|
Bastion Hill
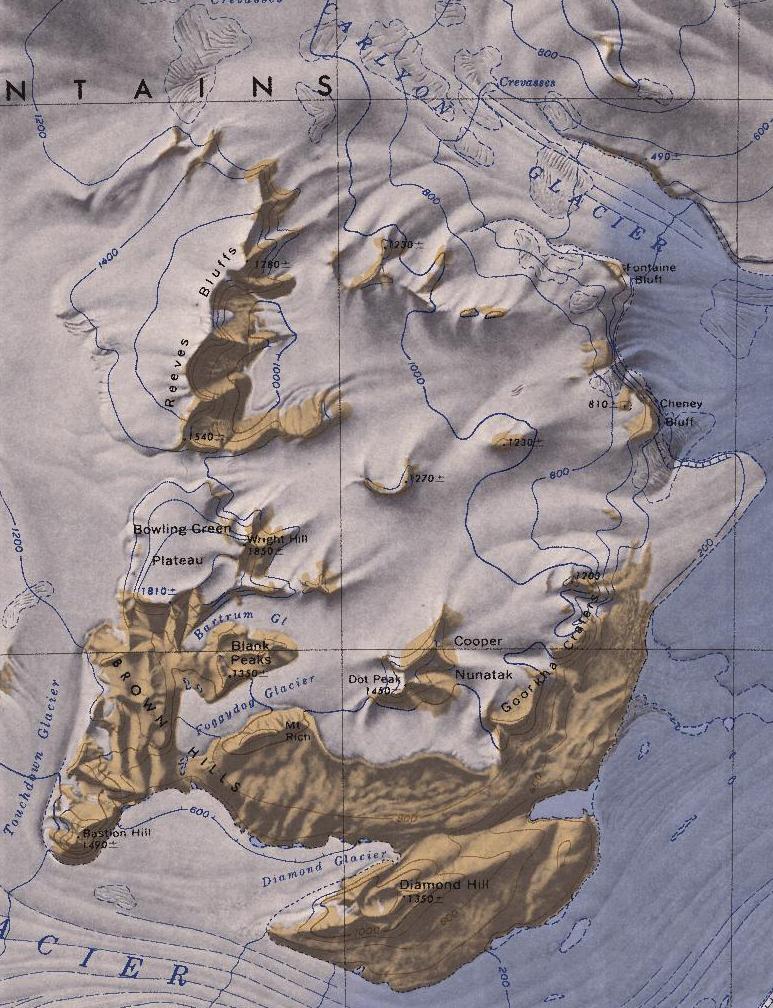
Bastion Hill () is a prominent ice-free feature in the Brown Hills of Antarctica, rising to and projecting southward into Darwin Glacier (Antarctica), Darwin Glacier just east of Touchdown Glacier. The descriptive name, the hill supposedly suggesting a bastion, was given by the Darwin Glacier Party of the Commonwealth Trans-Antarctic Expedition (1956–58). Localities *Relief Pass References * Hills of Oates Land {{OatesLand-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brown Hills
The Brown Hills () are a group of mainly snow-free hills in the Cook Mountains of Antarctica. Location The Brown Hills lie north of the lower reaches of Darwin Glacier. They are north of Diamond Hill and are adjacent to Diamond Glacier, a distributary of the Darwin Glacier. To the east they are bordered by the Ross Ice Shelf. On the west side, the Touchdown Glacier flows south to the Darwin Glacier between Roadend Nunatak and the Brown Hills. Reeves Bluffs are to the north of the hills. The hills were named for their color by the Darwin Glacier Party of the Commonwealth Trans-Antarctic Expedition (1956–58). Geology During glacial periods, Diamond Glacier would probably have flowed over the Brown Hills to the Ross Ice Shelf. Exposure ages of five glacial erratics from the Brown Hills range from 7,000 to 205,000 years ago, which implies that until 7,000 years ago the Brown Hills saddle was ice-covered. Simpson 2002 proposes that the Darwin calcic suite, a K-series, I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest continent, being about 40% larger than Europe, and has an area of . Most of Antarctica is covered by the Antarctic ice sheet, with an average thickness of . Antarctica is, on average, the coldest, driest, and windiest of the continents, and it has the highest average elevation. It is mainly a polar desert, with annual precipitation of over along the coast and far less inland. About 70% of the world's freshwater reserves are frozen in Antarctica, which, if melted, would raise global sea levels by almost . Antarctica holds the record for the lowest measured temperature on Earth, . The coastal regions can reach temperatures over in summer. Native species of animals include mites, nematodes, penguins, seals and tardigrades. Where ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Darwin Glacier (Antarctica)
Darwin Glacier () is a large glacier in Antarctica. It flows from the polar plateau eastward between the Darwin Mountains and the Cook Mountains to the Ross Ice Shelf. The lower part of the glacier was mapped by the British National Antarctic Expedition, 1901–04, and the whole area traversed by New Zealand parties of the Commonwealth Trans-Antarctic Expedition (1956–58). The glacier was named in association with the Darwin Mountains (themselves named after Leonard Darwin). Robertson Buttress is the westernmost in a series of large rock buttresses on the south side of Darwin Glacier between Alley Glacier and Gaussiran Glacier. See also * Erewhon Basin * List of glaciers in the Antarctic * Glaciology * The Nozzle The Nozzle is a comparatively narrow constriction through which the lower Darwin Glacier flows, causing the ice to bank up somewhat in the vicinity of Diamond Hill. The descriptive name was given by the Darwin Glacier Party of the Commonwealth Tran ... * Walker Cir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Touchdown Glacier
Darwin Glacier () is a large glacier in Antarctica. It flows from the polar plateau eastward between the Darwin Mountains and the Cook Mountains to the Ross Ice Shelf. The lower part of the glacier was mapped by the British National Antarctic Expedition, 1901–04, and the whole area traversed by New Zealand parties of the Commonwealth Trans-Antarctic Expedition (1956–58). The glacier was named in association with the Darwin Mountains (themselves named after Leonard Darwin). Robertson Buttress is the westernmost in a series of large rock buttresses on the south side of Darwin Glacier between Alley Glacier and Gaussiran Glacier. See also * Erewhon Basin * List of glaciers in the Antarctic * Glaciology * The Nozzle * Walker Cirque Walker Cirque () is a prominent glacier-filled cirque at the west side of the terminus of McCleary Glacier in Cook Mountains. The cirque opens to Darwin Glacier (Antarctica), Darwin Glacier near the head. Named after Carlton Walker, Facilities, M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bastion
A bastion or bulwark is a structure projecting outward from the curtain wall of a fortification, most commonly angular in shape and positioned at the corners of the fort. The fully developed bastion consists of two faces and two flanks, with fire from the flanks being able to protect the curtain wall and the adjacent bastions. Compared with the medieval fortified towers they replaced, bastion fortifications offered a greater degree of passive resistance and more scope for ranged defence in the age of gunpowder artillery. As military architecture, the bastion is one element in the style of fortification dominant from the mid 16th to mid 19th centuries. Evolution By the middle of the 15th century, artillery pieces had become powerful enough to make the traditional medieval round tower and curtain wall obsolete. This was exemplified by the campaigns of Charles VII of France who reduced the towns and castles held by the English during the latter stages of the Hundred Years W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commonwealth Trans-Antarctic Expedition
The Commonwealth Trans-Antarctic Expedition (CTAE) of 1955–1958 was a Commonwealth-sponsored expedition that successfully completed the first overland crossing of Antarctica, via the South Pole. It was the first expedition to reach the South Pole overland for 46 years, preceded only by Amundsen's expedition and Scott's expedition in 1911 and 1912. In keeping with the tradition of polar expeditions of the Heroic Age of Antarctic Exploration, the CTAE was a private venture, though it was supported by the governments of the United Kingdom, New Zealand, United States, Australia and South Africa, as well as many corporate and individual donations, under the patronage of Queen Elizabeth II. It was headed by British explorer Vivian Fuchs, with New Zealander Sir Edmund Hillary leading the New Zealand Ross Sea Support team. The New Zealand party included scientists participating in International Geophysical Year research while the British team were separately based at Hal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Relief Pass
Relief Pass () is a pass, about 1,000 m high, situated 1 nautical mile (1.9 km) north of Bastion Hill in the Brown Hills. Explored by the Victoria University of Wellington Antarctic Expedition The Antarctic Research Centre (ARC) is part of the School of Geography, Environment and Earth Sciences at Victoria University of Wellington. Its mission is to research " Antarctic climate history and processes, and their influence on the global clim ... (VUWAE), 1962–63, and so named by its members because of the relief it provided after ascent to this pass. References Mountain passes of Antarctica Landforms of Oates Land {{OatesLand-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)