|
Bartholomaeus Pitiscus
Bartholomaeus Pitiscus (also ''Barthélemy'' or ''Bartholomeo''; August 24, 1561 – August 24, 1613) was a 16th-century German trigonometrist, astronomer and theologian who first coined the word ''trigonometry''. Biography Pitiscus was born to poor parents in Grünberg (now Zielona Góra, Poland), then part of the Duchy of Glogau/Głogów, one of the Habsburg-ruled Duchies of Silesia. He studied theology in Zerbst and Heidelberg. A Calvinist, he was appointed to teach the ten-year-old Frederick IV, Elector Palatine of the Rhine, by Frederick's Calvinist uncle Johann Casimir of Simmern, as Frederick's father had died in 1583. Pitiscus was subsequently appointed court chaplain at Breslau (Wrocław) and court preacher to Frederick. Pitiscus supported Frederick's subsequent measures against the Roman Catholic Church. Pitiscus died in Heidelberg. The lunar crater Pitiscus is named after him. The classical scholar Samuel Pitiscus (1637–1727) was his nephew. Mathemat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heidelberg
Heidelberg (; ; ) is the List of cities in Baden-Württemberg by population, fifth-largest city in the States of Germany, German state of Baden-Württemberg, and with a population of about 163,000, of which roughly a quarter consists of students, it is List of cities in Germany by population, Germany's 51st-largest city. Located about south of Frankfurt, Heidelberg is part of the densely populated Rhine-Neckar, Rhine-Neckar Metropolitan Region which has its centre in Mannheim. Heidelberg is located on the Neckar River, at the point where it leaves its narrow valley between the Oden Forest and the Kleiner Odenwald, Little Oden Forest, and enters the wide Upper Rhine Plain. The old town lies in the valley, the end of which is flanked by the Königstuhl (Odenwald), Königstuhl in the south and the Heiligenberg (Heidelberg), Heiligenberg in the north. The majority of the population lives in the districts west of the mountains in the Upper Rhine Plain, into which the city has expan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allgemeine Deutsche Biographie
(ADB; ) is one of the most important and comprehensive biographical reference works in the German language. It was published by the Historical Commission of the Bavarian Academy of Sciences between 1875 and 1912 in 56 volumes, printed in Leipzig by Duncker & Humblot. The ADB contains biographies of about 26,500 people who died before 1900 and lived in the German language Sprachraum of their time, including people from the Netherlands before 1648. Its successor, the , was started in 1953 and is planned to be finished in 2023. The index and full-text articles of ADB and NDB are freely available online via the website ''German Biography'' ('' Deutsche Biographie''). Notes References * * External links * ''Allgemeine Deutsche Biographie'' – full-text articles at German Wikisource Wikisource is an online wiki-based digital library of free-content source text, textual sources operated by the Wikimedia Foundation. Wikisource is the name of the project as a whole; it i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mirifici Logarithmorum Canonis Descriptio
''Mirifici Logarithmorum Canonis Descriptio'' (Description of the Wonderful Canon of Logarithms, 1614) and ''Mirifici Logarithmorum Canonis Constructio'' (Construction of the Wonderful Canon of Logarithms, 1619) are two books in Latin by John Napier expounding the method of logarithms. While others had approached the idea of logarithms, notably Jost Bürgi, it was Napier who first published the concept, along with easily used Mathematical table, precomputed tables, in his ''Mirifici Logarithmorum Canonis Descriptio.'' Prior to the introduction of logarithms, high accuracy numerical calculations involving multiplication, division and root extraction were laborious and error prone. Logarithms greatly simplify such calculations. As Napier put it: “…nothing is more tedious, fellow mathematicians, in the practice of the mathematical arts, than the great delays suffered in the tedium of lengthy multiplications and divisions, the finding of ratios, and in the extraction of square ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Napier
John Napier of Merchiston ( ; Latinisation of names, Latinized as Ioannes Neper; 1 February 1550 – 4 April 1617), nicknamed Marvellous Merchiston, was a Scottish landowner known as a mathematician, physicist, and astronomer. He was the 8th Laird of Merchiston. John Napier is best known as the discoverer of logarithms. He also invented the so-called "Napier's bones" and made common the use of the decimal point in arithmetic and mathematics. Napier's birthplace, Merchiston Castle, Merchiston Tower in Edinburgh, is now part of the facilities of Edinburgh Napier University. There is a memorial to him at St Cuthbert's Parish Church, St Cuthbert's at the west side of Edinburgh.Monuments and monumental inscriptions in Scotland: The Grampian Society, 1871 Life Napier's father was Archibald Napier (landowner), Sir Archibald Napier of Merchiston Castle, and his mother was Janet Bothwell, daughter of the politician and judge Francis Bothwell, and a sister of Adam Bothwell who bec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decimal Point
FIle:Decimal separators.svg, alt=Four types of separating decimals: a) 1,234.56. b) 1.234,56. c) 1'234,56. d) ١٬٢٣٤٫٥٦., Both a comma and a full stop (or period) are generally accepted decimal separators for international use. The apostrophe and Arabic decimal separator are also used in certain contexts. A decimal separator is a symbol that separates the integer part from the fractional part of a number written in decimal form. Different countries officially designate different symbols for use as the separator. The choice of symbol can also affect the choice of symbol for the #Digit grouping, thousands separator used in digit grouping. Any such symbol can be called a decimal mark, decimal marker, or decimal sign. Symbol-specific names are also used; decimal point and decimal comma refer to a dot (either Baseline dot, baseline or Middle dot, middle) and comma respectively, when it is used as a decimal separator; these are the usual terms used in English, with the aforem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georg Joachim Rheticus
Georg Joachim de Porris, also known as Rheticus (; 16 February 1514 – 4 December 1574), was a mathematician, astronomer, cartographer, navigational-instrument maker, medical practitioner, and teacher. He is perhaps best known for his Trigonometry, trigonometric tables and as Nicolaus Copernicus's sole pupil.Danielson, p. 3. He facilitated the publication of his master's ''De revolutionibus orbium coelestium'' (''On the Revolutions of the Heavenly Spheres''). Surname Rheticus was born at Feldkirch, Vorarlberg, Feldkirch in the Archduchy of Austria. Both his parents, Georg Iserin and Thomasina de Porris, were of Italian heritage and possessed considerable wealth, his father being the town physician as well as a government official. He was educated by his father until the age of 14 when Georg (Iserin) abused the trust of many of his patients, stealing belongings and money from their homes. In 1528 he was convicted and executed for his crimes, and as a result his family was stripped ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canon Sinuum (Pitiscus)
The ''Canon Sinuum'' is the main part of Bartholomaeus Pitiscus' '' Thesaurus Mathematicus sive Canon Sinuum ad radium 1.00000.00000.00000'' published as a folio in 1613 (misprinted on two of the titles 1513, by omission of a C in the Roman numeral MLCXIII) in Frankfurt Frankfurt am Main () is the most populous city in the States of Germany, German state of Hesse. Its 773,068 inhabitants as of 2022 make it the List of cities in Germany by population, fifth-most populous city in Germany. Located in the forela .... It is a table of sines, originally computed by Rheticus, with the sines given every 10 seconds to 15 places, with first, second, and third differences. This table spans 270 pages. In addition, the ''Canon Sinuum'' gives the sines to 15 places for every second of the first and last degrees of the quadrant, as well as several other tables. References External links * {{URL, http://www.e-rara.ch/zut/content/titleinfo/5306212, Pitiscus: ''Thesaurus Mathematicus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
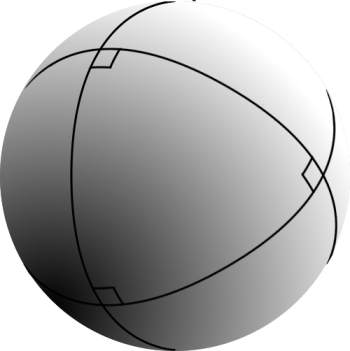
Spherical Trigonometry
Spherical trigonometry is the branch of spherical geometry that deals with the metrical relationships between the edge (geometry), sides and angles of spherical triangles, traditionally expressed using trigonometric functions. On the sphere, geodesics are great circles. Spherical trigonometry is of great importance for calculations in astronomy, geodesy, and navigation. The origins of spherical trigonometry in Greek mathematics and the major developments in Islamic mathematics are discussed fully in History of trigonometry and Mathematics in medieval Islam. The subject came to fruition in Early Modern times with important developments by John Napier, Jean Baptiste Joseph Delambre, Delambre and others, and attained an essentially complete form by the end of the nineteenth century with the publication of Todhunter's textbook ''Spherical trigonometry for the use of colleges and Schools''. Since then, significant developments have been the application of vector methods, quaternion m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plane Geometry
Euclidean geometry is a mathematical system attributed to ancient Greek mathematics, Greek mathematician Euclid, which he described in his textbook on geometry, ''Euclid's Elements, Elements''. Euclid's approach consists in assuming a small set of intuitively appealing axioms (postulates) and deducing many other propositions (theorems) from these. One of those is the parallel postulate which relates to parallel lines on a Euclidean plane. Although many of Euclid's results had been stated earlier,. Euclid was the first to organize these propositions into a logic, logical system in which each result is ''mathematical proof, proved'' from axioms and previously proved theorems. The ''Elements'' begins with plane geometry, still taught in secondary school (high school) as the first axiomatic system and the first examples of mathematical proofs. It goes on to the solid geometry of three dimensions. Much of the ''Elements'' states results of what are now called algebra and number theory ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abraham Scultetus
Abraham Scultetus (24 August 1566 – 24 October 1625) was a German professor of theology, and the court preacher for the Prince-elector, Elector of the Palatinate Frederick V, Elector Palatine, Frederick V. Biography Early life Abraham was born in Grünberg in Schlesien in Silesia (after 1945 Zielona Góra, Poland) and was brought up as a Lutheran. He began his studies in theology in 1588 in Wittenberg and then in 1590 in Heidelberg. When he became Reformed and gave up his Lutheranism is unknown. By 1595 he was working for the Elector of the Palatinate, who at that time was Frederick IV. He continued to serve the churches of the Palatinate and accompanied Frederick V on his honeymoon with his wife Elisabeth, daughter of King James I of England, in 1613. He served Frederick V as his court preacher and also became a Professor of Old Testament in Heidelberg in 1618. He also apparently helped introduce the Reformed Church order used in the Palatinate into the Hanau dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |