Koshang or Dongsheng. They acted as wardens of the marches for the Jin dynasty (1115–1234) to the north of Shanxi. History Origin The ancestors of the Ongud were the Shatuo Turks, who, in turn, descended mainly from the two remnant tribes of Western Turkic Khaganate: namely, the Chuyue, the Türgesh-associated Suoge, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Zhangzong Of Jin
Emperor Zhangzong of Jin (31 August 1168 – 29 December 1208), personal name Madage, sinicized name Wanyan Jing, was the sixth emperor of the Jurchen-led Jin dynasty of China. He reigned from 20 January 1189 to 29 December 1208.Tao, p. 85-86 During his rule, he is credited for ordering the construction of the beautiful Taiye Lake, an artificial lake in Beijing, that remains to this day. He also established many Confucian temples throughout Northeast China and was tolerant of both Han and Jurchen cultures and customs. However, the Jin dynasty began to decline as he started neglecting governmental affairs and showing favoritism to one of his concubines Li Shi'er and her family members in political office. The Tatar confederation who once allied with the Jin dynasty rebelled and joined the rising Mongol Empire. The Southern Song chancellor Han Tuozhou tried to take advantage of Madage's incompetency by launching an attack on the Jin. However the Jin dynasty defeated the Sout ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jin Dynasty (1115–1234)
The Jin dynasty (, ), officially known as the Great Jin (), was a Jurchen people, Jurchen-led Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China and empire ruled by the Wanyan clan that existed between 1115 and 1234. It is also often called the Jurchen dynasty or the Jurchen Jin after the ruling Jurchen people. At its peak, the empire extended from Outer Manchuria in the north to the Qinling–Huaihe Line in the south. The Jin dynasty emerged from Emperor Taizu of Jin, Wanyan Aguda's rebellion against the Liao dynasty (916–1125), which held sway over northern China until being driven by the nascent Jin to the Western Regions, where they would become known in Chinese historiography as the Qara Khitai, Western Liao. After conquering the Liao territory, the Jin launched a Jin–Song Wars, century-long campaign against the Song dynasty (960–1279) based in southern China, whose rulers were ethnically Han Chinese. Over the course of the Jin's rule, their emperors Sinicization, adap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Wall Of China
The Great Wall of China (, literally "ten thousand ''li'' long wall") is a series of fortifications in China. They were built across the historical northern borders of ancient Chinese states and Imperial China as protection against various nomadic groups from the Eurasian Steppe. The first walls date to the 7th century BC; these were joined together in the Qin dynasty. Successive dynasties expanded the wall system; the best-known sections were built by the Ming dynasty (1368–1644). To aid in defense, the Great Wall utilized watchtowers, troop barracks, garrison stations, signaling capabilities through the means of smoke or fire, and its status as a transportation corridor. Other purposes of the Great Wall have included border controls (allowing control of immigration and emigration, and the imposition of duties on goods transported along the Silk Road), and the regulation of trade. The collective fortifications constituting the Great Wall stretch from Liaodong in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |