|
Barishal District
Barisal District, officially Barishal District () is a district in south-central Bangladesh, it was formerly called Bakerganj district, and established in 1797. Its headquarters is in Barisal city, which is also the headquarters of Barisal Division.''About Barisal'' Local Government Engineering Department, Local Government Division, Ministry of Local Government, Rural Development & Cooperatives; retrieved 14 May 2014. History The early history of Barisal district is less well-known. It was likely slowly built over time from silt from the , Jamuna and |
Districts Of Bangladesh
The divisions of Bangladesh, divisions of Bangladesh are further divided into districts or (). The headquarters of a district is called the district seat (). There are 64 districts in Bangladesh. The districts are further subdivided into 495 subdistricts or upazilas. History Before independence, Bangladesh (then known as East Pakistan) had 19 districts. English spelling change In April 2018, the government changed the English spelling of five districts to avoid inconsistencies in the Bengali and English spellings and to make them consistent with the Bengali pronunciation. The spellings have been changed from Bogra to Bogura, Barisal to Barishal, Jessore to Jashore, Chittagong to Chattogram and Comilla to Cumilla. Administration Deputy commissioner A Deputy Commissioner (DC), popularly abbreviated to 'DC,' serves as the executive head of the district. Individuals appointed to the role are selected by the government from the Deputy Secretary BCS Administration Cadre. Dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Renamed Places In Bangladesh
The following is the list of places in Bangladesh that underwent a name change. The most common names in English are in bold letters. Barishal Division * Barisal → Barishal (2018) Dhaka Division *Anta Gharer Maidan → Victoria Park → Bahadur Shah Park (1957) *Ayub Nagar → Sher-e-Bangla Nagar *Bagh-e-Badshahi → Shahbag *Bikrampur → Munshiganj *Fatehabad → Faridpur *Dhaka → Jahangir Nagar → Dacca → Dhaka (1982) *Ramna Race Course → Suhrawardy Udyan Chattogram Division *Bhulua → Bhullooah → Bollua → Noakhali *Chittagong → Chattogram (2018) *Daruchini Dwip → Narikel Jinjira → St. Martin's Island *Panowa → Palongkee → Cox's Bazar *Sagarnaiya → Chhagalnaiya *Shamshernagar → Feni *Tippera → Roshnabad → Komolangk → Comilla → Cumilla (2018) Khulna Division * Bhoborpara → Baidyanathtala → Mujibnagar * Jessore → Jashore (2018) Mymensingh Division * Nasirabad → Mymensingh Rajshahi Division * Bogra → Bogu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sandwip
Sandwip (, ) is an island located in the southeastern coast of Bangladesh in the Chittagong District. Along with the island of Urir Char and Bhasan Char, this is part of Sandwip Upazila. Description Sandwip is located in the north-east of the Bay of Bengal, near the port city of Chittagong. It is close to the mouth of the Meghna River in the Bay of Bengal and is separated from the Chittagong coast by Sandwip Channel. It has a population of nearly 700,000. There are fifteen wards, 62 ''mahallas'' and 34 villages on Sandwip Island. The island is long and wide. The island is bounded by Companiganj Upazila, Noakhali, Companiganj on the north; the Bay of Bengal on the south; Sitakunda, Mirsharai, and Sandwip Channel on the east; and the Noakhali, Noakhali Sadar, Hatiya, Bangladesh, Hatiya and Meghna estuaries; on the west. History Some sources claim Sandwip island is around 3000 years old, and was a part of Samatata. The sources state that Sandwip was originally connected to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abul Fazl
Abu'l-Fazl ibn Mubarak (14 January 1551 – 22 August 1602), also known as Abul Fazl, Abu'l Fadl and Abu'l-Fadl 'Allami, was an Indian writer, historian, and politician who served as the grand vizier of the Mughal Empire from his appointment in 1579, until his death in 1602. His notable works include the ''Akbarnama'', ''Ain-i-Akbari,'' and a Persian translation of the Bible.Abu al Fazl Biography and Works persian.packhum.org. Abul Fazl was initially appointed into Akbar's court as a military commander serving in , where he was held in high regard. He was popularly known for his theory ''Padshahat'' which stated the established owner, the emperor, could not be overthrown, as he was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baro-Bhuiyan
The ''Baro-Bhuyans'' (or ''Baro-Bhuyan Raj''; also ''Baro-Bhuians'' and ''Baro-Bhuiyans'') were confederacies of soldier-landowners in Assam and Bengal in the late Middle Ages and the early modern period. The confederacies consisted of loosely independent entities, each led by a warrior chief or a landlord. The tradition of Baro-Bhuyan is peculiar to both Assam and Bengal and differ from the tradition of ''Bhuihar'' of Uttar Pradesh and Bihar—in Assam this phenomenon came into prominence in the 13th century when they resisted the invasion of Ghiyasuddin Iwaj Shah"The Bara Bhuyans of Kamarupa played a similar role in the country's history round about the thirteenth century...Jadunath Sarkar holds that Husamuddin Iwaz () reduced some of the Barabhuyans to submission when he attacked Kamarupa." and in Bengal when they resisted Mughal rule in the 16th century. ''Baro'' denotes the number twelve, but in general there were more than twelve chiefs or landlords, and the word ''bar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ain-i-Akbari
The ''Ain-i-Akbari'' (), or the "Administration of Akbar", is a 16th-century detailed document regarding the administration of the Mughal Empire under Emperor Akbar, written by his court historian, Abu'l Fazl, in the Persian language. It forms Volume III and the final part of the much larger document, the '' Akbarnama'' (''Account of Akbar''), also by Abu'l-Fazl, and is itself in three volumes. Contents The ''Ain-i-Akbari'' is the third volume of the ''Akbarnama'' containing information on Akbar's reign in the form of administrative reports, similar to a gazetteer. In Blochmann's explanation, "it contains the 'āīn' (i.e. mode of governing) of Emperor Akbar, and is the administrative report and statistical return of his government as it was about 1590."Blochmann, H. (tr.) (1927, reprint 1993). ''The Ain-I Akbari by Abu'l-Fazl Allami'', Vol. I, Calcutta: The Asiatic Society, preface (first edition) The ''Ain-i-Akbari'' is divided into five books. The first book called manzil- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chandradwip
Chandradwip was a historic principality and later a zamindari located in southern Bengal, largely corresponding to the present-day Barisal Division in Bangladesh. The principality first rose to prominence under the rule of Raja Danujamardana Deva in the 15th century. Chandradwip was known for maintaining a degree of autonomy whilst navigating relationships with larger entities such as the Sultanate of Bengal and the Bengal Subah. Following the conquest of Bakla in 1611, the rulers of Chandradwip were slowly reduced to zamindars, losing privileges over time especially with the coming of the Brits. Shortly after the independence of Pakistan, the final zamindar of Chandradwip Satindra Narayan moved to Calcutta and sold off his estate. Following the conquest of Bakla in 1611, the authority of Chandradwip’s rulers gradually diminished, and they were progressively reduced to the status of zamindars. Their privileges and territorial control further declined with the establishment of Br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
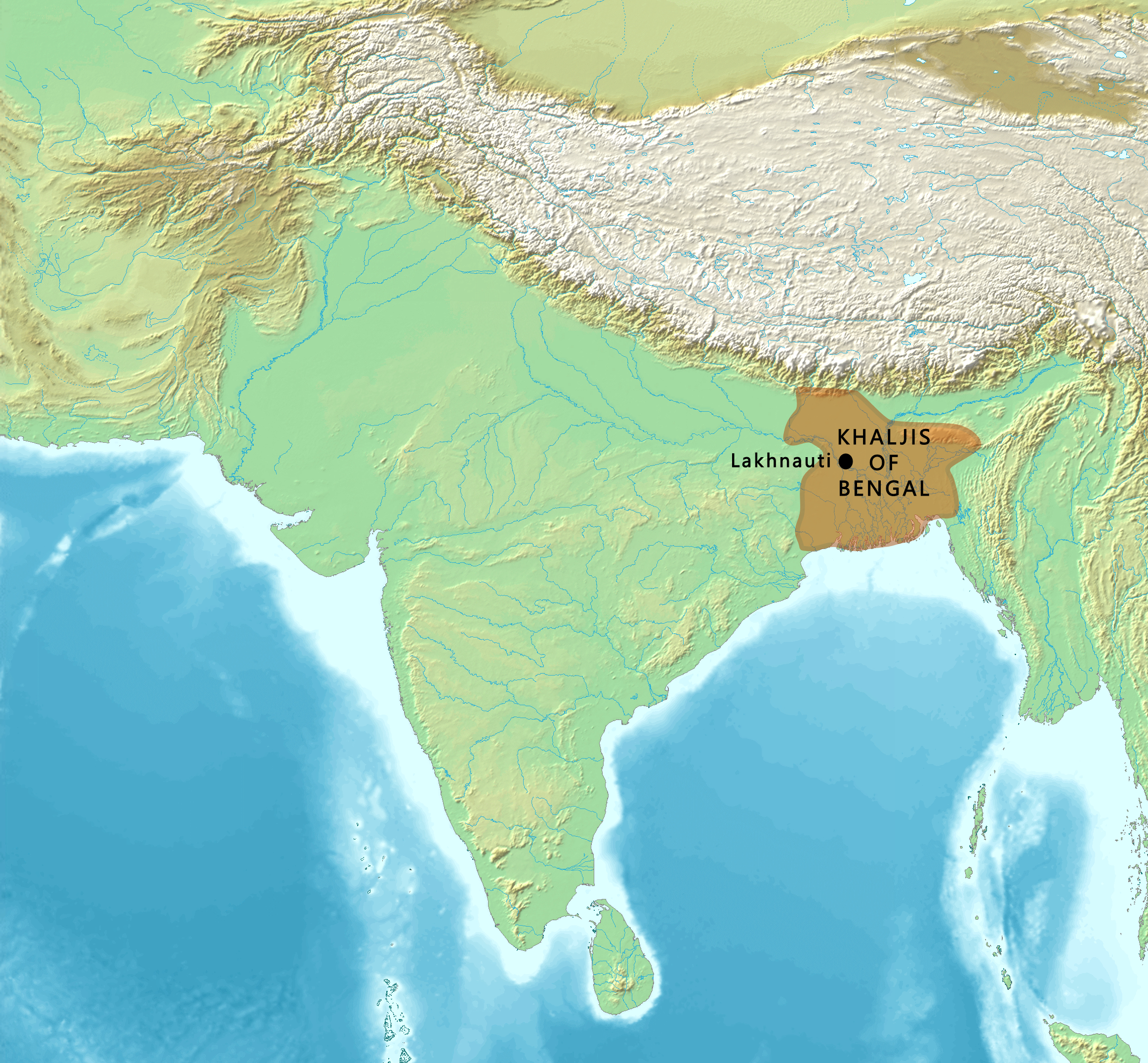
Bakhtiyar Khilji
Ikhtiyār al-Dīn Muḥammad Bin Bakhtiyār Khaljī, also known as Bakhtiyar Khalji, was a Turko-Afghan Military General of the Ghurid ruler Muhammad of Ghor, who led the Muslim conquests of the eastern Indian regions of Bengal and parts of Bihar and established himself as their deputy-ruler/governor, He was the founder of the Khalji dynasty of Bengal, ruling Bengal for a short period, from 1203 to 1227 CE. Khalji's invasions of the Indian subcontinent between A.D. 1197 and 1206 led to mass flight and massacres of monks, and caused damage to the traditional Buddhist institutions of higher learning in Northern India. In Bengal, Khalji's reign was responsible for the displacement of Buddhism. The leading centre of teaching for Mahayana Buddhism was Nalanda. At the end of the 12th century, Bakhityar Khalji demolished the monastery in a brutal sacking . His rule is said to have begun the Muslim rule in Bengal, most notably those of Bengal Sultanate and Mughal Bengal. Bakhtiyar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
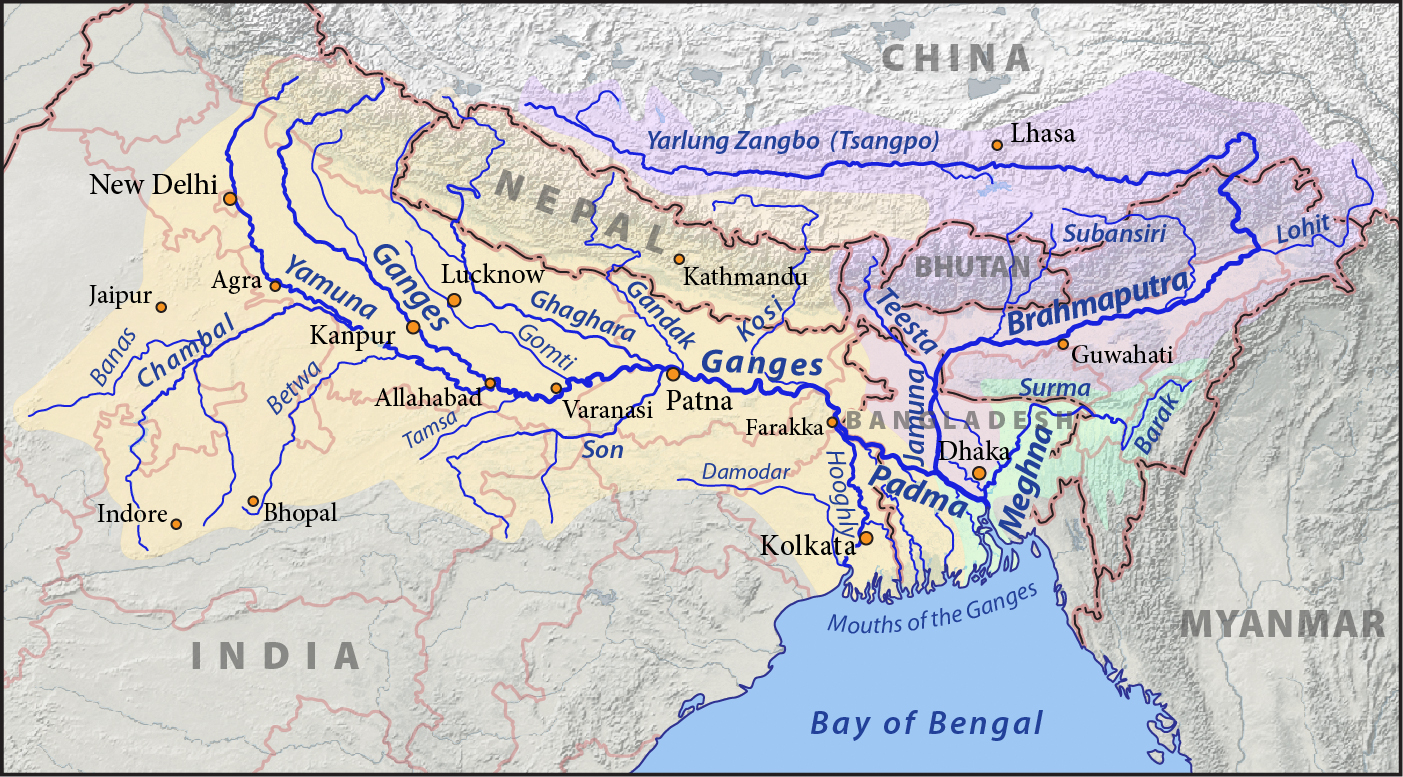
Meghna
The Meghna () is one of the major rivers in Bangladesh, one of the three that form the Ganges Delta, the largest delta on earth, which fans out to the Bay of Bengal. A part of the Surma-Meghna River System, the Meghna is formed inside Bangladesh in Kishoreganj District above the town of Bhairab Bazar by the joining of the Surma River, Surma and the Kushiyara River, Kushiyara, both of which originate in the hilly regions of eastern India as the Barak River. The Meghna meets its major tributary, the Padma River, Padma, in Chandpur District. Other major tributaries of the Meghna include the Dhaleshwari River, Dhaleshwari, the Gumti River (transboundary river), Gumti, and the Feni River, Feni. The Meghna empties into the Bay of Bengal in Bhola District via four principal mouths, named Tentulia River, Tetulia (Ilsha), Shahbazpur, Hatia, and Bamni. Upper Meghna Course The Meghna is formed by the confluence of the Surma River, Surma and Kushiyara River, Kushiyara rivers originating fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jamuna River
The Jamuna River () is one of the three main rivers of Bangladesh. The two other major rivers in Bangladesh are the Padma and the Meghna. The Jamuna is the lower stream of the Brahmaputra River, which originates in Tibet as Yarlung Tsangpo, before flowing through India and then southwest into Bangladesh. The Jamuna flows south and joins the Padma River near Goalundo Ghat, before meeting the Meghna River near Chandpur. The Meghna then flows into the Bay of Bengal. The Brahmaputra-Jamuna is a classic example of a braided river and is highly susceptible to channel migration and avulsion. It is characterised by a network of interlacing channels with numerous sandbars enclosed between them. The sandbars, known in Bengali as ''chars'', do not occupy a permanent position. The river deposits them in one year, very often to be destroyed later, and redeposits them in the next rainy season. The process of bank and deposit erosion, together with redeposition, has been going on cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Padma
The Padma () is a major river in Bangladesh. It is the eastern and main distributary of the Ganges, flowing generally southeast for to its confluence with the Meghna River, near the Bay of Bengal. The city of Rajshahi is situated on the banks of the river.Hossain ML, Mahmud J, Islam J, Khokon ZH and Islam S (eds.) (2005) Padma, Tatthyakosh Vol. 1 and 2, Dhaka, Bangladesh, p. 182 . Since 1966, over 66,000 hectares of land have been lost to erosion of the Padma. History Etymology The Padma, Sanskrit for lotus flower, is mentioned in ancient Hindu scripts as a byname for the Goddess Lakshmi. Geographic effects Eighteenth-century geographer James Rennell referred to a former course of the Ganges north of its present channel, as follows: Murshidabad District Murshidabad District is situated on the western bank of the Padma. It flows dividing the Rajshahi and Murshidabad District of West Bengal and created a natural river border between India and Bangladesh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barisal
Barisal ( or ; , ), officially known as Barishal, is a major city that lies on the banks of the Kirtankhola river in south-central Bangladesh. It is the largest city and the administrative headquarter of both Barisal District and Barisal Division. It is one of the oldest municipalities and river ports of the country. The city was once called the Venice of the East or the Venice of Bengal. Barisal municipality was established in 1876 during the British rule in India and upgraded to City Corporation on 25 July 2002. Barisal is Bangladesh's third largest financial hub after Dhaka and Chittagong. The city consists of 30 wards and 50 mahallas with a population of 533,000, according to the 2023 national census, and about 250,000 voters, according to the 2018 voter list of city election. The area of the city is 58 km2. History Barisal was part of the ancient kingdoms of Vanga, Gangaridai and Samatata. The region was ruled by Khadga, Pala, Chandra, Sena and Deva dynas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |