|
Bathyraja Maculata
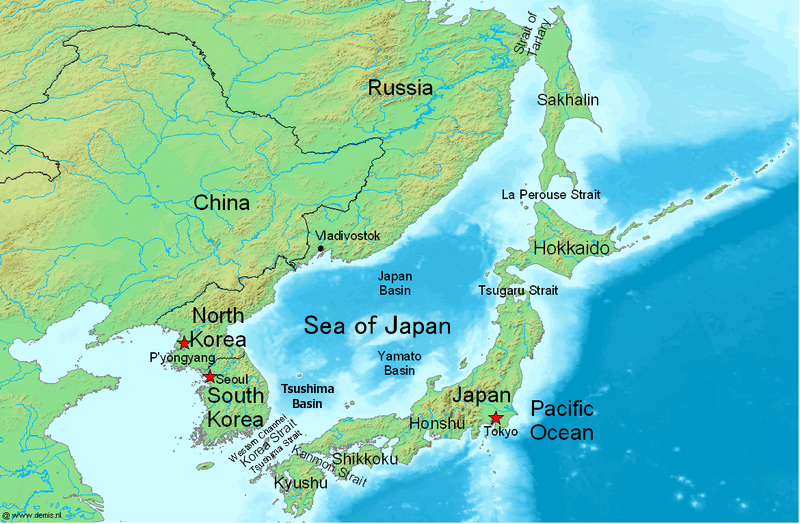
''Bathyraja maculata'', the white-blotched skate, is a species of Skate (fish), skate from the western North Pacific Ocean. An adult is approximately 1 meter in length, and is found at depths of up to 1 kilometer. Unlike any other known member of the genus ''Bathyraja'', the white-blotched skate has white blotches on a grey to brown dorsal surface, while the ventral side is lighter in color with darker blotches. Dorsal side is rough with spines, while the ventral side is smooth. Range The white-blotched skate is well established to inhabit waters in the Northern Sea of Japan, Sea of Okhotsk and Aleutian Islands. It was the most commonly caught skate in a NOAA bottom-trawl survey of the Aleutian Islands in 2006. Initially thought to inhabit only the western margin of the Gulf of Alaska, trawl surveys have now found specimens along the eastern margin as well. References Bathyraja, maculata Taxa named by Reizo Ishiyama Taxa named by Hajime Ishihara Fish described in 197 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hajime Ishihara
is the Japanese word meaning . In the Japanese traditional martial arts such as karate, judo is an unarmed modern Japanese martial art, Olympic sport (since 1964), and the most prominent form of jacket wrestling competed internationally.『日本大百科全書』電子版【柔道】(CD-ROM version of Encyclopedia Nipponica, "Judo") ..., aikido, Kūdō and kendo, it is a verbal command to "begin". Hajime is also a common Japanese given name for males. In the Amami Islands, Hajime (元) is a surname. Possible writings Hajime can be written using different kanji characters and can mean: *始め, "beginning" or "start" *初め, "beginning" or "first" ;as a given name *一, "first" *元, "beginning" or "origin" *始, "beginning" or "start" *肇, "beginning" *基, "fundamental" *創, "genesis" *孟, "beginning" or "chief" *朔, "first day of month" *甫, "beginning" or "great" The name can also be written in hiragana as はじめ and katakana as ハジメ People Given name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skate (fish)
Skates are cartilaginous fish belonging to the family Rajidae in the superorder Batoidea of rays. More than 150 species have been described, in 17 genera.LAST, P.R. & SÉRET, B. & STEHMANN, M.F.W. & WEIGMANN, S. (2016) Skates, Family Rajidae. In: Last, P.R., White, W.T., Carvalho, M.R. de, Séret, B., Stehmann, M.F.W & Naylor, G.J.P (Eds.) Rays of the World. CSIRO Publishing, Melbourne: 204–363 Softnose skates and pygmy skates were previously treated as subfamilies of Rajidae (Arhynchobatinae and Gurgesiellinae), but are now considered as distinct families. Alternatively, the name "skate" is used to refer to the entire order of Rajiformes (families Anacanthobatidae, Arhynchobatidae, Gurgesiellidae and Rajidae). Members of Rajidae are distinguished by a stiff snout and a rostrum that is not reduced. Taxonomy and systematics Evolution Skates belong to the ancient lineage of cartilaginous fishes. Fossil denticles (tooth-like scales in the skin) resembling those of toda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bathyraja
''Bathyraja'' is a large genus of skates in the family Arhynchobatidae. Species There are 55 recognized species in this genus:Orr, J.W., Stevenson, D.E., Hoff, G.R., Spies, I. & McEachran, J.D. (2011)Bathyraja panthera, ''a new species of skate (Rajidae: Arhynchobatinae) from the western Aleutian Islands, and resurrection of the subgenus'' Arctoraja ''Ishiyama.'' NOAA Professional Paper NMFS, 11: 50pp * ''Bathyraja abyssicola'' (Gilbert, 1896) (Deep-sea skate) * '' Bathyraja aguja'' ( Kendall & Radcliffe, 1912) (Aguja skate) * ''Bathyraja albomaculata'' (Norman, 1937) (White-dotted skate) * '' Bathyraja aleutica'' (Gilbert, 1896) (Aleutian skate) * '' Bathyraja andriashevi'' Dolganov, 1985 (Little-eyed skate) * '' Bathyraja bergi'' Dolganov, 1983 (Bottom skate) * '' Bathyraja brachyurops'' ( Fowler, 1910) (Broadnose skate) * '' Bathyraja cousseauae'' Díaz de Astarloa & Mabragaña, 2004 (Joined-fins skate) * ''Bathyraja diplotaenia'' (Ishiyama, 1952) (Dusky-pink skate) * ''Ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Of Japan
The Sea of Japan is the marginal sea between the Japanese archipelago, Sakhalin, the Korean Peninsula, and the mainland of the Russian Far East. The Japanese archipelago separates the sea from the Pacific Ocean. Like the Mediterranean Sea, it has almost no tides due to its nearly complete enclosure from the Pacific Ocean. This isolation also affects faunal diversity and salinity, both of which are lower than in the open ocean. The sea has no large islands, bays or capes. Its water balance is mostly determined by the inflow and outflow through the straits connecting it to the neighboring seas and the Pacific Ocean. Few rivers discharge into the sea and their total contribution to the water exchange is within 1%. The seawater has an elevated concentration of dissolved oxygen that results in high biological productivity. Therefore, fishing is the dominant economic activity in the region. The intensity of shipments across the sea has been moderate owing to political issues, but it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Of Okhotsk
The Sea of Okhotsk ( rus, Охо́тское мо́ре, Ohótskoye móre ; ja, オホーツク海, Ohōtsuku-kai) is a marginal sea of the western Pacific Ocean. It is located between Russia's Kamchatka Peninsula on the east, the Kuril Islands on the southeast, Japan's island of Hokkaido on the south, the island of Sakhalin along the west, and a stretch of eastern Siberian coast along the west and north. The northeast corner is the Shelikhov Gulf. The sea is named after the Okhota river, which in turn named after the Even word () meaning "river". Geography The Sea of Okhotsk covers an area of , with a mean depth of and a maximum depth of . It is connected to the Sea of Japan on either side of Sakhalin: on the west through the Sakhalin Gulf and the Gulf of Tartary; on the south through the La Pérouse Strait. In winter, navigation on the Sea of Okhotsk is impeded by ice floes. Ice floes form due to the large amount of freshwater from the Amur River, lowering the sal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aleutian Islands
The Aleutian Islands ( ; ; ale, Unangam Tanangin, "land of the Aleuts"; possibly from the Chukchi ''aliat'', or "island")—also called the Aleut Islands, Aleutic Islands, or, before 1867, the Catherine Archipelago—are a chain of 14 main, larger volcanic islands and 55 smaller ones. Most of the Aleutian Islands belong to the U.S. state of Alaska, with the archipelago encompassing the Aleutians West Census Area and the Aleutians East Borough. The Commander Islands, located further to the west, belong to the Russian federal subject of Kamchatka Krai, of the Russian Far East. The islands form part of the Aleutian Arc of the Northern Pacific Ocean, and occupy a land area of 6,821 sq mi (17,666 km2) that extends westward roughly from the Alaskan Peninsula mainland, in the direction of the Kamchatka Peninsula; the archipelago acts as a border between the Bering Sea to the north and the Pacific Ocean to the south. Crossing longitude 180°, at which point east and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NOAA
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (abbreviated as NOAA ) is an United States scientific and regulatory agency within the United States Department of Commerce that forecasts weather, monitors oceanic and atmospheric conditions, charts the seas, conducts deep sea exploration, and manages fishing and protection of marine mammals and endangered species in the U.S. exclusive economic zone. Purpose and function NOAA's specific roles include: * ''Supplying Environmental Information Products''. NOAA supplies to its customers and partners information pertaining to the state of the oceans and the atmosphere, such as weather warnings and forecasts via the National Weather Service. NOAA's information services extend as well to climate, ecosystems, and commerce. * ''Providing Environmental Stewardship Services''. NOAA is a steward of U.S. coastal and marine environments. In coordination with federal, state, local, tribal and international authorities, NOAA manages the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gulf Of Alaska
The Gulf of Alaska (Tlingit: ''Yéil T'ooch’'') is an arm of the Pacific Ocean defined by the curve of the southern coast of Alaska, stretching from the Alaska Peninsula and Kodiak Island in the west to the Alexander Archipelago in the east, where Glacier Bay and the Inside Passage are found. The Gulf shoreline is a combination of forest, mountain and a number of tidewater glaciers. Alaska's largest glaciers, the Malaspina Glacier and Bering Glacier, spill out onto the coastal line along the Gulf of Alaska. The coast is heavily indented with Cook Inlet and Prince William Sound, the two largest connected bodies of water. It includes Yakutat Bay and Cross Sound. Lituya Bay (a fjord north of Cross Sound, and south of Mount Fairweather) is the site of the largest recorded tsunami in history. It serves as a sheltered anchorage for fishing boats. Ecology The Gulf of Alaska is considered a Class I, productive ecosystem with more than 300 grams of carbon per square met ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxa Named By Reizo Ishiyama
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; plural taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and given a particular ranking, especially if and when it is accepted or becomes established. It is very common, however, for taxonomists to remain at odds over what belongs to a taxon and the criteria used for inclusion. If a taxon is given a formal scientific name, its use is then governed by one of the nomenclature codes specifying which scientific name is correct for a particular grouping. Initial attempts at classifying and ordering organisms (plants and animals) were set forth in Carl Linnaeus's system in ''Systema Naturae'', 10th edition (1758), as well as an unpublished work by Bernard and Antoine Laurent de Jussieu. The idea of a unit-based system of biological classification was first made widely available in 1805 in the int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)