|
Battle Of Das
The Battle of Das was fought in 1332 between the Ethiopian Empire under the command of Emperor Amda Seyon and a large Muslim coalition led by Salih of Adal. The Ethiopian army was victorious, and Salih was slain. Background According to the chronicler, the Imam of Adal, Salih would assemble a large Muslim army made up of 12,048 warriors from various regions such as Gidaya, Hubat, Fedis, Dawaro and Hargaya and form an alliance with Ifat sultan, Jamal ad-Din, who was a vassal king of Amda Seyon. Despite their alliance, tension between Ifat and Adal leaders was evident as Salih refused to wait for the arrival of Ifat's troops under sultan Jamal ad-Din I before attacking the Abyssinians in order to avoid allocating the spoils of war with Ifat. Battle In July 1332, Salih and his army set out to Amda Seyon's camp, surrounding him with their troops. According to the chronicler, most of the Ethiopian army left the camp to put down a revolt of the Beta Israel and the Emperor had w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Wynn Brereton Huntingford
George Wynn Brereton Huntingford (19 November 1901 – 19 February 1978) was an English linguist, anthropologist and historian. He lectured in East African languages and cultures at SOAS, University of London from 1950 until 1966. Archives Hub In 1966, Huntingford went to Canada to organise the Department of Anthropology at the at , and retired to |
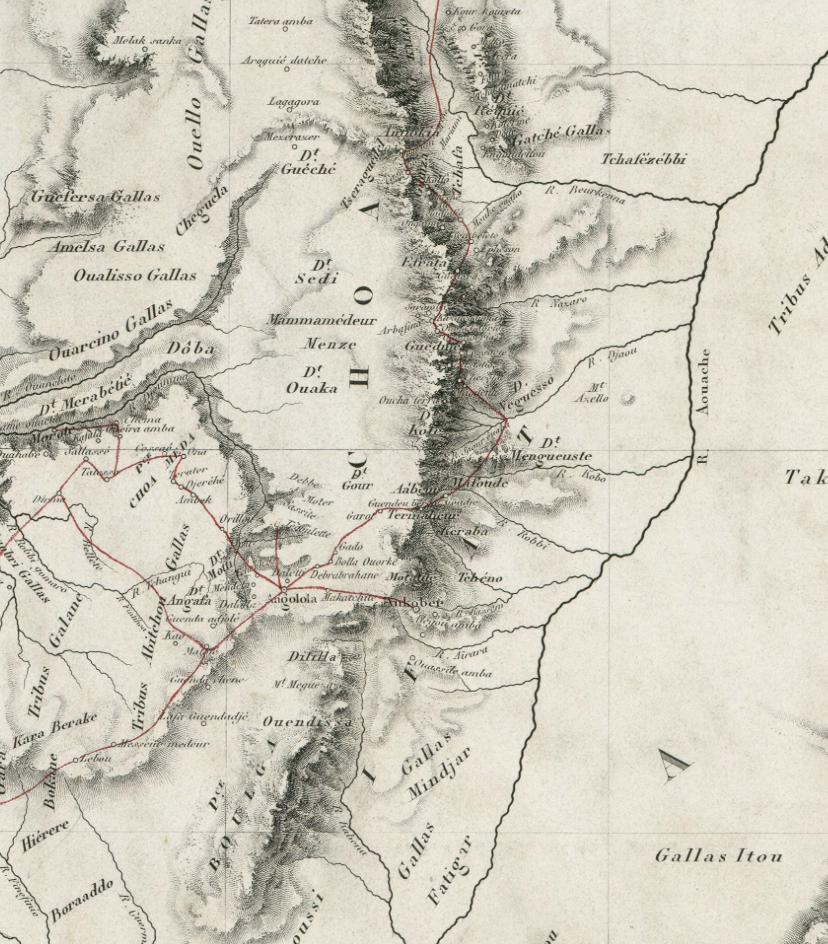
Dawaro
Dawaro or Doaro (Amharic: ደዋሮ) was a Muslim principality which laid near Hadiya. The state was originally independent until becoming a vassal and later a province due its subjugation by Emperor Amda Seyon I in the early 14th century. The region was situated east of Hadiya and north of Bali which covered much of Ethiopia's Arsi Province. The capital of Dawaro was called Sabboch. History The earliest mention of this province comes from the ''Royal Chronicle'' of Emperor Amda Seyon. After occupying Ifat, Amda Seyon then proceeded to garrison Dawaro. However, in the late 1320s the ruler of the province, Haydara, ended up siding with Sabr ad-Din I during his rebellion and "treacherously" executed some of the Emperor's messengers. Amda Seyon, incensed by this act of rebellion, at once set out with his troops. On reaching Dawaro he "laid waste the country from one end to the other". He killed young men, took women and children prisoners, seized livestock "without number" and "de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Massacres In Ethiopia
A massacre is an event of killing people who are not engaged in hostilities or are defenseless. It is generally used to describe a targeted killing of civilians en masse by an armed group or person. The word is a loan of a French term for "butchery" or "carnage". Other terms with overlapping scope include war crime, pogrom, mass killing, mass murder, and extrajudicial killing. Etymology ''Massacre'' derives from late 16th century Middle French word ''macacre'' meaning "slaughterhouse" or "butchery". Further origins are dubious, though the word may be related to Latin ''macellum'' "provisions store, butcher shop". The Middle French word ''macecr'' "butchery, carnage" is first recorded in the late 11th century. Its primary use remained the context of animal slaughter (in hunting terminology referring to the head of a stag) well into the 18th century. The use of ''macecre'' "butchery" of the mass killing of people dates to the 12th century, implying people being "slaughtered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battles Of The Middle Ages
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force commitment. An engagement with only limited commitment between the forces and without decisive results is sometimes called a skirmish. The word "battle" can also be used infrequently to refer to an entire operational campaign, although this usage greatly diverges from its conventional or customary meaning. Generally, the word "battle" is used for such campaigns if referring to a protracted combat encounter in which either one or both of the combatants had the same methods, resources, and strategic objectives throughout the encounter. Some prominent examples of this would be the Battle of the Atlantic, Battle of Britain, and the Battle of France, all in World War II. Wars and military campaigns are guided by military strategy, whereas b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battles Involving The Ethiopian Empire
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force commitment. An engagement with only limited commitment between the forces and without decisive results is sometimes called a skirmish. The word "battle" can also be used infrequently to refer to an entire operational campaign, although this usage greatly diverges from its conventional or customary meaning. Generally, the word "battle" is used for such campaigns if referring to a protracted combat encounter in which either one or both of the combatants had the same methods, resources, and strategic objectives throughout the encounter. Some prominent examples of this would be the Battle of the Atlantic, Battle of Britain, and the Battle of France, all in World War II. Wars and military campaigns are guided by military strategy, whereas batt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conflicts In 1332
Conflict may refer to: Social sciences * Conflict (process), the general pattern of groups dealing with disparate ideas * Conflict continuum from cooperation (low intensity), to contest, to higher intensity (violence and war) * Conflict of interest, involvement in multiple interests which could possibly corrupt the motivation or decision-making * Cultural conflict, a type of conflict that occurs when different cultural values and beliefs clash * Ethnic conflict, a conflict between two or more contending ethnic groups * Group conflict, conflict between groups * Intragroup conflict, conflict within groups * Organizational conflict, discord caused by opposition of needs, values, and interests between people working together * Role conflict, incompatible demands placed upon a person such that compliance with both would be difficult * Social conflict, the struggle for agency or power in something * Work–family conflict, incompatible demands between the work and family roles of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta Israel
Beta Israel, or Ethiopian Jews, is a Jewish group originating from the territory of the Amhara Region, Amhara and Tigray Region, Tigray regions in northern Ethiopia, where they are spread out across more than 500 small villages over a wide territory, alongside predominantly Christianity in Ethiopia, Christian and Islam in Ethiopia, Muslim populations. Most of them were concentrated mainly in what is today North Gondar Zone, Shire Inda Selassie, Welkait, Wolqayit, Tselemti, Dembia, Segelt, Qwara Province, Quara, and Belesa. After the founding of the Israel, State of Israel, most of the Beta Israel Aliyah, immigrated there or were evacuated through several initiatives by the Israeli government starting from 1979. The ethnogenesis of the Beta Israel is disputed with Genetic studies of Jews, genetic studies showing them to cluster closely with non-Jewish Amhara people, Amharas and Tigrayans with no indications of gene flow with Yemenite Jews in spite of their geographic proximity. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ifat Sultanate
The Sultanate of Ifat, known as Wafāt or Awfāt in Arabic texts, or the Kingdom of Zeila was a medieval Sunni Muslim state in the eastern regions of the Horn of Africa between the late 13th century and early 15th century. It was formed in present-day Ethiopia around eastern Shewa in Ifat. Led by the Walashma dynasty, the polity stretched from Zequalla to the port city of Zeila. The kingdom ruled over parts of what are now Ethiopia, Djibouti, Somaliland, Somalia. Location The earliest account of Ifat Sultanate comes from Ibn Sa'id al-Maghribi. He says that the region is called Jabarta and its capital is called Wafāt. Its population, who are Muslim, are ethnically mixed. The city sat upon an elevated place in a valley next to a river and the inhabitants cultivate banana and sugar cane. He calculates the astronomical position of the city being 8 latitude and 57 longitude according to Arab computation, which is located on the eastern edge of Shewa. Ifat Sultanate was also alter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jamal Ad-Din I
Jamal ad-Din () (flourished mid-14th century) was a governor of Ifat. He was the son of Nahwi b. Mansur b. Umar Walashma (Umar ibn Dunya-huz) and a brother of Haqq ad-Din I. Reign The Emperor of Ethiopia Amda Seyon I made Jamal ad-Din Governor of Ifat after the defeat and imprisonment of his brother Sabr ad-Din I. Taddesse Tamrat notes that Jamal ad-Din had been released from prison upon his appointment, and speculates that the Emperor had held onto the noble as a hostage to guarantee the loyalty of Ifat. However, according to the ''Glorious Victories of Amda Seyon'', Jamal ad-Din proved unfaithful to Emperor Amda Seyon. First, he allegedly was part of the alliance with Adal led by Salih that attacked, and was defeated by, the Emperor in the Battle of Das; towards the end of that same year, Jamal ad-Din was ordered to deliver apostate Christians to the Emperor for punishment, but refused, although he did produce the "son of his brother". For this, Emperor Amda Seyon ravaged I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ifat (historical Region)
Ifat (Harari language, Harari: ኢፋት; ; Somali Language, Somali: Awfat) also known as Yifat, Awfat or Wafat was a historical Muslim region in the Horn of Africa. It was located on the eastern edge of Shewa. Geography According to thirteenth century Arab geographer Ibn Sa'id al-Maghribi, Ifat was alternatively known as ''Jabarta''. In the fourteenth century Ibn Fadlallah al-Umari, Al Umari mentioned seven cities or domains within Ifat: Biqulzar, Adal (historical region), Adal, Shewa, Kwelgora, Shimi, Jamme and Laboo. Ifat designated the Muslim dominated portion of Shewa in Abyssinia according to post seventeenth century Harari language, Harari texts, its territory extended from the Shewan uplands east, towards the Awash River. History During Islam's inception tradition states the Banu Makhzum and Umayyad Caliphate, Umayyad coalitions quarreled in Ifat. According to historian Enrico Cerulli, in thirteenth century Sultan Umar Walasma founded the Ifat Sultanate in Ifat after ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |