|
Bato (Dardanian Chieftain)
Bato (ruled c. 206 – 176 BC) was an Illyrian king of the Dardanian Kingdom, Dardanian State. Bato was the son of Longarus whom he succeeded and the brother of Monunius II who ruled after him. Bato fought alongside the Roman Republic, Romans against Macedon during the Second Macedonian War; he became a major threat to the Macedonians, and is known for using advanced war tactics against Athenagoras of Macedon, Athenagoras, However, after the war was over relations between Rome and the Dardanians soon deteriorated. Military activities When the Romans returned to Illyria in 200 BC under the experienced commander Publius Sulpicius Galba Maximus, P. Sulpicius Galba, they expected support from their former allies. After the Roman victories many kings, enemies of Macedonia came to the Roman camp: Pleuratus III of the Ardiaean Kingdom, Amynander of Athamania, Amynander, king of the Athamanians and Bato of the Dardanian State. The Roman commander told them he would call on their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Longarus
Longarus (ruled c. 231 – 206 BC) was an Illyrian king of the Dardanian Kingdom. Longarus was at war with various Macedonian kings and managed to conquer at different times part of Macedonia. Longarus was an ally of the Paeonia (kingdom), Paeonian State and liberated the Paeonians in order to open the routes towards Macedonia. Longarus' influence grew and many other Illyrians from the Ardiaean Kingdom joined him. Military activities After the Gallic invasions of Dardania, the Dardanians were not heard of for four decades; probably as they were in the process of recovering from the consequences of the Gallic invasions. During that time, the Dardanian State grew stronger and extended its borders in the south and in the north. During the second half of the 3rd century BC, the Illyrian-Macedonian Wars continued because of the desire for territorial expansion by the Macedonian kings against the Dardanians, particularly against Paeonia. The Paeonians had continually rebelled again ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perseus Of Macedon
Perseus (; – 166 BC) was king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon from 179 until 168BC. He is widely regarded as the last List of kings of Macedonia, king of Macedonia and the last ruler from the Antigonid dynasty, Antigonid Dynasty, as his defeat by Ancient Rome, Rome at the Battle of Pydna during the Third Macedonian War effectively ended Macedonia as an independent political entity. Early life Perseus was the son of king Philip V of Macedon and a concubine, probably Polycratia of Argos. His father spent most of his reign attempting to maintain Macedonian hegemony over Greece against heavy Greek resistance and, in his later reign, against an expansionist Roman Republic. Philip V failed in this endeavor: following defeat in the Second Macedonian War he was compelled to accept Roman power in Greece, and later helped Rome in the War against Nabis (195 BC) and the Aetolian War (191–189 BC). Perseus is recorded as having commanded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3rd-century BC Monarchs In Europe
The 3rd century was the period from AD 201 (represented by the Roman numerals CCI) to AD 300 (CCC) in accordance with the Julian calendar. In this century, the Roman Empire saw a crisis, starting with the assassination of the Roman Emperor Severus Alexander in 235, plunging the empire into a period of economic troubles, barbarian incursions, political upheavals, civil wars, and the split of the Roman Empire through the Gallic Empire in the west and the Palmyrene Empire in the east, which all together threatened to destroy the Roman Empire in its entirety, but the reconquests of the seceded territories by Emperor Aurelian and the stabilization period under Emperor Diocletian due to the administrative strengthening of the empire caused an end to the crisis by 284. This crisis would also mark the beginning of Late Antiquity. While in North Africa, Roman rule continued with growing Christian influence, particularly in the region of Carthage. In Persia, the Parthian Empire was s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Illyrian Kings
The Illyrians (; ) were a conglomeration of Indo-European peoples and tribes in the Balkan Peninsula, Southeastern Europe. They spoke the Illyrian language and practiced a multitude of common religious and cultural practices. Many Illyrian groups formed a distinct tribal mode of social organisation, which survived much later in the form of the Albanian tribal system. In late Iron Age and early classical antiquity, the first polities of the area would be created by tribal groupings, including the Taulantii and Dardani. The most powerful Illyrian states of the area, the Ardiaean kingdom, emerged in the 3rd century BC during the rule of Agron and Teuta. The Illyrians came into conflict with Roman Republic and were defeated in the Illyrian Wars, which were followed by many revolts. The largest and last of them was the Great Illyrian Revolt (6-9 BC). The beginning of the integration of the region of Illyria in the Roman world followed the revolt and saw many Illyrians rise thro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land border, as well as List of islands of Italy, nearly 800 islands, notably Sicily and Sardinia. Italy shares land borders with France to the west; Switzerland and Austria to the north; Slovenia to the east; and the two enclaves of Vatican City and San Marino. It is the List of European countries by area, tenth-largest country in Europe by area, covering , and the third-most populous member state of the European Union, with nearly 59 million inhabitants. Italy's capital and List of cities in Italy, largest city is Rome; other major cities include Milan, Naples, Turin, Palermo, Bologna, Florence, Genoa, and Venice. The history of Italy goes back to numerous List of ancient peoples of Italy, Italic peoples—notably including the ancient Romans, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
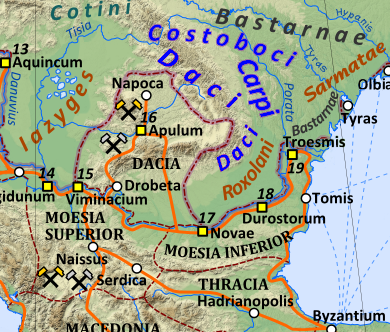
Bastarnae
The Bastarnae, Bastarni or Basternae, also known as the Peuci or Peucini, were an ancient people who are known from Greek and Roman records to have inhabited areas north and east of the Carpathian Mountains between about 300 BC and about 300 AD, stretching in an ark from the sources of the Vistula in present-day Poland and Slovakia, to the Lower Danube, and including all or most of present-day Moldava. The Peucini were sometimes described as a subtribe, who settled the Peuke Island in the Danube Delta, but apparently due to their importance their name was sometimes used for the Bastarnae as a whole. Near the sources of the Vistula another part of the Bastarnae were the Sidones, while the Atmoni, another tribe of the Bastarnae are only mentioned in one listing by Strabo. The earliest Graeco-Roman historians to refer to the Bastarnae imply that they were culturally La Tène culture, Celtic. Also consistent with connections to the cultures to their west, later Roman-era sources stat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Celts
The Celts ( , see Names of the Celts#Pronunciation, pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples ( ) were a collection of Indo-European languages, Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancient Indo-European people, reached the apogee of their influence and territorial expansion during the 4th century BC, extending across the length of Europe from Britain to Asia Minor."; . "[T]he Celts, were Indo-Europeans, a fact that explains a certain compatibility between Celtic, Roman, and Germanic mythology."; . "The Celts and Germans were two Indo-European groups whose civilizations had some common characteristics."; . "Celts and Germans were of course derived from the same Indo-European stock."; . "Celt, also spelled Kelt, Latin Celta, plural Celtae, a member of an early Indo-European people who from the 2nd millennium bce to the 1st century bce spread over much of Europe." in Europe and Anatolia, identified by their use of Celtic languages and other cultural similarities.. "C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
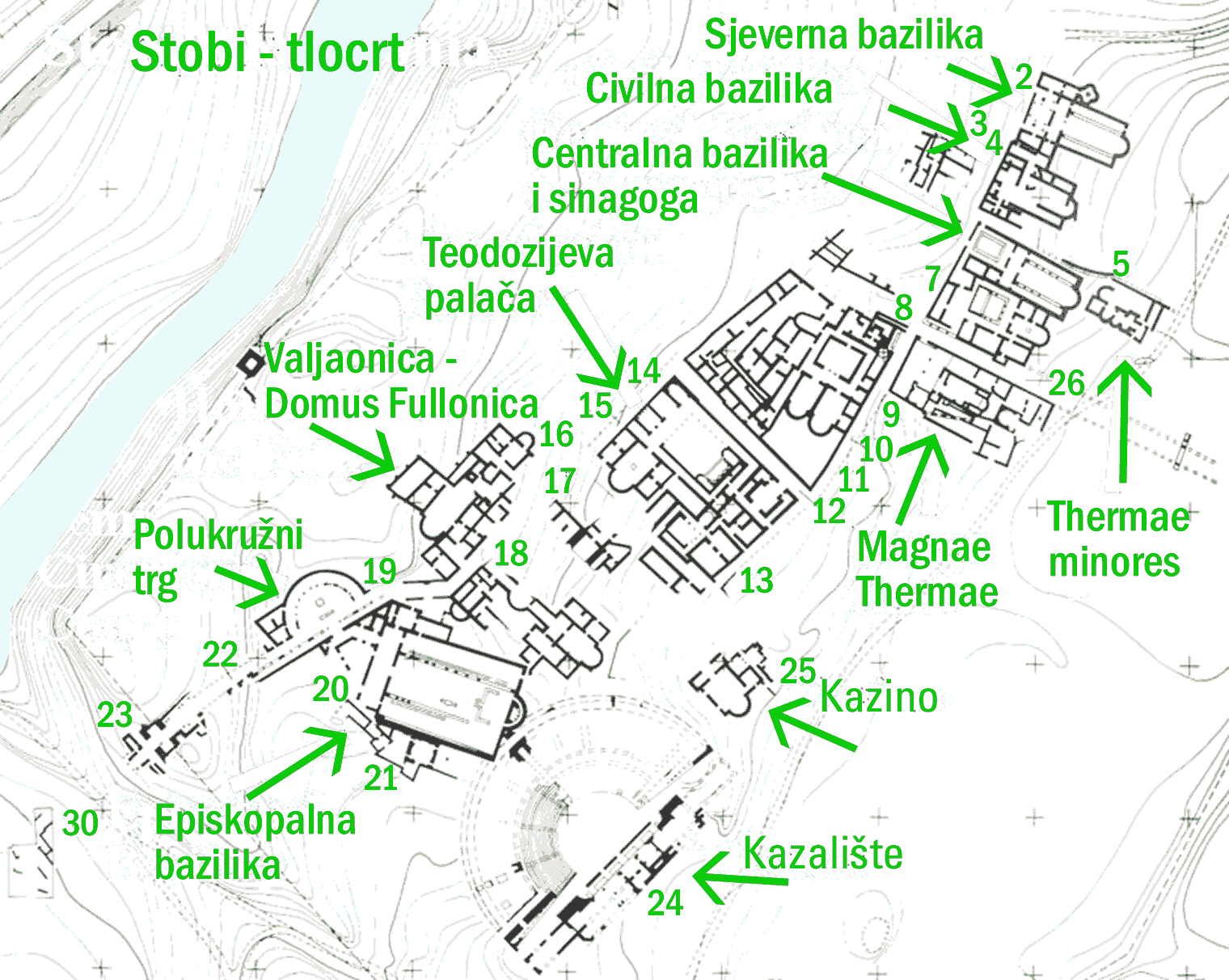
Stobi
Stobi or Stoboi (; ; ; ), was an ancient town of Paeonia (kingdom), Paeonia, later conquered by Macedon, and finally turned into the capital of the Ancient Rome, Roman province of Macedonia Salutaris. It is located near Gradsko, North Macedonia, Gradsko, North Macedonia, on the main road that leads from the Danube to the Aegean Sea and is considered by many to be the most famous archaeological site in North Macedonia. Stobi was built where the Crna River (Vardar), Erigon (Crna River) joins the Vardar, Axios (Vardar), making it strategically important as a center for both trade and warfare. The pre-Roman period Stobi developed from a Paeonian settlement established in the Archaic Greece, Archaic period. Located on the northern side of a terrace, the early town covered an area of about . Its proximity to the junction of the Erigón and Axiós Rivers as well as its position in the fertile central Vardar valley allowed it quickly to develop a flourishing economy and to establish t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vardar
The Vardar (; , , ) or Axios (, ) is the longest river in North Macedonia and a major river in Greece, where it reaches the Aegean Sea at Thessaloniki. It is long, out of which are in Greece, and drains an area of around . The maximum depth of the river is . Etymology The name ''Vardar'' for the river may have been derived from Thracian, although Dardanian, Paeonian, Ancient Macedonian and Ancient Greek were also spoken in the lands drained by the river. The modern Vardar is thought to derive from an earlier *''Vardários'', which may ultimately derive from Proto-Indo-European (PIE) *''(s)wordo-wori-'' "black water". The name ''Vardários'' (Βαρδάριος) was sometimes used by the Ancient Greeks in the 3rd century BC. The same name was widely used in the Byzantine era. Vardar/Vardarios may be a translation of (or otherwise have a similar meaning as) ''Axios'', which may be Thracian and may have meant "not-shining" from PIE *''n.-sk(e)i'' (cf. Avestan ''axšaēna'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apollonia, Illyria
Apollonia (Ancient Greek, Koine Greek: Ἀπολλωνία; demonym: Ἀπολλωνιάτης, ''Apolloniates''; ) was an ancient Greece, Ancient Greek trade colony which developed into an independent polis, and later a Ancient Rome, Roman Municipium, city, in southern Illyria. It was located on the right bank of the Vjosa, Aoös/Vjosë river, approximately 10 km from the eastern coast of the Adriatic Sea. Its ruins are situated in the Fier County, county of Fier, close to the village of Pojan, in Albania. Apollonia was perhaps the most important of Apollonia (other), the several classical towns of the same name. It was founded around 600 BC by Greek colonists from Ancient Corinth, Corinth and possibly Korkyra (polis), Corcyra, who established a trading settlement on a largely abandoned coastal site by invitation of the local Illyrians. Corinthian colonial policy seems to have been relatively liberal, focused on resource extraction for the support of their homeland, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pelagonia
Pelagonia (; ) is a geographical region of Macedonia named after the ancient kingdom. Ancient Pelagonia roughly corresponded to the present-day municipalities of Bitola, Prilep, Mogila, Novaci, Kruševo, and Krivogaštani in North Macedonia and to the municipalities of Florina, Amyntaio and Prespes in Greece. History In antiquity, Pelagonia was roughly bounded by Paeonia to the north and east, Lynkestis and Almopia to the south and Illyria to the west; and was inhabited by the Pelagones, an Ancient Greek tribe of Upper Macedonia, who were centered at the Pelagonian plain and belonged to the Molossian tribal state or '' koinon''. The region was annexed to the Macedonian kingdom during the 4th century BC and became one of its administrative provinces. In medieval times, when the names of Lynkestis and Orestis had become obsolete, Pelagonia acquired a broader meaning. This is why the Battle of Pelagonia (1259) between Byzantines and Latins includes also the cur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |