|
Bathynerita
''Bathynerita'' is a genus of sea snails, marine gastropod mollusks in the family Neritidae. Species Species within the genus ''Bathynerita'' include: * ''Bathynerita naticoidea ''Bathynerita naticoidea'' is a species of small sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusc in the family Neritidae, the nerites. This species is endemic to underwater cold seeps (oil seeps and gas seeps) in the northern Gulf of Mexico and in the Ca ...'' Clarke, 1989 References External links * Neritidae Monotypic gastropod genera {{Neritidae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bathynerita Naticoidea
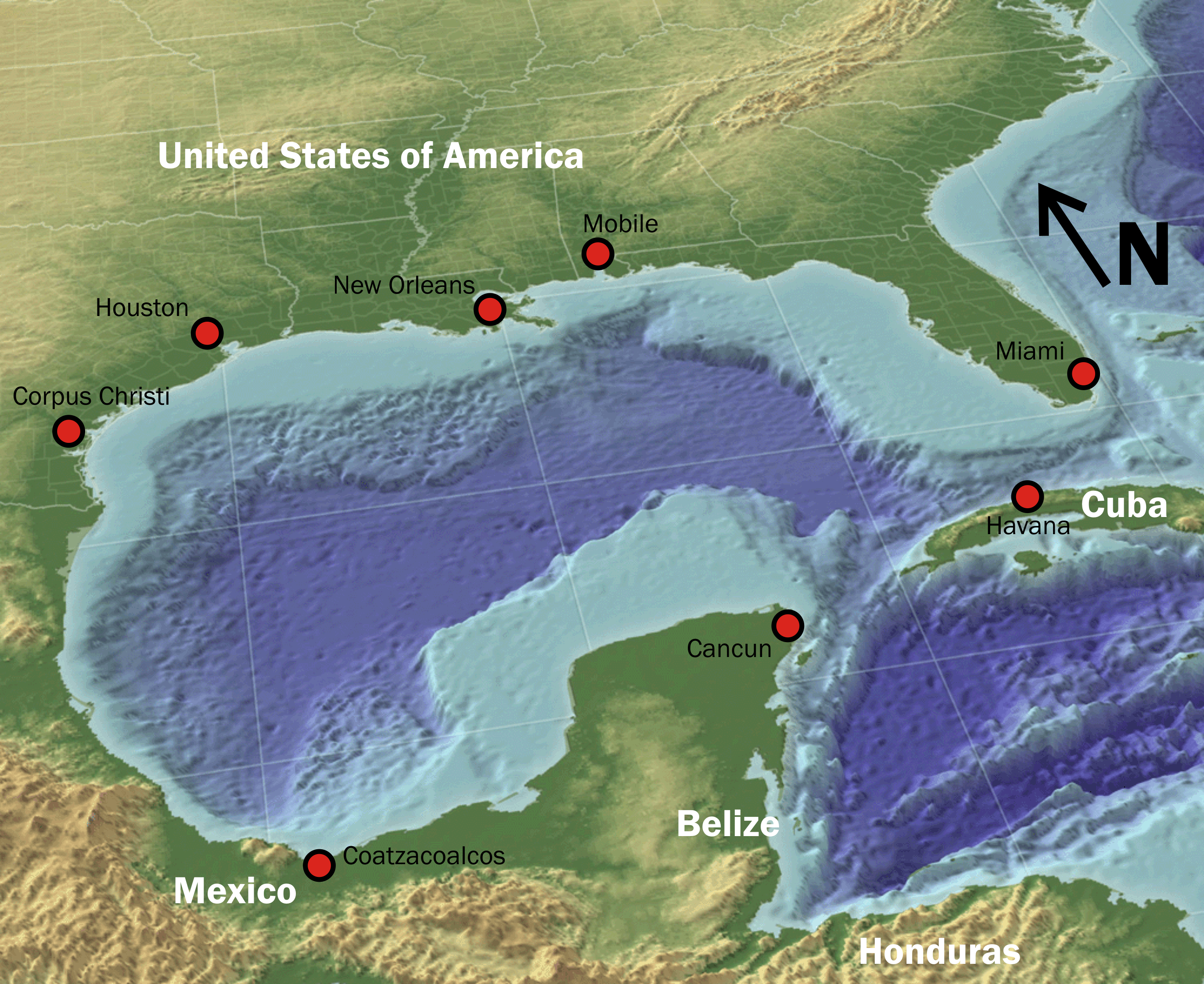
''Bathynerita naticoidea'' is a species of small sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusc in the family Neritidae, the nerites. This species is endemic to underwater cold seeps ( oil seeps and gas seeps) in the northern Gulf of Mexico and in the Caribbean. The possible placement of this species within the closely allied family Phenacolepadidae has been under discussion. Species from these habitats can be collected by manned submersibles or by remotely operated underwater vehicles. Distribution This species lives in cold seeps in the northern Gulf of Mexico and in the accretionary wedge of Barbados in the Caribbean in the upper continental slope, in depths from 400 to 2100 m. Examples of localities include: * "Bush Hill" (27°46.9478 N; 91°30.5266 W) * methane seep "Brine Pool NR-1" in depth 650 m (27°43.415 N; 91°16.756 W) [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neritidae
Neritidae, common name the nerites, is a taxonomic family of small to medium-sized saltwater and freshwater snails which have a gill and a distinctive operculum. MolluscaBase eds. (2021). MolluscaBase. Neritininae Poey, 1852. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at: http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=411639 on 2021-09-25 The family Neritidae includes marine genera such as ''Nerita'', marine and freshwater genera such as ''Neritina'', and freshwater and brackish water genera such as ''Theodoxus''. The common name "nerite" as well as the family name Neritidae and the genus name '' Nerita'', are derived from the name of Nerites, who was a sea god in Greek mythology. Distribution Neritidae live primarily in the southern hemisphere, but there are some exceptions, such as a genus '' Theodoxus'' which can be found in Europe and Northern Africa Bunje P. M. & Lindberg D. R. (2007). "Lineage divergence of a freshwater snail clade associated with po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Snail
Sea snail is a common name for slow-moving marine gastropod molluscs, usually with visible external shells, such as whelk or abalone. They share the taxonomic class Gastropoda with slugs, which are distinguished from snails primarily by the absence of a visible shell. Definition Determining whether some gastropods should be called sea snails is not always easy. Some species that live in brackish water (such as certain neritids) can be listed as either freshwater snails or marine snails, and some species that live at or just above the high tide level (for example species in the genus '' Truncatella'') are sometimes considered to be sea snails and sometimes listed as land snails A land snail is any of the numerous species of snail that live on land, as opposed to the sea snails and freshwater snails. ''Land snail'' is the common name for terrestrial gastropod mollusks that have shells (those without shells are known .... Anatomy Sea snails are a very large group o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can reproduction, produce Fertility, fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology (biology), morphology, behaviour or ecological niche. In addition, paleontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined. The most recent rigorous estimate for the total number of species of eukaryotes is between 8 and 8.7 million. However, only about 14% of these had been described by 2011. All species (except viruses) are given a binomial nomenclature, two-part name, a "binomial". The first part of a binomial is the genus to which the species belongs. The second part is called the specifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Family (biology)
Family ( la, familia, plural ') is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between order and genus. A family may be divided into subfamilies, which are intermediate ranks between the ranks of family and genus. The official family names are Latin in origin; however, popular names are often used: for example, walnut trees and hickory trees belong to the family Juglandaceae, but that family is commonly referred to as the "walnut family". What belongs to a family—or if a described family should be recognized at all—are proposed and determined by practicing taxonomists. There are no hard rules for describing or recognizing a family, but in plants, they can be characterized on the basis of both vegetative and reproductive features of plant species. Taxonomists often take different positions about descriptions, and there may be no broad consensus across the scientific community for some time. The publishing of new data and opi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mollusk
Mollusca is the second-largest phylum of invertebrate animals after the Arthropoda, the members of which are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 85,000 extant species of molluscs are recognized. The number of fossil species is estimated between 60,000 and 100,000 additional species. The proportion of undescribed species is very high. Many taxa remain poorly studied. Molluscs are the largest marine phylum, comprising about 23% of all the named marine organisms. Numerous molluscs also live in freshwater and terrestrial habitats. They are highly diverse, not just in size and anatomical structure, but also in behaviour and habitat. The phylum is typically divided into 7 or 8 taxonomic classes, of which two are entirely extinct. Cephalopod molluscs, such as squid, cuttlefish, and octopuses, are among the most neurologically advanced of all invertebrates—and either the giant squid or the colossal squid is the largest known invertebrate species. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastropod
The gastropods (), commonly known as snails and slugs, belong to a large taxonomic class of invertebrates within the phylum Mollusca called Gastropoda (). This class comprises snails and slugs from saltwater, from freshwater, and from land. There are many thousands of species of sea snails and slugs, as well as freshwater snails, freshwater limpets, and land snails and slugs. The class Gastropoda contains a vast total of named species, second only to the insects in overall number. The fossil history of this class goes back to the Late Cambrian. , 721 families of gastropods are known, of which 245 are extinct and appear only in the fossil record, while 476 are currently extant with or without a fossil record. Gastropoda (previously known as univalves and sometimes spelled "Gasteropoda") are a major part of the phylum Mollusca, and are the most highly diversified class in the phylum, with 65,000 to 80,000 living snail and slug species. The anatomy, behavior, feeding, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marine (ocean)
The ocean (also the sea or the world ocean) is the body of salt water that covers approximately 70.8% of the surface of Earth and contains 97% of Earth's water. An ocean can also refer to any of the large bodies of water into which the world ocean is conventionally divided."Ocean." ''Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary'', Merriam-Webster, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Miocene
The Early Miocene (also known as Lower Miocene) is a sub-epoch of the Miocene Epoch made up of two stages: the Aquitanian and Burdigalian stages. The sub-epoch lasted from 23.03 ± 0.05 Ma to 15.97 ± 0.05 Ma (million years ago). It was preceded by the Oligocene epoch. As the climate started to get cooler, the landscape started to change. New mammals evolved to replace the extinct animals of the Oligocene epoch. The first members of the hyena and weasel family started to evolve to replace the extinct '' Hyaenodon'', entelodonts and bear-dogs. The chalicotheres survived the Oligocene epoch. A new genus of entelodont called '' Daeodon'' evolved in order to adapt to the new habitats and hunt the new prey animals of the Early Miocene epoch; it quickly became the top predator of North America. But it became extinct due to competition from ''Amphicyon ''Amphicyon'' ("ambiguous dog") is an extinct genus of large carnivorous bone-crushing mammals, popularly known as bear dogs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. '' Panthera leo'' (lion) and '' Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants of an ancestral taxon are grouped together (i.e. phylogenetic analysis should c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Kingdom (biology), biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals Heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, are Motility, able to move, can Sexual reproduction, reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage in which their body consists of a hollow sphere of Cell (biology), cells, the blastula, during Embryogenesis, embryonic development. Over 1.5 million Extant taxon, living animal species have been Species description, described—of which around 1 million are Insecta, insects—but it has been estimated there are over 7 million animal species in total. Animals range in length from to . They have Ecology, complex interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as zoology. Most living animal species are in Bilateria, a clade whose members have a Symmetry in biology#Bilate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neritoidea
Neritoidea is a taxonomic superfamily of mostly sea snails, nerites and their allies, marine gastropod mollusks in the order Cycloneritida (according to the taxonomy of the Gastropoda by Bouchet & Rocroi, 2005). MolluscaBase eds. (2020). MolluscaBase. Neritoidea Rafinesque, 1815. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at: http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=196314 on 2020-08-21 Previously this superfamily was in the order Neritoida in the superorder Neritopsina. Families Families within the superfamily Neritoidea are as follows (according to the taxonomy of the Gastropoda by Bouchet & Rocroi, 2005): * † Cortinellidae Bandel, 2000 * † Neridomidae Bandel, 2008 * † Neritariidae Wenz, 1938 * Neritidae, the nerites, freshwater and marine species * † Otostomidae Bandel, 2008 * † Parvulatopsidae Gründel, Keupp & Lang, 2015 * Phenacolepadidae Pilsbry, 1895, false limpets * † Pileolidae ''Pileolidae'' is an extinct family of fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)




