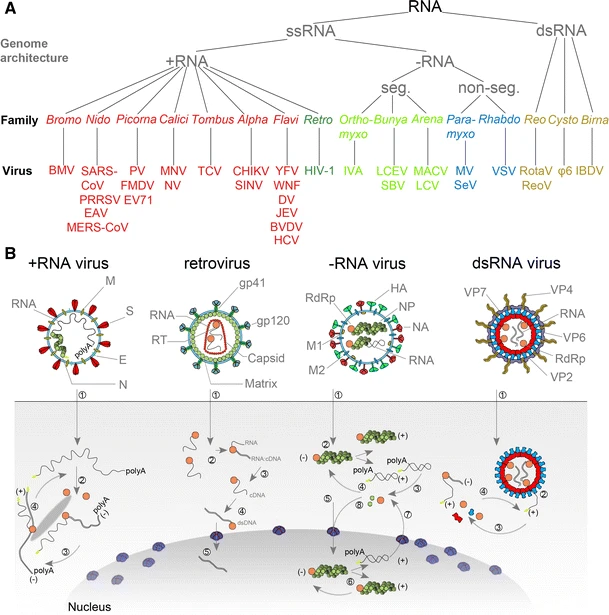
|
Batai Virus
Batai virus (BATV) is a RNA virus belonging to the genus '' Orthobunyavirus''. Introduction Batai virus (BATV) is an enveloped, single-stranded, negative sense RNA genome. It is a member of the genus '' Orthobunyavirus''. It was first isolated from ''Culex'' mosquitoes in Malaysia in 1955. Evidence from serological surveillance and virus isolation shows that this virus is widely distributed around the world. Similar to other orthobunyaviruses it contributes to both human and animal disease. In humans it has been noted in causing severe fever, and in bovines has been associated with premature birth, birth defects, and increased abortion rates. It is transmitted through mosquito bites, ticks, and biting midges, and occurs from cold to tropical regions of Africa, Asia, and Europe. Structure The structure of Batai virus (BATV) consists of an enveloped nucleocapsid that is composed of three RNA segments: small (S), medium (M), and large (L). The S segment encodes the nucleocapsid (N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RNA Virus
An RNA virus is a virus characterized by a ribonucleic acid (RNA) based genome. The genome can be single-stranded RNA (ssRNA) or double-stranded (Double-stranded RNA, dsRNA). Notable human diseases caused by RNA viruses include influenza, SARS, MERS, COVID-19, Dengue virus, hepatitis C, hepatitis E, West Nile fever, Ebola virus disease, rabies, polio, mumps, and measles. All known RNA viruses, that is viruses that use a homologous RNA-dependent polymerase for replication, are categorized by the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) into the realm ''Riboviria''. This includes RNA viruses belonging to ''Group III'', ''Group IV'' or ''Group V'' of the Virus classification#Baltimore classification, Baltimore classification system as well as ''Group VI. Group VI'' viruses are retroviruses, viruses with RNA genetic material that use DNA intermediates in their Viral life cycle, life cycle including HIV-1 and HIV-2 which cause AIDS. The majority of such RNA viruses fall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leukopenia
Leukopenia () is a decrease in the number of white blood cells (leukocytes). It places individuals at increased risk of infection as white blood cells are the body's primary defense against infections. Signs and symptoms Symptoms may include: * skin or mouth ulcers * sore throat * cough * difficulty in breathing * light-headedness * fever * chills * body aches Leukopenia vs. neutropenia Neutropenia, a subtype of leukopenia, refers to a decrease in the number of circulating neutrophil granulocytes, the most abundant white blood cells. The terms ''leukopenia'' and ''neutropenia'' may occasionally be used interchangeably, as the neutrophil count is the most important indicator of infection risk. Agranulocytosis is an acute form of neutropenia. Causes Medical conditions Low white cell count may be due to acute viral infections, such as a cold or influenza. It has been associated with chemotherapy, radiation therapy, myelofibrosis, aplastic anemia (failure of white cell, red ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thrombocytopenia
In hematology, thrombocytopenia is a condition characterized by abnormally low levels of platelets (also known as thrombocytes) in the blood. Low levels of platelets in turn may lead to prolonged or excessive bleeding. It is the most common coagulation disorder among intensive care units, intensive care patients and is seen in a fifth of medical patients and a third of surgical patients. A normal human platelet count ranges from 150,000 to 450,000 platelets/microliter (μL) of blood. Values outside this range do not necessarily indicate disease. One common definition of thrombocytopenia requiring emergency treatment is a platelet count below 50,000/μL. Thrombocytopenia can be contrasted with the conditions associated with an abnormally ''high'' level of platelets in the blood – thrombocythemia (when the cause is unknown), and thrombocytosis (when the cause is known). Signs and symptoms Thrombocytopenia usually asymptomatic, has no symptoms and is picked up on a routine comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bunyamwera Virus
Bunyamwera virus (BUNV) is a negative-sense, single-stranded enveloped RNA virus. It is assigned to the '' Orthobunyavirus'' genus, in the ''Peribunyaviridae'' family. Bunyamwera virus can infect both humans and ''Aedes aegypti'' (yellow fever mosquito). It is named for Bunyamwera, a town in western Uganda, where it was isolated in 1943. Reassortant viruses derived from Bunyamwera virus, such as Ngari virus, have been associated with large outbreaks of viral haemorrhagic fever in Kenya and Somalia. Molecular biology The genetic structure of Bunyamwera virus is typical for viruses in '' Bunyaviricetes'', which are a class of enveloped negative-sense, single-stranded RNA viruses with a genome split into three parts—Small (S), Middle (M), and Large (L). The L RNA segment encodes an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (L protein), the M RNA segment encodes two surface glycoproteins (Gc and Gn) and a nonstructural protein (NSm), while the S RNA segment encodes a nucleocapsid pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RNA Polymerase II
RNA polymerase II (RNAP II and Pol II) is a Protein complex, multiprotein complex that Transcription (biology), transcribes DNA into precursors of messenger RNA (mRNA) and most small nuclear RNA (snRNA) and microRNA. It is one of the three RNA polymerase, RNAP enzymes found in the nucleus of eukaryote, eukaryotic cells. A 550 kDa complex of 12 subunits, RNAP II is the most studied type of RNA polymerase. A wide range of transcription factors are required for it to bind to upstream gene promoter (biology), promoters and begin transcription. Discovery Early studies suggested a minimum of two RNAPs: one which synthesized rRNA in the nucleolus, and one which synthesized other RNA in the nucleoplasm, part of the nucleus but outside the nucleolus. In 1969, biochemists Robert G. Roeder and William J. Rutter, William Rutter discovered there are total three distinct nuclear RNA polymerases, an additional RNAP that was responsible for transcription of some kind of RNA in the nucleoplasm. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Golgi Apparatus
The Golgi apparatus (), also known as the Golgi complex, Golgi body, or simply the Golgi, is an organelle found in most eukaryotic Cell (biology), cells. Part of the endomembrane system in the cytoplasm, it protein targeting, packages proteins into membrane-bound Vesicle (biology and chemistry), vesicles inside the cell before the vesicles are sent to their destination. It resides at the intersection of the secretory, lysosomal, and Endocytosis, endocytic pathways. It is of particular importance in processing proteins for secretion, containing a set of glycosylation enzymes that attach various sugar monomers to proteins as the proteins move through the apparatus. The Golgi apparatus was identified in 1898 by the Italian biologist and pathologist Camillo Golgi. The organelle was later named after him in the 1910s. Discovery Because of its large size and distinctive structure, the Golgi apparatus was one of the first organelles to be discovered and observed in detail. It was d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endonuclease
In molecular biology, endonucleases are enzymes that cleave the phosphodiester bond within a polynucleotide chain (namely DNA or RNA). Some, such as deoxyribonuclease I, cut DNA relatively nonspecifically (with regard to sequence), while many, typically called '' restriction endonucleases'' or ''restriction enzymes'', cleave only at very specific nucleotide sequences. Endonucleases differ from exonucleases, which cleave the ends of recognition sequences instead of the middle (''endo'') portion. Some enzymes known as "exo-endonucleases", however, are not limited to either nuclease function, displaying qualities that are both endo- and exo-like. Evidence suggests that endonuclease activity experiences a lag compared to exonuclease activity. Restriction enzymes are endonucleases from eubacteria and archaea that recognize a specific DNA sequence. The nucleotide sequence recognized for cleavage by a restriction enzyme is called the ''restriction site''. Typically, a restriction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oligonucleotides
Oligonucleotides are short DNA or RNA molecules, oligomers, that have a wide range of applications in genetic testing, research, and forensics. Commonly made in the laboratory by solid-phase chemical synthesis, these small fragments of nucleic acids can be manufactured as single-stranded molecules with any user-specified sequence, and so are vital for artificial gene synthesis, polymerase chain reaction (PCR), DNA sequencing, molecular cloning and as molecular probes. In nature, oligonucleotides are usually found as small RNA molecules that function in the regulation of gene expression (e.g. microRNA), or are degradation intermediates derived from the breakdown of larger nucleic acid molecules. Oligonucleotides are characterized by the sequence of nucleotide residues that make up the entire molecule. The length of the oligonucleotide is usually denoted by " -mer" (from Greek ''meros'', "part"). For example, an oligonucleotide of six nucleotides (nt) is a hexamer, while one of 25 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vacuole
A vacuole () is a membrane-bound organelle which is present in Plant cell, plant and Fungus, fungal Cell (biology), cells and some protist, animal, and bacterial cells. Vacuoles are essentially enclosed compartments which are filled with water containing inorganic and organic molecules including enzymes in Solutes, solution, though in certain cases they may contain solids which have been engulfed. Vacuoles are formed by the fusion of multiple membrane Vesicle (biology), vesicles and are effectively just larger forms of these. The organelle has no basic shape or size; its structure varies according to the requirements of the cell. Discovery Antonie van Leeuwenhoek described the plant vacuole in 1676. Contractile vacuoles ("stars") were first observed by Spallanzani (1776) in protozoa, although mistaken for respiratory organs. Félix Dujardin, Dujardin (1841) named these "stars" as ''vacuoles''. In 1842, Matthias Jakob Schleiden, Schleiden applied the term for plant cells, to dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ochlerotatus
''Ochlerotatus'' is a genus of mosquito. Until 2000, it was ranked as a subgenus of ''Aedes'' but was reclassified as a distinct genus based on taxonomic studies. This change resulted in the renaming of many subgenus species, and revisions of related taxa in the Aedini tribe are ongoing. Some authors, however, still use traditional taxonomic names in their publications. Taxonomy ''Ochlerotatus'' was originally established as a genus in 1891.Félix Lynch Arribálzaga. 1891. Dipterologia Argentina, Culicidae. ''Revista del Museo de la Plata'', i: 345–377; p. 374. In 1917, a researcher by the name of Edwards transferred it to the Aedini, aedine subgenus; however, as of 2000, ''Ochlerotatus'' has resumed its role as a genus (a revision made by Reinhert, due to common traits in genitalia). Based on taxonomic characteristics, many species and subgenera of ''Aedes'' mosquitoes have been transferred to the ''Ochlerotatus'' genus. After a contentious worldwide debate regarding the eff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |