|
Barras, Alpes-de-Haute-Provence
Barras (; ) is a commune in the Alpes-de-Haute-Provence department in the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur region of south-eastern France. The inhabitants of the commune are known as ''Barrasiens'' or ''Barrasiennes''. Geography Barras is located some 6 km west of Digne-les-Bains and 14 km south-east of Sisteron. The highest point in the commune is the summit of Ruth (1298m). The sole access to the commune is the D17 road which branches from Route nationale N85 at Mallemoisson and goes north through the commune and the village and continues north to join the D3 near Thoard. Apart from the village there are the hamlets of Les Bourguignons and Les Beauduns. The commune is mostly farmland on a fairly rugged landscape. ''Les Duyes'' stream forms the eastern border of the commune as it flows south to join the Bléone west of ''Les Grillons''. The ''Ravin de Vaunaves'' forms most of the north-eastern border as it flows south-east to join Les Duyes. The ''Ravin de Fulgon'' a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communes Of France
A () is a level of administrative divisions of France, administrative division in the France, French Republic. French are analogous to civil townships and incorporated municipality, municipalities in Canada and the United States; ' in Germany; ' in Italy; ' in Spain; or civil parishes in the United Kingdom. are based on historical geographic communities or villages and are vested with significant powers to manage the populations and land of the geographic area covered. The are the fourth-level administrative divisions of France. vary widely in size and area, from large sprawling cities with millions of inhabitants like Paris, to small hamlet (place), hamlets with only a handful of inhabitants. typically are based on pre-existing villages and facilitate local governance. All have names, but not all named geographic areas or groups of people residing together are ( or ), the difference residing in the lack of administrative powers. Except for the Municipal arrondissem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canton Of Digne-les-Bains-2
The canton of Digne-les-Bains-2 is an administrative division of the Alpes-de-Haute-Provence department, in southeastern France. It was created at the French canton reorganisation which came into effect in March 2015. Its seat is in Digne-les-Bains. It consists of the following communes: # Aiglun # Barras # Champtercier #Digne-les-Bains Digne-les-Bains (; Occitan language, Occitan: ''Dinha dei Banhs''), or simply and historically Digne (''Dinha'' in the Franco-Provençal, classical norm or ''Digno'' in the Mistralian norm), is the Prefectures in France, prefecture of the Alpe ... (partly) # Malijai # Mallemoisson # Mirabeau References Cantons of Alpes-de-Haute-Provence {{AlpesHauteProvence-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hundred Years War
The Hundred Years' War (; 1337–1453) was a conflict between the kingdoms of England and France and a civil war in France during the Late Middle Ages. It emerged from feudal disputes over the Duchy of Aquitaine and was triggered by a claim to the French throne made by Edward III of England. The war grew into a broader military, economic, and political struggle involving factions from across Western Europe, fuelled by emerging nationalism on both sides. The periodisation of the war typically charts it as taking place over 116 years. However, it was an intermittent conflict which was frequently interrupted by external factors, such as the Black Death, and several years of truces. The Hundred Years' War was a significant conflict in the Middle Ages. During the war, five generations of kings from two rival dynasties fought for the throne of France, then the wealthiest and most populous kingdom in Western Europe. The war had a lasting effect on European history: both sides p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Death
The Black Death was a bubonic plague pandemic that occurred in Europe from 1346 to 1353. It was one of the list of epidemics, most fatal pandemics in human history; as many as people perished, perhaps 50% of Europe's 14th century population. The disease is caused by the Bacteria, bacterium ''Yersinia pestis'' and spread by Flea, fleas and through the air. One of the most significant events in European history, the Black Death had far-reaching population, economic, and cultural impacts. It was the beginning of the second plague pandemic. The plague created religious, social and economic upheavals, with profound effects on the course of European history. The origin of the Black Death is disputed. Genetic analysis suggests ''Yersinia pestis'' bacteria evolved approximately 7,000 years ago, at the beginning of the Neolithic, with flea-mediated strains emerging around 3,800 years ago during the late Bronze Age. The immediate territorial origins of the Black Death and its outbreak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feu Fiscal
The term "feu" (French for "fire" from the Latin ''focus'' meaning ''hearth'') meant, especially in the Middle Ages, the hearth, first in the strict sense (the place where the fire burns) and figuratively: the family home (cf. the expression "without fire or place") or the family itself. Very quickly, it was used as the basic unit for assessment, calculation, and collection of tax and it was called the "feu fiscal" meaning "fire tax". Use of taxes in the Middle Ages For tax allocation, the principle was to divide the total amount required to be collected by the number of fires, which necessitated a census of fires which was called "réel". The task was relatively simple to perform to the level of an urban district, however it took on a whole different scale in a rural area or across a kingdom. Thus, the king of France only made a single fire census in his territory – in 1328. Yet the result was incomplete as it excluded the great fiefs (e.g. Guyenne and Flanders) and some Appanages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bishop Of Gap
The Diocese of Gap and Embrun (Latin: ''Dioecesis Vapincensis et Ebrodunensis''; French: ''Diocèse de Gap et d'Embrun'') is a Latin Church ecclesiastical territory or diocese of the Catholic Church in Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur region of Southern France."Diocese of Gap" ''GCatholic.org''. Gabriel Chow. Retrieved 10 April 2017 The is Gap Cathedral, in the city of Gap. It has a |
Abbey Of St
An abbey is a type of monastery used by members of a religious order under the governance of an abbot or abbess. Abbeys provide a complex of buildings and land for religious activities, work, and housing of Christian monks and nuns. The concept of the abbey has developed over many centuries from the early monastic ways of religious men and women where they would live isolated from the lay community about them. Religious life in an abbey may be monastic. An abbey may be the home of an enclosed religious order or may be open to visitors. The layout of the church and associated buildings of an abbey often follows a set plan determined by the founding religious order. Abbeys are often self-sufficient while using any abundance of produce or skill to provide care to the poor and needy, refuge to the persecuted, or education to the young. Some abbeys offer accommodation to people who are seeking spiritual retreat. There are many famous abbeys across the Mediterranean Basin and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ganagobie Abbey
Ganagobie Abbey () is a Benedictine monastery in Ganagobie in the department of Alpes-de-Haute-Provence, France. It is part of the Solesmes Congregation of the Benedictine Confederation and as such focuses on Gregorian chant. A Cluniac Priory The first monastic foundation on this remote and mountainous site appears to date from the 9th or 10th century. Among the first documentary records is a bull of Pope Stephen VIII in 939 confirming the possessions of Cluny Abbey, among them the monastery at Ganagobie. It was suppressed in 1789 under the Ancien Régime and sold off in 1791 during the course of the French Revolution, after which large parts of the buildings were demolished. Gift to Marseilles Priory In 1865 the Benedictines of Solesmes under Dom Prosper Guéranger Dom or DOM may refer to: People and fictional characters * Dom (given name), including fictional characters * Dom (surname) * Dom La Nena (born 1989), stage name of Brazilian-born cellist, singer and songwriter Dom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Priory
A priory is a monastery of men or women under religious vows that is headed by a prior or prioress. They were created by the Catholic Church. Priories may be monastic houses of monks or nuns (such as the Benedictines, the Cistercians, or the Charterhouses). Houses of canons & canonesses regular also use this term, the alternative being "canonry". Mendicant houses, of friars, nuns, or tertiary sisters (such as the Friars Preachers, Augustinian Hermits, and Carmelites) also exclusively use this term. In pre-Reformation England, if an abbey church was raised to cathedral status, the abbey became a cathedral priory. The bishop, in effect, took the place of the abbot, and the monastery itself was headed by a prior. History Priories first came to existence as subsidiaries to the Abbey of Cluny. Many new houses were formed that were all subservient to the abbey of Cluny and called Priories. As such, the priory came to represent the Benedictine ideals espoused by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
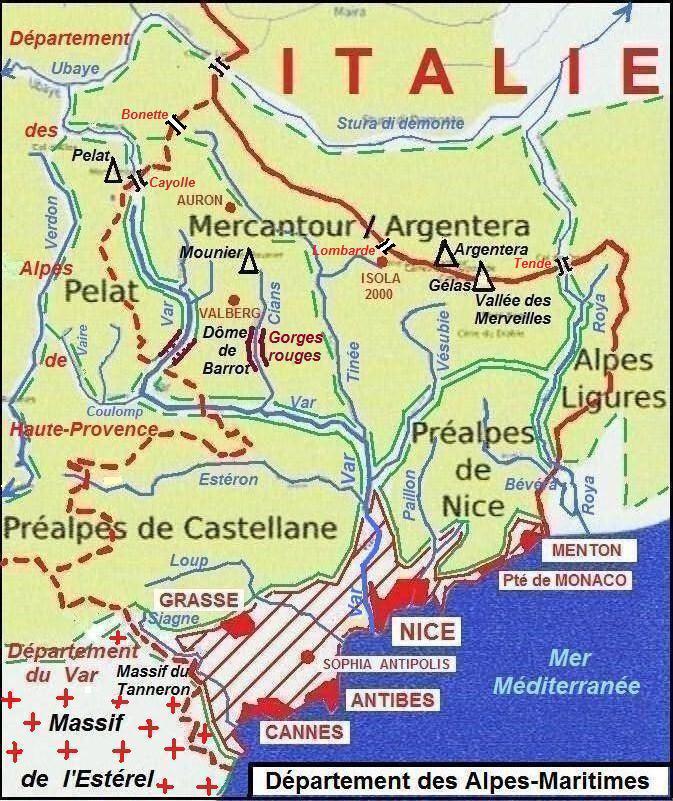
Alpes-Maritimes
Alpes-Maritimes (; ; ; ) is a Departments of France, department of France located in the country's southeast corner, on the France–Italy border, Italian border and Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean coast. Part of the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur Regions of France, region, it encompasses the French Riviera alongside neighbouring Var (department), Var. Alpes-Maritimes had a population of 1,094,283 in 2019.Populations légales 2019: 06 Alpes-Maritimes INSEE Its Prefectures in France, prefecture (and largest city) is Nice, with Grasse as the sole Subprefectures in France, subprefecture. Alpes-Maritimes has become one of the world's most attractive tourist destinations in recent decades, featuring renowned cities and towns such as Nice, Grasse, Cannes, Antibes, Menton, Èze, Roquebrune-Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropaeum Alpium
The Tropaeum Alpium (; ) is a Roman trophy ('' tropaeum'') celebrating the emperor Augustus's decisive victory over the tribes who populated the Alps. The monument's ruins are in La Turbie (France), a few kilometers from the Principality of Monaco. Construction The Trophy was built in honor of Augustus to celebrate his definitive victory over the 45 tribes who populated the Alps. The Alpine populations were defeated during the military campaign to subdue the Alps conducted by the Romans between 16 and 7 BC. The monument was built of stone from the Roman quarry located about away, where traces of sections of carved columns are visible in the stone. The monument as partially restored is high. When built, according to the architect, the base measured in length, the first platform in height, and the rotunda of 24 columns with its statue of an enthroned Augustus is high. Inscription One of the stones of the tower contained the names of the tribes. The inscription was o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Augustus
Gaius Julius Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian (), was the founder of the Roman Empire, who reigned as the first Roman emperor from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. The reign of Augustus initiated an Roman imperial cult, imperial cult and an era of regional hegemony, imperial peace (the or ) in which the Roman world was largely free of armed conflict. The Principate system of government was established during his reign and lasted until the Crisis of the Third Century. Octavian was born into an equites, equestrian branch of the plebeian Octavia gens, Octavia. Following his maternal great-uncle Julius Caesar's assassination of Julius Caesar, assassination in 44 BC, Octavian was named in Caesar's will as his Adoption in ancient Rome, adopted son and heir, and inherited Caesar's name, estate, and the loyalty of his legions. He, Mark Antony, and Marcus Lepidus formed the Second Triumvirat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |