|
Bareqet
Bareket ( he, בַּרֶקֶת, , Emerald) is a moshav in central Israel. Located in the Shephelah around five kilometres north-east of Ben Gurion International Airport and covering 2,500 dunams, it falls under the jurisdiction of Hevel Modi'in Regional Council. In it had a population of . History Prior to 1948, Bareket was the site of the Palestinian Arab village of al-Tira (Tirat Dandan). It belonged to the Nahiyeh (sub-district) of Lod that encompassed the area of the present-day city of Modi'in-Maccabim-Re'ut in the south to the present-day city of El'ad in the north, and from the foothills in the east, through the Lod Valley to the outskirts of Jaffa in the west. In the 1945 statistics its population was 1,290, all Arab Muslim. p 30/ref> However, the village was depopulated on 10 July 1948 after a military assault by the Israeli army., p. xviiivillage #216. Also gives cause of depopulation. On the same day, Operation Danny headquarters ordered the Yiftach Brigade to b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Tira, Ramle
:''See Tira for other sites with similar names.'' Al-Tira was a Palestinian village in the Ramle Subdistrict. It was depopulated during the 1948 Arab–Israeli War on July 10, 1948, by the Alexandroni and Armored (Eighth) brigades under Operation Dani. It was located 12 km northeast of Ramla. al-Tira was mostly destroyed with the exception of a few houses survived destruction. History Archeological remains from Early Bronze Age,Masarwa, 2012Khirbat et-Tira/ref> Iron Age II, Hellenistic and Roman era have been found. A wine-press, dating to late Roman or early Byzantine era have been excavated, together with a cistern, dating from the pre-Byzantine era. Crusader era remains have been found,Itach and Zuckerman-Cooper, 2016Khirbat et-Tira (Bareket)/ref> together with remains from the Mamluk era. Ottoman era In 1517, Tira was incorporated into the Ottoman Empire along with the rest of Palestine, and by 1596 it was a part of the ''nahiya'' ("subdistrict") of Ramla, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nofekh
Nofekh ( he, נֹפֶךְ, נופך) is a community settlement in central Israel. Located in the Shephelah, it falls under the jurisdiction of Hevel Modi'in Regional Council. In it had a population of . Etymology Its name is taken from one of the 12 stones in the Hoshen The priestly breastplate or breastpiece of judgment ( he, חֹשֶׁן ''ḥōšen'') was a sacred breastplate worn by the High Priest of the Israelites, according to the Book of Exodus. In the biblical account, the breastplate is termed the ''br ..., the sacred breastplate worn by a Jewish high priest, mentioned in Exodus 28:18. Nearby Shoham, Bareqet, Leshem and Ahlama (the former name of Beit Arif) were also named after the Hoshen stones. History The village was established by immigrants from Morocco in 1949 on the land of the depopulated Palestinian village of Rantiya. References {{Hevel Modi'in Regional Council Community settlements Populated places established in 1949 Populated places i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Habban District
Habban District is a district of the Shabwah Governorate in Yemen. As of 2003, the district had a population of 29,846 inhabitants. The district takes its name after the town Habban which lies in As Said District, located at 14o21'N. latitude, 47o04'E. longitude. The town is some 275 km. East by Northeast of Aden by air (425 km overland by the most common route), some 75 km inland from the Gulf of Aden. Habban, during the period of British influence, was a trading town of several thousand, located on the western border of the Wahidi Sultanate, which, for the British, defined the boundary of Eastern and Western Aden Protectorate. The British, who conquered Aden in 1839, made very few visits to the area and despite the presence of "air-fields" at nearby 'Ataq and Mahfid, with rare exceptions, left political and military control of the area to the local authorities. The district was once the home of many Jews, who have since migrated to Israel.Ma`atuf, Sa`adia bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yemen
Yemen (; ar, ٱلْيَمَن, al-Yaman), officially the Republic of Yemen,, ) is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula, and borders Saudi Arabia to the north and Oman to the northeast and shares maritime borders with Eritrea, Djibouti, and Somalia. Yemen is the second-largest Arab sovereign state in the peninsula, occupying , with a coastline stretching about . Its constitutionally stated capital, and largest city, is Sanaa. As of 2021, Yemen has an estimated population of some 30.4 million. In ancient times, Yemen was the home of the Sabaeans, a trading state that included parts of modern-day Ethiopia and Eritrea. Later in 275 AD, the Himyarite Kingdom was influenced by Judaism. Christianity arrived in the fourth century. Islam spread quickly in the seventh century and Yemenite troops were crucial in the early Islamic conquests. Several dynasties emerged in the 9th to 16th centuries, such as the Rasulid dynasty. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aliyah
Aliyah (, ; he, עֲלִיָּה ''ʿălīyyā'', ) is the immigration of Jews from the diaspora to, historically, the geographical Land of Israel, which is in the modern era chiefly represented by the State of Israel. Traditionally described as "the act of going up" (towards the Jewish holy city of Jerusalem), moving to the Land of Israel or "making aliyah" is one of the most basic tenets of Zionism. The opposite action—emigration by Jews from the Land of Israel—is referred to in the Hebrew language as '' yerida'' (). The Law of Return that was passed by the Israeli parliament in 1950 gives all diaspora Jews, as well as their children and grandchildren, the right to relocate to Israel and acquire Israeli citizenship on the basis of connecting to their Jewish identity. For much of their history, most Jews have lived in the diaspora outside of the Land of Israel due to various historical conflicts that led to their persecution alongside multiple instances of expu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Highway 40 (Israel)
Highway 40 ( he, כביש 40) is a north-south intercity road in Israel. At 302 km long, it is the second longest highway in Israel, after Highway 90. The highway runs from Kfar Saba in the center of Israel to the Arabah in the south, serving as a main connection between central Israel and Be'er Sheva. Route description The highway starts at an intersection with Highway 90 near Ketura, about 50 km north of Eilat as a two-lane undivided road. It then continues north, winding through the mountains of the southern Negev. This section includes the "Meishar", which is a completely straight and leveled 12 km stretch of road. The highway descends into the Ramon Crater, crosses it and then ascends 250 meters along "Ma'ale HaAtzmaut" to reach Mitzpe Ramon. From Mitzpe Ramon the highway continues past Ramon Air Force Base and Sde Boker. The section between Ketura and Sde Boker is a scenic route, and some drivers use this road when driving to Eilat because it provides more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. is a city in Western Asia. Situated on a plateau in the Judaean Mountains between the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and the Dead Sea, it is one of the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest cities in the world and is considered to be a holy city for the three major Abrahamic religions: Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. Both Israelis and Palestinians claim Jerusalem as their Capital city, capital, as Israel maintains its primary governmental institutions there and the State of Palestine ultimately foresees it as its seat of power. Because of this dispute, Status of Jerusalem, neither claim is widely recognized internationally. Throughout History of Jerusalem, its long history, Jerusalem has been destroyed at least twice, Sie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Highway 1 (Israel–Palestine)
Highway 1 ( he, כביש 1, ''Kvish Ahat''; ar, الطريق السريع 1) is the main highway in Israel, connecting Tel Aviv and Jerusalem, and continuing eastwards to the Jordan Valley in the West Bank. Highway Tel Aviv to Jerusalem The coastal plain and Judean foothills The route begins as a six lane freeway as it splits off from the Ayalon Highway (Highway 20) just north of the Kibbutz Galuyot Interchange in Tel Aviv at an elevation of 16 meters above sea level travelling 0.7 km due south-southeast following the course of the Ayalon Stream. It then turns southeast, continuing past the 70 meter high Hiriya landfill, intersects Highway 4 and Route 412 and passes the Tel Aviv toll express lanes and park-and-ride facility. Israel Railways maintains tracks along the median of the highway along this section. A separated express toll lane runs along the three westbound lanes between Ben Gurion and Kibbutz Galuyot interchanges. The road then makes an S-curve as it passe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
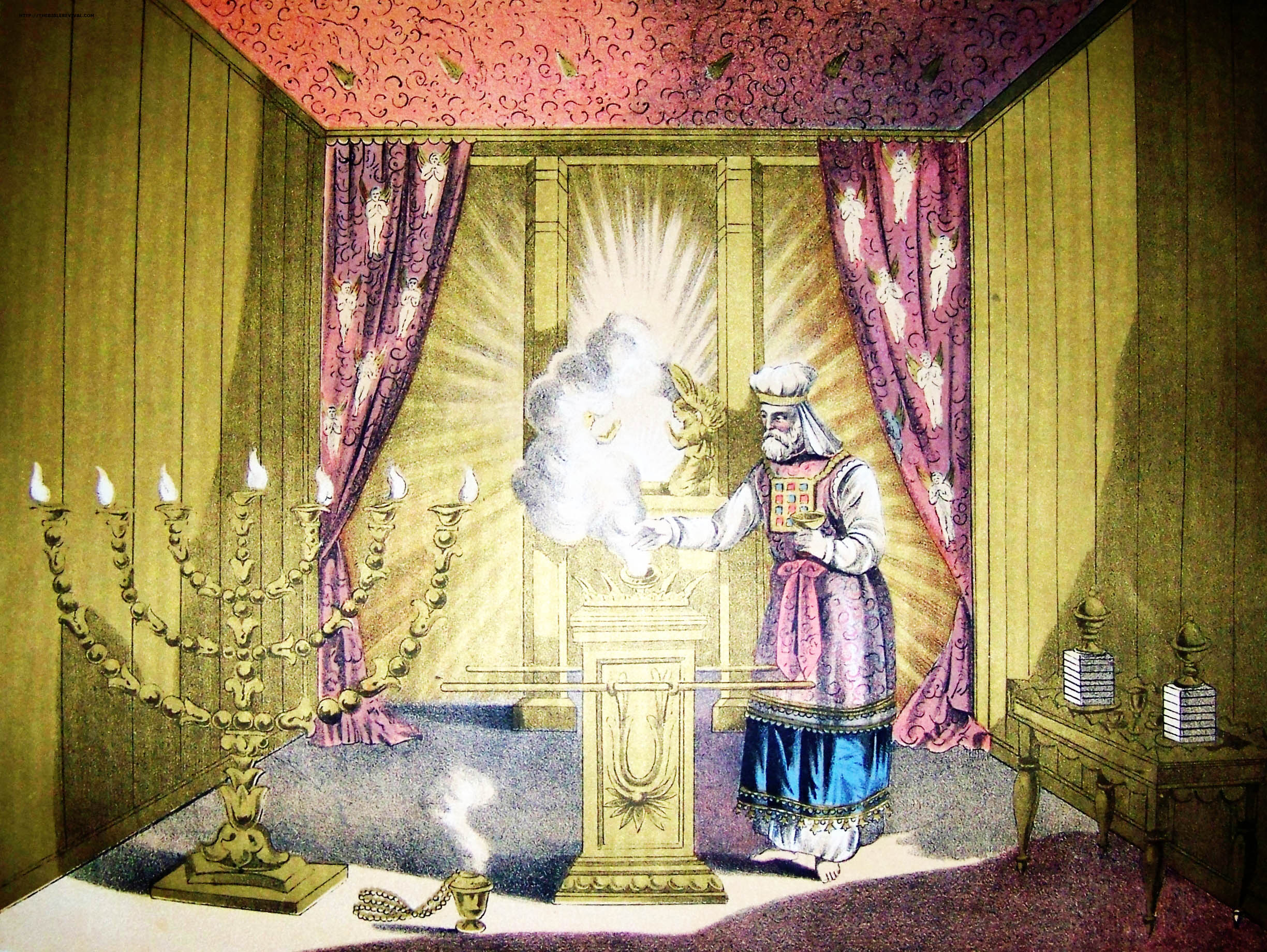
Cohen Gadol
High Priest ( he, כהן גדול, translit=Kohen Gadol or ; ) was the title of the chief religious official of Judaism from the early post-Exilic times until the destruction of the Second Temple in Jerusalem by the Romans in 70 CE. Previously, in the Israelite religion, including during the time of the kingdoms of Israel and Judah, other terms were used to designate the leading priests; however, as long as a king was in place, the supreme ecclesiastical authority lay with him. The official introduction of the term "high priest" went hand-in-hand with a greatly enhanced ritual and political significance bestowed upon the chief priest of the Israelites in the post-Exilic period, especially from 411 BCE onward due to the religious transformations brought about during the time of the Babylonian captivity and due to the lack of a Jewish king and kingdom. The high priests belonged to the Jewish priestly families that trace their paternal line back to Aaron—the first high pries ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hoshen
The priestly breastplate or breastpiece of judgment ( he, חֹשֶׁן ''ḥōšen'') was a sacred breastplate worn by the High Priest of the Israelites, according to the Book of Exodus. In the biblical account, the breastplate is termed the ''breastplate of judgment'' ( he, חֹשֶׁן מִשְׁפָּט ''ḥōšen mišpāṭ'' - ), because the Urim and Thummim ( he, הָאוּרִים וְהַתֻּמִּים ''hāʾūrīm wəhattummīm'') were placed upon it.(). These elements of the breastplate are said in the Exodus verse to carry the judgement ( he, מִשְׁפָּט ''mišpāṭ'') of God concerning the Israelites at all times. Hebrew Bible According to the description in Exodus, this breastplate was attached to the tunic-like garment known as an ephod by gold chains/cords tied to the gold rings on the ephod's shoulder straps, and by blue ribbon tied to the gold rings at the belt of the ephod. The biblical description states that the breastplate was also to be made ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beit Arif
Beit Arif ( he, בֵּית עָרִיף, ''lit.'' House of Cloud) is a moshav in central Israel. Located near Shoham, it falls under the jurisdiction of Hevel Modi'in Regional Council. In it had a population of . History During the 18th and 19th centuries, Beit Arif was the site of the village of Dayr Tarif. It belonged to the Nahiyeh (sub-district) of Lod that encompassed the area of the present-day city of Modi'in-Maccabim-Re'ut in the south to the present-day city of El'ad in the north, and from the foothills in the east, through the Lod Valley to the outskirts of Jaffa in the west. This area was home to thousands of inhabitants in about 20 villages, who had at their disposal tens of thousands of hectares of prime agricultural land. The moshav was founded in 1949 by immigrants from Bulgaria on the ruins of the depopulated Palestinian village of Dayr Tarif (the Romans referred to Dayr Tarif as Bethariph). It was originally named Ahlama ( he, אחלמה) (Exodus 28:19), aft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leshem (Israeli Settlement)
Leshem (Hebrew: לֶשֶם) is a religious Israeli unauthorized settlement in the West Bank. It is located on Route 446, about 13 km (8 miles) west of the Palestinian city of Salfit and about 37 km (23 miles) northwest of Jerusalem, in the Palestinian side of the Israeli West Bank barrier. Leshem is neighbored by the Israeli settlements of Alei Zahav (of which Leshem is officially "a neighborhood"), Peduel, Bruchin, Beit Aryeh-Ofarim, the archeological site of Deir Samaan, and the Palestinian villages Rafat, Kafr ad-Dik, and Deir Ballut. Leshem settlement rises to a height of 360 meters (1181.1 feet) above sea level and is stretched across two hills, the eastern hill and the western hill which altogether cover about 497 dunam (122.811 acres). The international community considers Israeli settlements in the West Bank illegal under international law, but the Israeli government dispute this. History In 1999, Lubavitcher Chassidim expressed their interest in putting down ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |