|
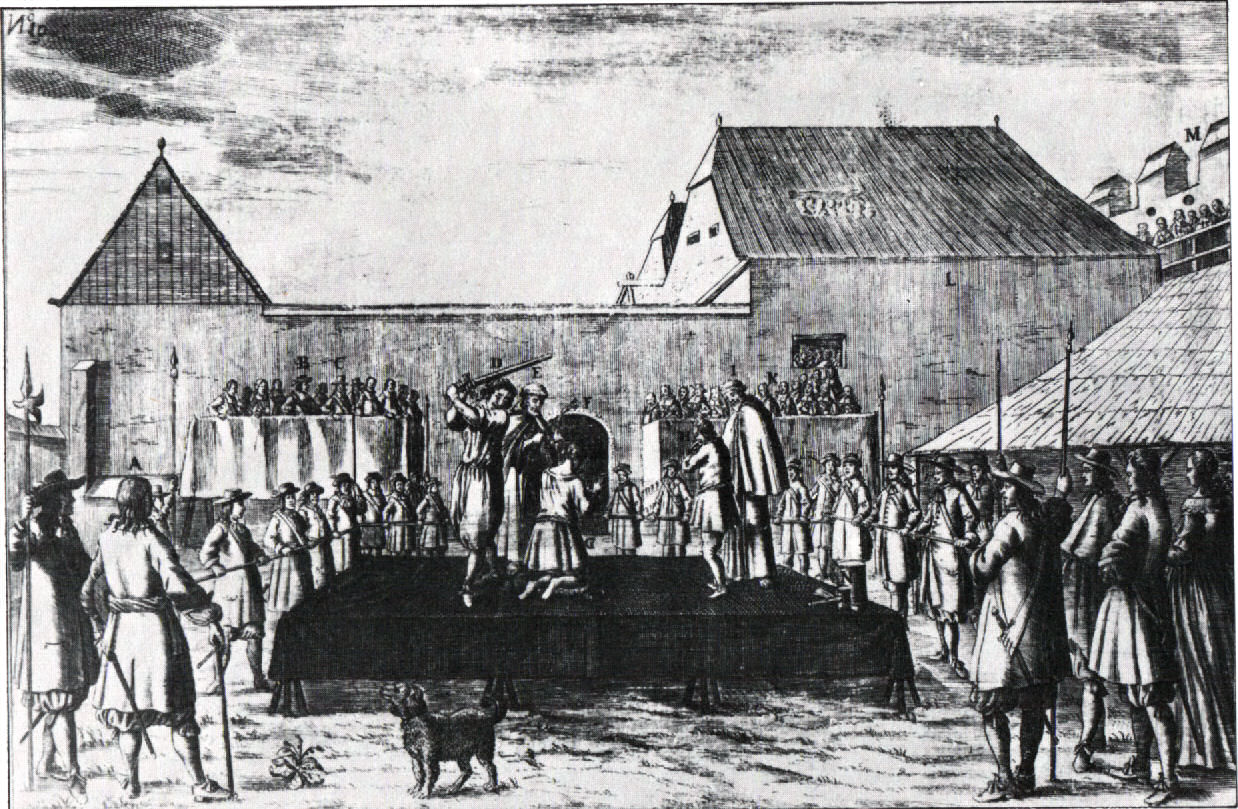
Battle Of Perast
The Battle of Perast () was a battle for control over Venetian Republic, Venetian held Perast (modern day Montenegro) fought in 1654 between defending forces of Venetian Republic from Perast accompanied by hajduks and attacking forces of Ottoman Empire from Sanjak of Herzegovina. Commander of defending Perast forces was Krsto Vicković while Ottoman forces were led by Dizdar Mehmed Rizvanbegović. Venetian forces from Perast were victorious and successfully repelled the Ottoman attack in the battle which is in some sources referred to as most glorious victory in their history. Background In 1654, Ottoman forces controlled almost whole north-western part of the Kotor Bay, so they perceived Perast as some kind of thorn in their side. On the other hand, Perast had important strategic importance for the Venetian Republic because it protected important Venetian-held city of Kotor. Battle of Perast followed an unsuccessful attempt of Venetian forces to capture Knin in early 1654. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cretan War (1645–69) , a battle of World War II
{{disambiguation ...
Cretan War may refer to multiple wars involving the island of Crete, including: *Cretan War (205–200 BC), a war between King Philip V of Macedon and Rhodes *Cretan War (1645–1669), a war between the Republic of Venice and the Ottoman Empire See also *Cretan Revolt (other), various uprisings on Crete *Battle of Crete The Battle of Crete (, ), codenamed Operation Mercury (), was a major Axis Powers, Axis Airborne forces, airborne and amphibious assault, amphibious operation during World War II to capture the island of Crete. It began on the morning of 20 May ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dizdar
Dizdar (; ) was the title given in the Ottoman Empire to a castle warden or fortress commander, appointed to manage troops and keep the fortress in its role as a defence point. The word is of Persian language, Persian origin, meaning gatekeeper, Security guard, watchman, guardsman or castellan. It spread to the west following the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman conquest of the Balkans. Dizdar commanded military unit in the fortress, but at the same time he was responsible for the settlement (village or town) under or around it as well, because the purpose of fortress was to defend the area. As a commanding person, dizdar had his deputy, called ''chekhaya'' ({{langx, tr, kâhya), and other Subordinate officer, subordinates (e.g. yasakci). His superiors were Captain (armed forces), captain, sanjakbeg and other senior military officers. In 1839 after the Tanzimat reforms, the Ottoman Empire abolished Captaincy, captaincies; the titles like captain and dizdar ceased to exist. See also * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyrillic
The Cyrillic script ( ) is a writing system used for various languages across Eurasia. It is the designated national script in various Slavic, Turkic, Mongolic, Uralic, Caucasian and Iranic-speaking countries in Southeastern Europe, Eastern Europe, the Caucasus, Central Asia, North Asia, and East Asia, and used by many other minority languages. , around 250 million people in Eurasia use Cyrillic as the official script for their national languages, with Russia accounting for about half of them. With the accession of Bulgaria to the European Union on 1 January 2007, Cyrillic became the third official script of the European Union, following the Latin and Greek alphabets. The Early Cyrillic alphabet was developed during the 9th century AD at the Preslav Literary School in the First Bulgarian Empire during the reign of Tsar Simeon I the Great, probably by the disciples of the two Byzantine brothers Cyril and Methodius, who had previously created the Gl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petar Zrinski
Petar IV Zrinski () (6 June 1621 – 30 April 1671) was Ban of Croatia (Viceroy) from 1665 to 1670, general and a writer. A member of the Zrinski noble family, he was noted for his role in the attempted Croatian-Hungarian Magnate conspiracy to overthrow the Habsburgs, which ultimately led to his execution for high treason. Zrinski family Petar Zrinski was born in Vrbovec, a small town near Zagreb, the son of Juraj V Zrinski and Magdalena Széchy. His father Juraj VI and great-grandfather Nikola IV had been viceroys or ''Ban'' of Croatia, which was then a nominal Kingdom in personal union with the Hungarian Kingdom. His brother was the Croatian-Hungarian general and poet Miklós Zrínyi (Nikola VII Zrinski). His family had possessed large estates throughout all of Croatia and had family ties with the second largest Croatian landowners, the Frankopan family. He married Ana Katarina, the half-sister of Fran Krsto Frankopan, and they lived in large castles of Ozalj (in Cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trebinje
Trebinje ( sr-Cyrl, Требиње, ) is a city and municipality in Republika Srpska, Bosnia and Herzegovina. It is the southernmost city in Bosnia and Herzegovina and is situated on the banks of the Trebišnjica river in the region of East Herzegovina. As of 2013, it has a population of 31,433 inhabitants. The city's old town quarter dates to the 18th-century Ottoman period and includes the Arslanagić Bridge, also known as Perovića Bridge. Geography Physical geography The city lies in the Trebišnjica river valley, at the foot of Leotar, in southeastern Herzegovina, some by road from Dubrovnik, Croatia, on the Adriatic coast. There are several watermill, mills along the river, as well as several bridges, including three in the city of Trebinje itself, as well as a historic Ottoman Empire, Ottoman Arslanagić Bridge nearby. The river is heavily exploited for hydro-electric energy. After it passes through the Popovo polje, Popovo Polje area southwest of the city, the river ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
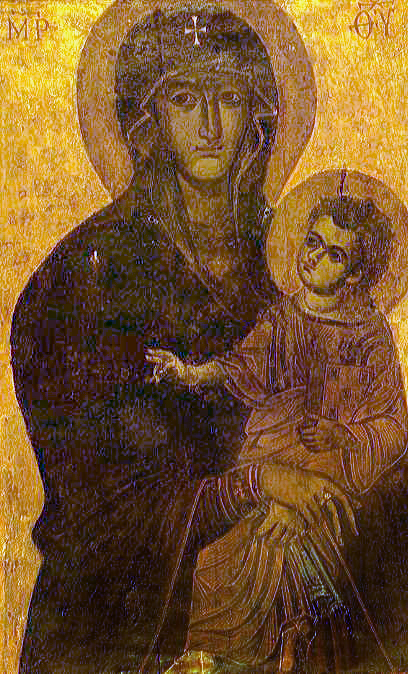
Our Lady Of The Rocks
Our Lady of the Rocks is one of the two islets off the coast of Perast in the Bay of Kotor, Montenegro (the other being Sveti Đorđe island). It is an artificial island created by bulwark of rocks and by sinking old and seized ships loaded with rocks. The Catholic Church of Our Lady of the Rocks () is the largest building on the islet, and has a museum attached to it. There is also a small gift shop close to the church and a navigation light at the northern end of the islet. According to legend, the islet was made over the centuries by local seamen who kept an ancient oath after finding the icon of Madonna and Child on the rock in the sea on 22 July 1452. Upon returning from each successful voyage, they laid a rock in the Bay. Over time, the islet gradually emerged from the sea. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Madonna And Child
In Christian art, a Madonna () is a religious depiction of the Blessed Virgin Mary in a singular form or sometimes accompanied by the Child Jesus. These images are central icons for both the Roman Catholic and Orthodox churches. The word is (archaic). The Madonna and Child type is very prevalent in Christian iconography, divided into many traditional subtypes especially in Eastern Orthodox iconography, often known after the location of a notable icon of the type, such as the '' Theotokos of Vladimir'', '' Agiosoritissa'', '' Blachernitissa'', etc., or descriptive of the depicted posture, as in '' Hodegetria'', '' Eleusa'', etc. The term ''Madonna'' in the sense of "picture or statue of the Virgin Mary" enters English usage in the 17th century, primarily in reference to works of the Italian Renaissance. In an Eastern Orthodox context, such images are typically known as '' Theotokos''. "Madonna" may be generally used of representations of Mary, with or without the infant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kotor Bay
The Bay of Kotor ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, Boka kotorska, Бока которска, separator=" / ", ), also known as the Boka ( sh-Cyrl, Бока), is a winding bay of the Adriatic Sea in southwestern Montenegro and the region of Montenegro concentrated around the bay. It is also the southernmost part of the historical region of Dalmatia. At the entrance to the Bay there is Prevlaka, a small peninsula in southern Croatia. The bay has been inhabited since antiquity. Its well-preserved medieval towns of Kotor, Risan, Tivat, Perast, Prčanj and Herceg Novi, along with their natural surroundings, are major tourist attractions. The Natural and Culturo-Historical Region of Kotor was designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1979. Its numerous Orthodox and Catholic churches and monasteries attract numerous religious pilgrims and other visitors. Geography The bay is about long with a shoreline extending . It is surrounded by two massifs of the Dinaric Alps: the Orjen mountains to the west, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radul Of Riđani
Radul of Riđani (; 1650–66) was a Serbian Orthodox priest and chieftain (''knez'') of Riđani, a tribe in Old Herzegovina (later annexed by the Principality of Montenegro). He was also influential among the Banjani and Nikšići tribes. Radul hailed from the tribe of Riđani (at the time part of the Sanjak of Herzegovina), and was a priest in Dvrsno (now Dragalj, in Krivošije). In the spring of 1650 the Riđani, including Radul, suffered from their neighbours in the Bay of Kotor, namely from the Orahovčani and Dobroćani and Đuro Vučinić. Radul used to write letters to the authorities of Perast to inform them about the preparations of Ottoman forces for the Battle of Perast. Thanks to Radul Perast authorities were able to hide civilians into shelters before the battle. Fourteen letters written by Radul are preserved in contemporary archives. In one of his letters written in 1661 to Vicko Mažarović, captain of Perast, Radul presented information about Ali Paša Čeng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herceg Novi
Herceg Novi (Cyrillic script, Cyrillic: Херцег Нови, ) is a town in Coastal Montenegro, Coastal region of Montenegro located at the Western entrance to the Bay of Kotor and at the foot of Mount Orjen. It is the administrative center of the Herceg Novi Municipality with around 33,000 inhabitants. The town was founded as a fortress in 1382 by the King of Bosnia, Tvrtko I of Bosnia, Tvrtko I Kotromanić, and named after Saint Stephen but the name did not stick, instead it became known as Novi (), also Castelnuovo in Italian (). Between 1482 and 1687 it was part of the Ottoman Empire and then from 1687 to 1797 the Albania Veneta of the Republic of Venice. It was a Catholic bishopric and remains a Latin titular see as Novi. Herceg Novi has had a turbulent past, despite being one of the youngest settlements on the Adriatic. A History of Montenegro, history of varied occupations has created a blend of diverse and picturesque architectural styles in the city. Names and etymolog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fusta
The fusta or fuste (also called foist) was a narrow, light and fast ship with shallow draft, powered by both oars and sail—in essence a small galley. It typically had 12 to 18 two-man rowing benches on each side, a single mast with a lateen (triangular) sail, and usually carried two or three guns. The sail was used to cruise and save the rowers’ energy, while the oars propelled the ship in and out of harbor and during combat. The fusta was the favorite ship of the North African corsairs of Salé and the Barbary Coast. Its speed, mobility, capability to move without wind, and its ability to operate in shallow water—crucial for hiding in coastal waters before pouncing on a passing ship—made it ideal for war and piracy. It was mainly with fustas that the Barbarossa brothers, Baba Aruj and Khair ad Din, carried out the Ottoman conquest of North Africa and the rescue of Mudéjars and Moriscos from Spain after the fall of Granada Granada ( ; ) is the capital city of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |