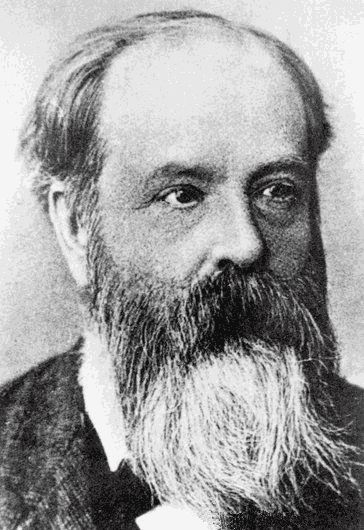|
Basil John Mason
Sir Basil John Mason (18 August 1923 – 6 January 2015) was an expert on cloud physics and former Director-General of the Meteorological Office from 1965 to 1983 and Chancellor of the University of Manchester Institute of Science and Technology (UMIST) from 1994 to 1996. Education and early life Mason was born in Docking, Norfolk. and educated at Fakenham Grammar School and University College, Nottingham. He served in the Radar branch of the RAF during the Second World War as a Flight-lieutenant. After being awarded a first class degree in physics by the University of London he was in 1948 appointed lecturer in the postgraduate Department of Meteorology at Imperial College, London. He married Doreen Jones, with whom he had two sons. Career He worked at Imperial College from 1948 to 1965, being appointed Professor of Cloud Physics in 1961. His work concerned the physical processes involved in the formation of clouds and the release of rain, snow or hail and led to the Mason ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order Of The Bath
The Most Honourable Order of the Bath is a British order of chivalry founded by King George I of Great Britain, George I on 18 May 1725. Recipients of the Order are usually senior British Armed Forces, military officers or senior Civil Service (United Kingdom), civil servants, and the monarch awards it on the advice of His Majesty's Government. The name derives from an elaborate medieval ceremony for preparing a candidate to receive his knighthood, of which ritual bathing (as a symbol of Ritual purification, purification) was an element. While not all knights went through such an elaborate ceremony, knights so created were known as "knights of the Bath". George I constituted the Knights of the Bath as a regular Order (honour), military order. He did not revive the order, which did not previously exist, in the sense of a body of knights governed by a set of statutes and whose numbers were replenished when vacancies occurred. The Order consists of the Sovereign of the United King ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mason Equation
The Mason equation is an approximate analytical expression for the growth (due to condensation) or evaporation of a water droplet—it is due to the meteorologist B. J. Mason.1. B. J. Mason ''The Physics of Clouds'' (1957) Oxford Univ. Press. The expression is found by recognising that mass diffusion towards the water drop in a supersaturated environment transports energy as latent heat, and this has to be balanced by the diffusion of sensible heat back across the boundary layer, (and the energy of heatup of the drop, but for a cloud-sized drop this last term is usually small). Equation In Mason's formulation the changes in temperature across the boundary layer can be related to the changes in saturated vapour pressure by the Clausius–Clapeyron relation; the two energy transport terms must be nearly equal but opposite in sign and so this sets the interface temperature of the drop. The resulting expression for the growth rate is significantly lower than that expected if the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Medal
The Royal Medal, also known as The Queen's Medal and The King's Medal (depending on the gender of the monarch at the time of the award), is a silver-gilt medal, of which three are awarded each year by the Royal Society. Two are given for "the most important contributions to the advancement of natural knowledge," and one for "distinguished contributions in the applied sciences", all of which are done within the Commonwealth of Nations. Background The award was created by George IV and awarded first during 1826. Initially there were two medals awarded, both for the most important discovery within the year previous, a time period which was lengthened to five years and then shortened to three. The format was endorsed by William IV and Victoria, who had the conditions changed during 1837 so that mathematics was a subject for which a Royal Medal could be awarded, albeit only every third year. The conditions were changed again during 1850 so that: ... the Royal Medals in each year sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rutherford Memorial Lecture
The Institute of Physics (IOP) is a UK-based not-for-profit learned society and professional body that works to advance physics education, research and application. It was founded in 1874 and has a worldwide membership of over 20,000. The IOP is the Physical Society for the UK and Ireland and supports physics in education, research and industry. In addition to this, the IOP provides services to its members including careers advice and professional development and grants the professional qualification of Chartered Physicist (CPhys), as well as Chartered Engineer (CEng) as a nominated body of the Engineering Council; it also holds its own separate Royal Charter. The IOP's publishing company, IOP Publishing, publishes 85 academic titles. History The Institute of Physics was formed in 1960 from the merger of the Physical Society, founded as the Physical Society of London in 1874, and the Institute of Physics, founded in 1918. The Physical Society of London had been official ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rumford Medal
The Rumford Medal is an award bestowed by the Royal Society for "outstanding contributions in the field of physics". The award is named in honour of British scientist Sir Benjamin Thompson, Count Rumford, who is noted for his works on thermodynamics and for establishing the Royal Institution. The award was created in 1796 after Thompson transferred £1,000 to the Royal Society in stocks, instructing the latter to grant the awardee the fund's interest as a premium. Thompson was awarded the inaugural award in 1800. The award initially consisted of two medals, one each in silver and gold, struck in the same die. This was later replaced with a single medal made of silver gilt. The medal is awarded with a cash prize of £2,000. British painter Robert Smirke created the original design of the medal. The diameter of the medal is 3 inches (7.62 cm). The obverse featured a tripod altar with a flame upon it, circumscribed by a Latin inscription from Lucretius' poem ''De rerum natura'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Fellows Of The Royal Society Elected In 1965
This article lists fellows of the Royal Society elected in 1965. Fellows # Robert Edward Bell #George Douglas Hutton Bell #Sydney Brenner # Giles Skey Brindley # Bertram Neville Brockhouse #Arthur Roderick Collar #Sir Edward Foyle Collingwood # Robert Royston Amos Coombs # Kenneth George Denbigh #Gordon Elliott Fogg # Charles Edmund Ford #Roderic Alfred Gregory #Dorothy Hill # Alan Woodworth Johnson #Reginald Victor Jones #Charles Kemball # John Stodart Kennedy #Tom Kilburn #Sir Hans Leo Kornberg # Hans Kronberger # Charles Philippe Leblond # Panchanan Maheshwari #Sir Basil John Mason #William Valentine Mayneord #Sir Robert Gordon Menzies #Sir Gilbert Roberts # Stanley Keith Runcorn # Philip MacDonald Sheppard #Keith Stewartson # John Marion Thoday #John Clive Ward # Gerald Beresford Whitham #Sir Geoffrey Wilkinson Foreign Members #Theodosius Dobzhansky #Richard Feynman # Jaroslav Heyrovsky #Severo Ochoa References {{Fellows of the Royal Society 1965 Even ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Institution Of Engineers And Shipbuilders In Scotland
The Institution of Engineers in Scotland (IES) is a multi-disciplinary professional body and learned society, founded in Scotland, for professional engineers in all disciplines and for those associated with or taking an interest in their work. Its main activities are an annual series of evening talks on engineering, open to all, and a range of school events aimed at encouraging young people to consider engineering careers. Between 1870 and 2020 the institution was known as the Institution of Engineers and Shipbuilders in Scotland (IESIS). IES is registered as a Scottish Charity, No SC011583 and is the fourth oldest, still-active, registered Company in Scotland. Members, Fellows, Graduates or Companions are entitled to use the abbreviated distinctive letters after their name - MIES, FIES, GIES, CIES. Foundation The inaugural meeting of the Institution of Engineers in Scotland was held on 1 May 1857. Office bearers were appointed and the principal objective of the new institution ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symons Gold Medal
The Symons Gold Medal is awarded biennially by the Royal Meteorological Society for distinguished work in the field of meteorological science. It was established in 1901 in memory of George James Symons, a notable British meteorologist. Recipients Source (1978-)Royal Metereological Society See also * List of meteorology awards This list of earth sciences awards is an index to articles on notable awards for earth sciences, or natural science related to the planet Earth. It includes awards for meteorology, oceanography and paleontology, but excludes awards for environment ... * List of prizes named after people References {{reflist Meteorology awards British science and technology awards Awards established in 1901 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Institute Of Physics
The Institute of Physics (IOP) is a UK-based not-for-profit learned society and professional body that works to advance physics education, physics research, research and applied physics, application. It was founded in 1874 and has a worldwide membership of over 20,000. The IOP is the Physical Society for the UK and Ireland and supports physics in education, research and industry. In addition to this, the IOP provides services to its members including careers advice and professional development and grants the Professional qualifications in the United Kingdom, professional qualification of Chartered Physicist (CPhys), as well as Chartered Engineer (UK), Chartered Engineer (CEng) as a nominated body of the Engineering Council; it also holds its own separate Royal Charter. The IOP's publishing company, IOP Publishing, publishes 85 academic titles. History The Institute of Physics was formed in 1960 from the merger of the Physical Society of London, Physical Society, founded as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glazebrook Medal
The Richard Glazebrook Medal and Prize is awarded annually by the Institute of Physics to recognise leadership in the field of physics. It was established in 1966 and named in honour of Richard Glazebrook, Sir Richard T. Glazebrook, the first president of the Institute of Physics. It was originally a silver medal with a £250 prize. The award consists of the medal, a cash prize and a certificate. In 1992, the Institute decided that the medal and prize should become one of its Premier Awards and that, from 2008, it should be one of its gold medals. Recipients The following have received the award: See also * Institute of Physics Awards * List of physics awards * List of awards named after people References {{DEFAULTSORT:Glazebrook Medal and Prize, Richard 1966 establishments in the United Kingdom Awards established in 1966 Awards of the Institute of Physics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chree Medal
The Edward Appleton Medal and Prize is awarded by the Institute of Physics for distinguished research in environmental, earth or atmospheric physics. Originally named after Charles Chree, the British physicist and former President of the Physical Society of London, it was renamed in 2008 to commemorate Edward Victor Appleton, winner of the Nobel Prize for proving the existence of the ionosphere. History The prize was established in 1941 by Chree's sister, Jessie, after his death, and it was originally awarded biennially. It was first awarded to Sydney Chapman. From 2001 it was awarded annually. After the 2008 renaming the prize was awarded in even-dated years until 2016, then as and when required. The cash prize part of the award has risen in value since its inception, reported at £150 in 1985 and £300 in 1987, to its present-day value of £1000. Winners Recipients of the Appleton medal and prize *2024 Nicolas Bellouin *2021 Philip Stier *2020 Adam Scaife *2019 Cathryn M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Kent
The University of Kent (formerly the University of Kent at Canterbury, abbreviated as UKC) is a Collegiate university, collegiate public university, public research university based in Kent, United Kingdom. The university was granted its royal charter on 4 January 1965 and the following year Princess Marina of Greece and Denmark, Princess Marina, Duchess of Kent, was formally installed as the first Chancellor (education), Chancellor. The university has its main campus north of Canterbury situated within of parkland, housing over 6,000 students, as well as a campus in Medway in Kent and a postgraduate centre in Paris. The university is international, with students from 158 different nationalities and 41% of its academic and research staff being from outside the United Kingdom. It is a member of the Santander Network of European universities encouraging social and economic development. History Origins A university in the city of Canterbury was first considered in 1947, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |