|
Base (cheerleading)
Base or BASE may refer to: Brands and enterprises *BASE (mobile operator), a Belgian mobile telecommunications operator *Base CRM, an enterprise software company founded in 2009 with offices in Mountain View and Kraków, Poland *Base Design, an international design, communications, audiovisual, copywriting and publishing firm *Base FX, a visual effects and animation company founded in 2006 with studios in Beijing, Wuxi and Xiamen, China *Budapest Aircraft Services, callsign BASE Computing *BASE (search engine), Bielefeld Academic Search Engine *, an HTML element#base, HTML element *Basically Available, Soft state, Eventual consistency (BASE), a consistency model *Google Base, an online database provided by Google *LibreOffice Base, LibreOffice's database module *OpenOffice.org Base, OpenOffice.org's database module, also known as ooBase Mathematics *Base of computation, commonly called ''radix'', the number of distinct digits in a positional numeral system *Base of a logarithm, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BASE (mobile Operator)
Base (stylized as BASE) is the third largest of Belgium's three mobile telecommunications operators. It is a subsidiary of Telenet. It competes with Proximus and Orange Belgium. It was previously owned by KPN and sold to Telenet in 2015. History Base was founded as Belgium's third major mobile network operator in 1999 under the brand name of KPN Orange. It was a joint venture between the Dutch KPN Mobile and the then British Orange telcos. After the acquisition of Orange by France Télécom, its shares were sold to KPN Mobile. In 2002, the brand name was changed from Orange to Base. The fixed line and broadband operations were started in 2007 after the acquisition of Tele2 Belgium. In October 2009 the fixed line and broadband ADSL Asymmetric digital subscriber line (ADSL) is a type of digital subscriber line (DSL) technology, a data communications technology that enables faster data transmission over Copper wire, copper telephone lines than a conventional voiceband modem . ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Backward Society Education
Backward Society Education (BASE) is a nonprofit non-governmental organization that works with Tharu in Western Nepal to fight illiteracy, bonded labor from the Kamaiya system, and a number of other issues in the region. The group received the 2002 Anti-Slavery Award from the Anti-Slavery International for its work in combating bonded labor, and the Danish International Development Agency reported in 2002, "BASE is running the only literacy campaign in the country." They are currently working on initiatives to help people who have been freed from bonded labor. Organization Founding and campaign against Kamiya The eventual founder of BASE, Dilli Bahadur Chaudhari, formed a group called the 4-H Club which was funded through intermediaries by USAID as a forum for discussing agricultural techniques with Tharu farmers. This club quickly grew in size and scope, and club meetings often railed against oppression from the upper castes of Nepal against the Tharu. In 1991, the organizati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleobase
Nucleotide bases (also nucleobases, nitrogenous bases) are nitrogen-containing biological compounds that form nucleosides, which, in turn, are components of nucleotides, with all of these monomers constituting the basic building blocks of nucleic acids. The ability of nucleobases to form base pairs and to stack one upon another leads directly to long-chain helical structures such as ribonucleic acid (RNA) and deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). Five nucleobases— adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), thymine (T), and uracil (U)—are called ''primary'' or ''canonical''. They function as the fundamental units of the genetic code, with the bases A, G, C, and T being found in DNA while A, G, C, and U are found in RNA. Thymine and uracil are distinguished by merely the presence or absence of a methyl group on the fifth carbon (C5) of these heterocyclic six-membered rings. In addition, some viruses have aminoadenine (Z) instead of adenine. It differs in having an extra amine group, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta-alumina Solid Electrolyte
Beta-alumina solid electrolyte (BASE) is a fast-ion conductor material used as a membrane in several types of molten salt electrochemical cell. Currently there is no known substitute available. β-Alumina exhibits an unusual layered crystal structure which enables very fast-ion transport. β-Alumina is not an isomorphic form of aluminium oxide (Al2O3), but a sodium polyaluminate. It is a hard polycrystalline ceramic, which, when prepared as an electrolyte, is complexed with a mobile ion, such as Na+, K+, Li+, Ag+, H+, Pb2+, Sr2+ or Ba2+ depending on the application. β-Alumina is a good conductor of its mobile ion yet allows no non-ionic (i.e., electronic) conductivity. The crystal structure of the β-alumina provides an essential rigid framework with channels along which the ionic species of the solid can migrate. Ion transport involves hopping from site to site along these channels. Since the 1970s this technology has been thoroughly developed, resulting in interesting ap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Base Pair
A base pair (bp) is a fundamental unit of double-stranded nucleic acids consisting of two nucleobases bound to each other by hydrogen bonds. They form the building blocks of the DNA double helix and contribute to the folded structure of both DNA and RNA. Dictated by specific hydrogen bonding patterns, "Watson–Crick" (or "Watson–Crick–Franklin") base pairs (guanine–cytosine and adenine–thymine) allow the DNA helix to maintain a regular helical structure that is subtly dependent on its nucleotide sequence. The Complementarity (molecular biology), complementary nature of this based-paired structure provides a Redundancy (information theory), redundant copy of the genetic information encoded within each strand of DNA. The regular structure and data redundancy provided by the DNA double helix make DNA well suited to the storage of genetic information, while base-pairing between DNA and incoming nucleotides provides the mechanism through which DNA polymerase replicates DNA and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BASE Experiment
BASE (Baryon Antibaryon Symmetry Experiment), AD-8, is a multinational collaboration at the Antiproton Decelerator facility at CERN, Geneva. The goal of the Japanese and German BASE collaboration are high-precision investigations of the fundamental properties of the antiproton, namely the Mass-to-charge ratio, charge-to-mass ratio and the magnetic moment. Experimental setup The single antiprotons are stored in an advanced Penning trap system, which has a multi-trap system at its core. It consists of a reservoir trap, a precision trap, an analysis trap and a cooling trap. The reservoir trap has the capability to store antiprotons for several years and allows BASE to operate experiments independent from accelerator cycles. The precision trap is for high precision frequency measurements, and the analysis trap has a strong magnetic field inhomogeneity superimposed, which is used for single particle Spin-flip, spin flip spectroscopy. By measuring the Spin-flip, spin flip rate as a f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bipolar Junction Transistor
A bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is a type of transistor that uses both electrons and electron holes as charge carriers. In contrast, a unipolar transistor, such as a field-effect transistor (FET), uses only one kind of charge carrier. A bipolar transistor allows a small current injected at one of its terminals to control a much larger current between the remaining two terminals, making the device capable of amplification or switching. BJTs use two p–n junctions between two semiconductor types, n-type and p-type, which are regions in a single crystal of material. The junctions can be made in several different ways, such as changing the doping of the semiconductor material as it is grown, by depositing metal pellets to form alloy junctions, or by such methods as diffusion of n-type and p-type doping substances into the crystal. The superior predictability and performance of junction transistors quickly displaced the original point-contact transistor. Diffused trans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
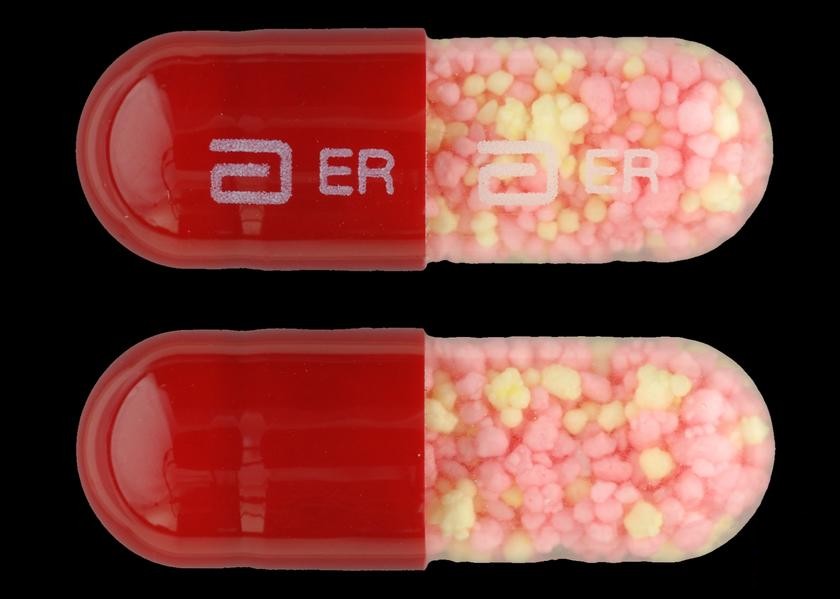
Erythromycin Base
Erythromycin is an antibiotic used for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. This includes respiratory tract infections, skin infections, chlamydia infections, pelvic inflammatory disease, and syphilis. It may also be used during pregnancy to prevent Group B streptococcal infection in the newborn, and to improve delayed stomach emptying. It can be given intravenously and by mouth. An eye ointment is routinely recommended after delivery to prevent eye infections in the newborn. Common side effects include abdominal cramps, vomiting, and diarrhea. More serious side effects may include ''Clostridioides difficile'' colitis, liver problems, prolonged QT, and allergic reactions. It is generally safe in those who are allergic to penicillin. Erythromycin also appears to be safe to use during pregnancy. While generally regarded as safe during breastfeeding, its use by the mother during the first two weeks of life may increase the risk of pyloric stenosis in the baby. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Base (chemistry)
In chemistry, there are three definitions in common use of the word "base": '' Arrhenius bases'', '' Brønsted bases'', and '' Lewis bases''. All definitions agree that bases are substances that react with acid An acid is a molecule or ion capable of either donating a proton (i.e. Hydron, hydrogen cation, H+), known as a Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory, Brønsted–Lowry acid, or forming a covalent bond with an electron pair, known as a Lewis ...s, as originally proposed by Guillaume-François Rouelle, G.-F. Rouelle in the mid-18th century. In 1884, Svante Arrhenius proposed that a base is a substance which dissociates in aqueous solution to form hydroxide ions OH−. These ions can react with Hydron (chemistry), hydrogen ions (H+ according to Arrhenius) from the dissociation of acids to form water in an acid–base reaction. A base was therefore a metal hydroxide such as NaOH or Calcium hydroxide, Ca(OH)2. Such aqueous hydroxide solutions were also described by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brooklyn Academy Of Science And The Environment
Brooklyn is a borough of New York City located at the westernmost end of Long Island in the State of New York. Formerly an independent city, the borough is coextensive with Kings County, one of twelve original counties established under English rule in 1683 in what was then the Province of New York. As of the 2020 United States census, the population stood at 2,736,074, making it the most populous of the five boroughs of New York City, and the most populous county in the state.Table 2: Population, Land Area, and Population Density by County, New York State - 2020 |