|
Battery Point Formation
The Battery Point Formation is a geologic formation in Quebec. It preserves fossils dating back to the early Emsian to early Eifelian the lower Devonian period. Description A part of the Gaspé Sandstones, the Battery Point Formation is believed to have been deposited in a fluvial environment based on the presence of rootlets as well as the abundance of trough and planar-tabular cross bedding, and the lower part resembles modern braided systems more than meandering systems. It rests unconformably on the shallow marine sandstones of the York River Formation (the basal unit of the Gaspé Sandstones and making the Battery Point Formation the first continental unit of the sequence), transitioning upwards into the Malbaie Formation, and is 2,300 meters (7,550 feet) thick. Fossil content Limited intervals in the lower part of the formation contain remains of a few brachiopods and bivalves Bivalvia (), in previous centuries referred to as the Lamellibranchiata and Pelecypoda, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geological Formation
A geological formation, or simply formation, is a body of rock having a consistent set of physical characteristics (lithology) that distinguishes it from adjacent bodies of rock, and which occupies a particular position in the layers of rock exposed in a geographical region (the stratigraphic column). It is the fundamental unit of lithostratigraphy, the study of strata or rock layers. A formation must be large enough that it can be mapped at the surface or traced in the subsurface. Formations are otherwise not defined by the thickness (geology), thickness of their rock strata, which can vary widely. They are usually, but not universally, tabular in form. They may consist of a single lithology (rock type), or of alternating beds of two or more lithologies, or even a heterogeneous mixture of lithologies, so long as this distinguishes them from adjacent bodies of rock. The concept of a geologic formation goes back to the beginnings of modern scientific geology. The term was used by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bivalvia
Bivalvia (), in previous centuries referred to as the Lamellibranchiata and Pelecypoda, is a class of marine and freshwater molluscs that have laterally compressed bodies enclosed by a shell consisting of two hinged parts. As a group, bivalves have no head and they lack some usual molluscan organs, like the radula and the odontophore. They include the clams, oysters, cockles, mussels, scallops, and numerous other families that live in saltwater, as well as a number of families that live in freshwater. The majority are filter feeders. The gills have evolved into ctenidia, specialised organs for feeding and breathing. Most bivalves bury themselves in sediment, where they are relatively safe from predation. Others lie on the sea floor or attach themselves to rocks or other hard surfaces. Some bivalves, such as the scallops and file shells, can swim. The shipworms bore into wood, clay, or stone and live inside these substances. The shell of a bivalve is composed o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
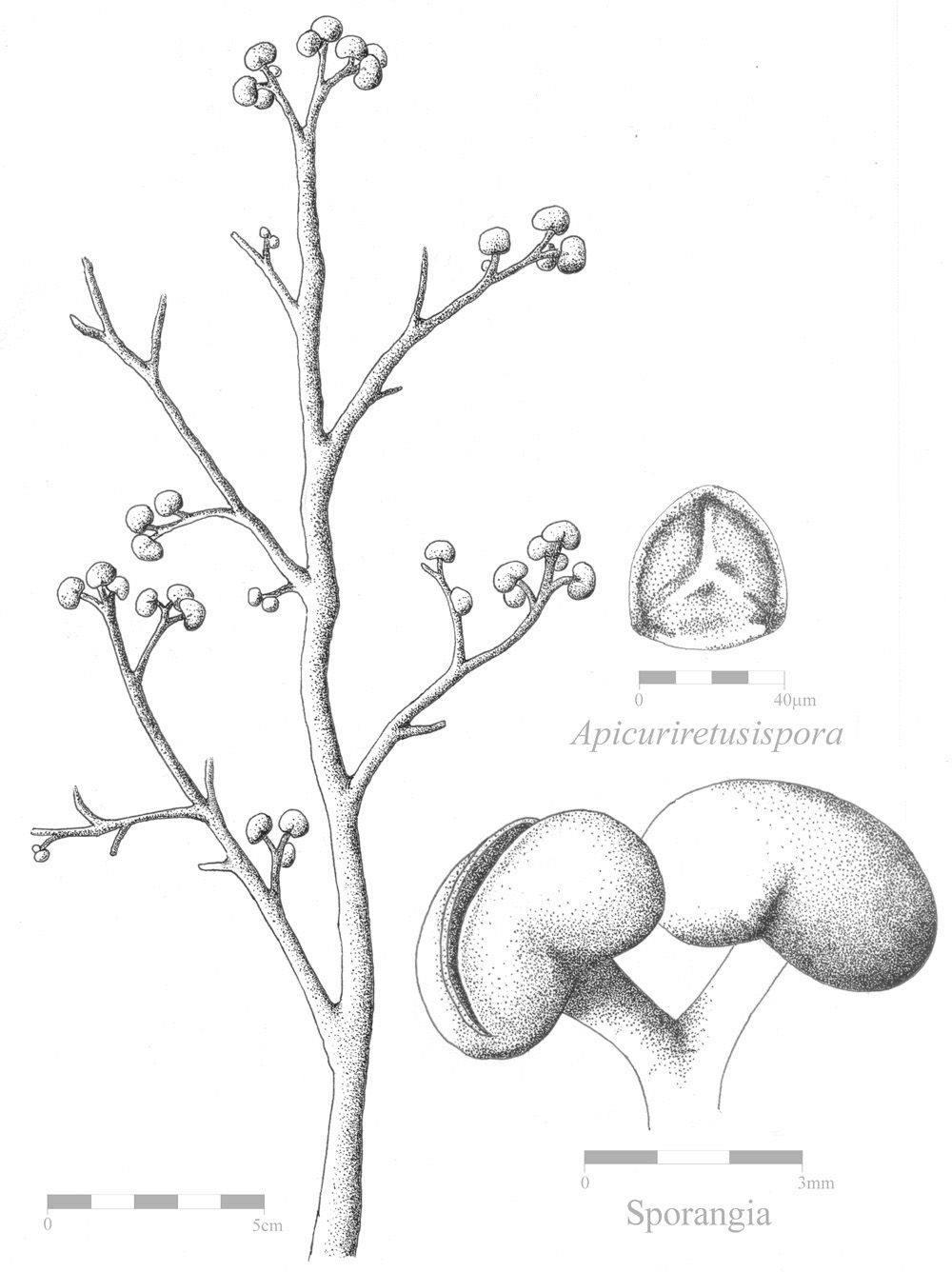
Cladoxylopsida
The cladoxylopsids are an extinct group of plants related to ferns and sphenopsids. They had a central trunk, from the top of which several lateral branches were attached. Fossils of these plants originate in the Middle Devonian to Early Carboniferous periods (around ), mostly just as stems. Cladoxylopsida contains two orders. The order Hyeniales is now included in Pseudosporochnales. Intact fossils of the Middle Devonian cladoxylopsid '' Wattieza'' show it to have been a tree, the earliest identified in the fossil record as of 2007. In 2019, experts from Cardiff University, UK; Binghamton University and the New York State Museum discovered more fossils of Cladoxylopsida and Archaeopteris in a quarry in Cairo, New York. A recent (2017) discovery in Xinjiang in China of early Late Devonian (Frasnian The Frasnian is one of two faunal stages in the Late Devonian Period. It lasted from million years ago to million years ago. It was preceded by the Givetian Stage and follo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plants
Plants are predominantly photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae. Historically, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi; however, all current definitions of Plantae exclude the fungi and some algae, as well as the prokaryotes (the archaea and bacteria). By one definition, plants form the clade Viridiplantae (Latin name for "green plants") which is sister of the Glaucophyta, and consists of the green algae and Embryophyta (land plants). The latter includes the flowering plants, conifers and other gymnosperms, ferns and their allies, hornworts, liverworts, and mosses. Most plants are multicellular organisms. Green plants obtain most of their energy from sunlight via photosynthesis by primary chloroplasts that are derived from endosymbiosis with cyanobacteria. Their chloroplasts contain chlorophylls a and b, which gives them their green color. Some plants are parasitic or mycotrophic and have lost the a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Campbellton Formation
The Campbellton Formation is a geologic formation in New Brunswick. It preserves fossils dating back to the latest Pragian and Emsian of the Devonian period. Description The Campbellton Formation is the southernmost representative of the Gaspé Sandstones group and can be divided into 6 facies associations (restricted lacustrine, marginal lacustrine, near-shore lacustrine, coastal-deltaic, sandy to gravelly alluvial plain, and gravelly proximal alluvial environments), and is nearly a kilometer thick. Lacustrine facies are prevalent in the lower parts of the eastern belt (representing a large open lake) while upper parts of the formation are dominated by alluvial facies (representing an eastward-flowing axial braided river A braided river, or braided channel, consists of a network of river channels separated by small, often temporary, islands called braid bars or, in English usage, ''aits'' or ''eyots''. Braided streams tend to occur in rivers with high sediment l ... system). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fin Spine
Fish anatomy is the study of the form or morphology of fish. It can be contrasted with fish physiology, which is the study of how the component parts of fish function together in the living fish. In practice, fish anatomy and fish physiology complement each other, the former dealing with the structure of a fish, its organs or component parts and how they are put together, such as might be observed on the dissecting table or under the microscope, and the latter dealing with how those components function together in living fish. The anatomy of fish is often shaped by the physical characteristics of water, the medium in which fish live. Water is much denser than air, holds a relatively small amount of dissolved oxygen, and absorbs more light than air does. The body of a fish is divided into a head, trunk and tail, although the divisions between the three are not always externally visible. The skeleton, which forms the support structure inside the fish, is either made of cartilage ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaspé Bay
Gaspé Bay () is a bay located on the northeast coast of the Gaspé Peninsula, Quebec, in the Gulf of St. Lawrence. The town of Gaspé, Quebec lies on a part of its southern shore, while most of its northern shore is in the Forillon National Park. The main rivers draining to the bay are the Dartmouth River and the York River (the latter one has its mouth in the city center of Gaspé). Gaspé Bay is where Jacques Cartier took possession of New France (now part of Canada) in the name of François I of France on July 24, 1534 - the beginning of France's overseas expansion. British General James Wolfe raided the Bay in the Gulf of St. Lawrence Campaign (1758), the year before the Siege of Quebec. Paleobotanical fossils and trace fossils of Archaeognatha from the Devonian period The Devonian ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic era, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the Silurian, million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Carbonif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chondrichthyan
Chondrichthyes (; ) is a class that contains the cartilaginous fishes that have skeletons primarily composed of cartilage. They can be contrasted with the Osteichthyes or ''bony fishes'', which have skeletons primarily composed of bone tissue. Chondrichthyes are jawed vertebrates with paired fins, paired nares, scales, and a heart with its chambers in series. Extant chondrichthyes range in size from the 10 cm (3.9 in) finless sleeper ray to the 10 m (32 ft) whale shark. The class is divided into two subclasses: Elasmobranchii (sharks, rays, skates, and sawfish) and Holocephali (chimaeras, sometimes called ghost sharks, which are sometimes separated into their own class). Within the infraphylum Gnathostomata, cartilaginous fishes are distinct from all other jawed vertebrates. Anatomy Skeleton The skeleton is cartilaginous. The notochord is gradually replaced by a vertebral column during development, except in Holocephali, where the notochord stays intact. In some deepwater s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gyracanthidae
Gyracanthidae is an family of extinct fish belonging to the class Acanthodii, known from early Devonian to late Carboniferous. Members are characterized by large, broad-based, paired fin spines with the pectoral fin spines having a distinct longitudinal curvature. Although it is originally classified in order Climatiiformes The Climatiiformes is an order of extinct fish belonging to the class Acanthodii. Like most other "spiny sharks", the Climatiiformes had sharp spines. These animals were often fairly small in size and lived from the Late Silurian to the Early Car ..., but later study questioned this. References Acanthodii Prehistoric fish families {{Carboniferous-animal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |