|
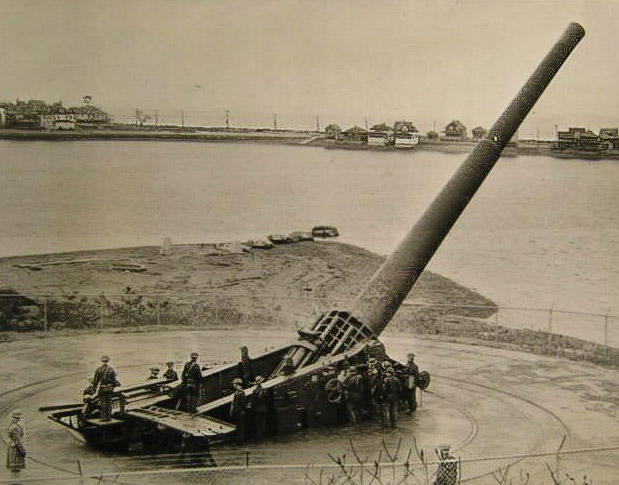
Barbettes
Barbettes are several types of gun emplacement in terrestrial fortifications or on naval ships. In recent naval usage, a barbette is a protective circular armour support for a heavy gun turret. This evolved from earlier forms of gun protection that eventually led to the pre-dreadnought. The name ''barbette'' ultimately comes from fortification: it originally meant a raised platform or mound, as in the French phrase ''en barbette'', which refers to the practice of firing a cannon over a parapet rather than through an embrasure in a fortification's casemate. The former gives better angles of fire but less protection than the latter. The disappearing gun was a variation on the barbette gun; it consisted of a heavy gun on a carriage that would retract behind a parapet or into a gunpit for reloading. Barbettes were primarily used in coastal defences, but saw some use in a handful of warships, and some inland fortifications. The term is also used for certain aircraft gun mounts. Shi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ironclad Warship
An ironclad was a steam-propelled warship protected by steel or iron armor constructed from 1859 to the early 1890s. The ironclad was developed as a result of the vulnerability of wooden warships to explosive or incendiary shells. The first ironclad battleship, , was launched by the French Navy in November 1859, narrowly preempting the British Royal Navy. However, Britain built the first completely iron-hulled warships. Ironclads were first used in warfare in 1862 during the American Civil War, when they operated against wooden ships, and against each other at the Battle of Hampton Roads in Virginia. Their performance demonstrated that the ironclad had replaced the unarmored ship of the line as the most powerful warship afloat. Ironclad gunboats became very successful in the American Civil War. Ironclads were designed for several uses, including as high-seas battleships, long-range cruisers, and coastal defense ships. Rapid development of warship design in the late 19th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pre-dreadnought
Pre-dreadnought battleships were sea-going battleships built from the mid- to late- 1880s to the early 1900s. Their designs were conceived before the appearance of in 1906 and their classification as "pre-dreadnought" is retrospectively applied. In their day, they were simply known as "battleships" or else more rank-specific terms such as "first-class battleship" and so forth. The pre-dreadnought battleships were the pre-eminent warships of their time and replaced the ironclad battleships of the 1870s and 1880s. In contrast to the multifarious development of ironclads in preceding decades, the 1890s saw navies worldwide start to build battleships to a common design as dozens of ships essentially followed the design of the Royal Navy's . Built from steel, protected by compound, nickel steel or case-hardened steel armor, pre-dreadnought battleships were driven by coal-fired boilers powering compound reciprocating steam engines which turned underwater screws. These ships dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
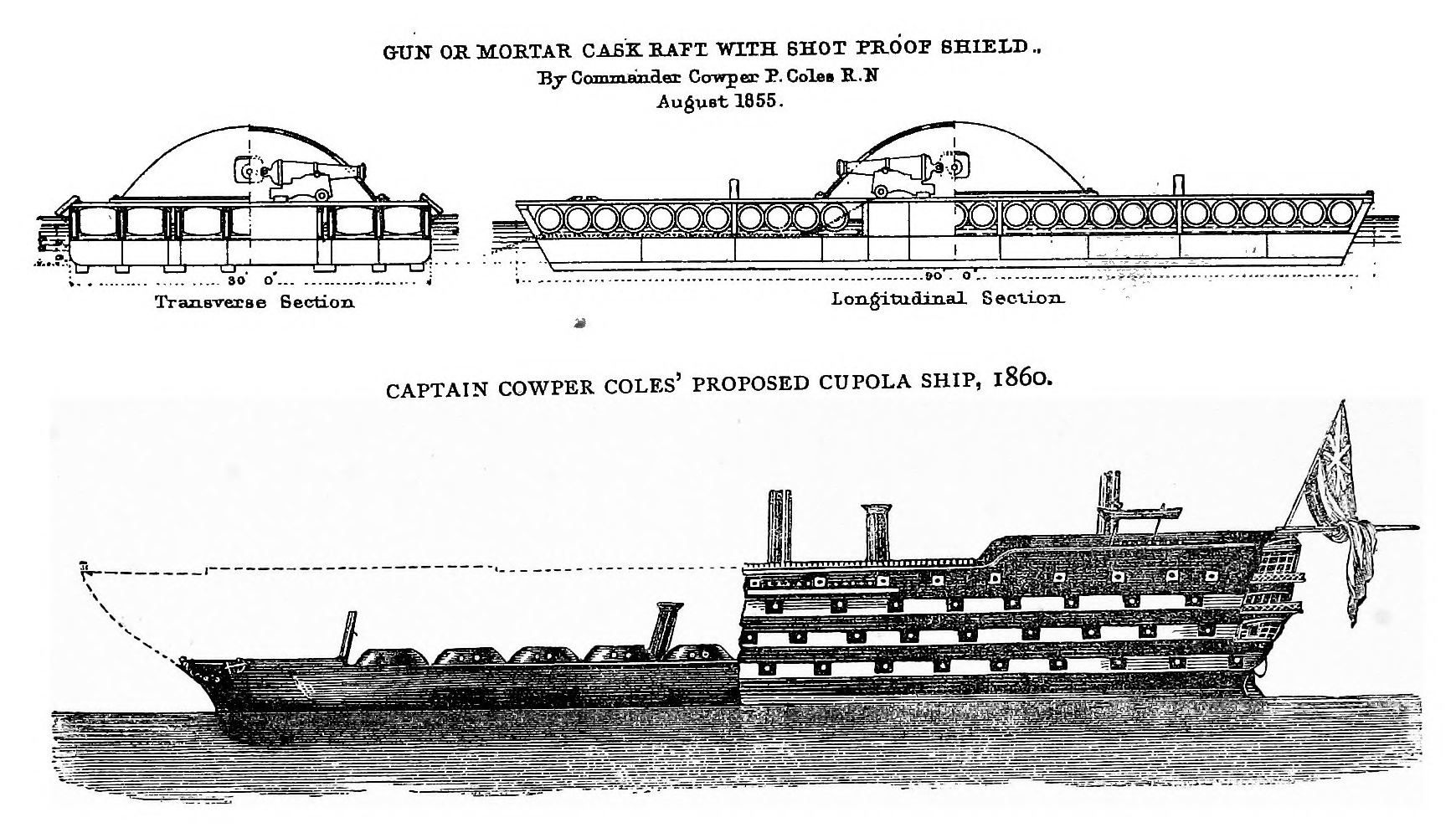
Gunhouse
A gun turret (or simply turret) is a weapon mount, mounting platform from which weapons can be fired that affords protection, visibility and ability to turn and aim. A modern gun turret is generally a rotatable weapon mount that houses the crew or mechanism (engineering), mechanism of a artillery, projectile-firing weapon and at the same time lets the weapon be aimed and fired in some degree of azimuth and elevation (ballistics), elevation (cone of fire). Description Rotating gun turrets protect the weapon and its crew as they rotate. When this meaning of the word "turret" started being used at the beginning of the 1860s, turrets were normally cylindrical. Barbettes were an alternative to turrets; with a barbette the protection was fixed, and the weapon and crew were on a rotating platform inside the barbette. In the 1890s, armoured hoods (also known as "gun houses") were added to barbettes; these rotated with the platform (hence the term "hooded barbette"). By the early 20th c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gun Turret
A gun turret (or simply turret) is a mounting platform from which weapons can be fired that affords protection, visibility and ability to turn and aim. A modern gun turret is generally a rotatable weapon mount that houses the crew or mechanism of a projectile-firing weapon and at the same time lets the weapon be aimed and fired in some degree of azimuth and elevation (cone of fire). Description Rotating gun turrets protect the weapon and its crew as they rotate. When this meaning of the word "turret" started being used at the beginning of the 1860s, turrets were normally cylindrical. Barbettes were an alternative to turrets; with a barbette the protection was fixed, and the weapon and crew were on a rotating platform inside the barbette. In the 1890s, armoured hoods (also known as "gun houses") were added to barbettes; these rotated with the platform (hence the term "hooded barbette"). By the early 20th century, these hoods were known as turrets. Modern warships have gun-m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Howitzer
The howitzer () is an artillery weapon that falls between a cannon (or field gun) and a mortar. It is capable of both low angle fire like a field gun and high angle fire like a mortar, given the distinction between low and high angle fire breaks at 45 degrees or 800 mils (NATO). With their long-range capabilities, howitzers can be used to great effect in a battery formation with other artillery pieces, such as long-barreled guns, mortars, and rocket artillery. Howitzers were valued for their ability to fire explosive shells and incendiary materials into fortifications. Unlike mortars, which had fixed firing angles, howitzers could be fired at various angles, providing greater flexibility in combat. Throughout the 18th and 19th centuries, howitzers evolved to become more mobile and versatile. The introduction of rifling in the mid-19th century led to significant changes in howitzer design and usage. By the early 20th century, howitzers were classified into different categor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freeboard (nautical)
In sailing and boating, a vessel's freeboard is the distance from the waterline to the upper deck level, measured at the lowest point of sheer where water can enter the boat or ship. In commercial vessels, the latter criterion measured relative to the ship's load line, regardless of deck arrangements, is the mandated and regulated meaning. In yachts, a low freeboard is often found on racing boats, for increased speed (by reducing weight and therefore drag). A higher freeboard will give more room in the cabin, but will increase weight and drag, compromising speed. A higher freeboard, such as used on ocean liners, also helps weather waves and so reduce the likelihood of being washed over by full water waves. A low-freeboard vessel is susceptible to taking in water in rough seas. Freighter ships and warships use high freeboard designs to increase internal volume, which also allows them to satisfy International Maritime Organization The International Maritime Organizatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Lissa (1866)
The Battle of Lissa (or Battle of Vis) () was a naval battle between an Kingdom of Italy, Italian and an Austrian Empire, Austrian fleet during the Third Italian War of Independence. It took place on July 20, 1866, near the island of Vis (island), Vis (then Lissa), which is now part of Croatia. The Kingdom of Italy intended to capture Habsburg Venetia and break Austria's naval dominance in the Adriatic. However, the Imperial Austrian Navy managed to secure victory despite the numerical and technical superiority of the Italian fleet by employing ramming tactics. This battle was the first naval engagement in which newly developed ironclad warships were used on a significant scale. Both naval forces at Lissa exhibited notable technical deficiencies, while the Italian Navy also suffered from severe rivalries within its command staff and inadequate training of its crews. Background In order to seize the last areas of the Apennine Peninsula that were still in the hands of the Habsburg m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naval Ram
A ram on the bow of ''Olympias'', a modern reconstruction of an ancient Athenian trireme A naval ram is a weapon fitted to varied types of ships, dating back to antiquity. The weapon comprised an underwater prolongation of the bow of the ship to form an armoured beak, usually between in length. This would be driven into the hull of an enemy ship to puncture, sink or disable it. Antiquity It was possibly developed in late Bronze Age Egypt, but it only became widely used in later Iron Age Mediterranean galleys. The ram was a naval weapon in the Greek/ Roman antiquity and was used in such naval battles as Salamis and Actium. Naval warfare in the Mediterranean rarely used sails, and the use of rams specifically required oarsmen rather than sails in order to maneuver with accuracy and speed, and particularly to reverse the movement of a ramming ship to disentangle it from its sinking victim, lest it be pulled down when its victim sank. The Athenians were especially known fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Box Battery
The box battery is a disposition of the main armament in a battleship, commonly used in ships built in the latter half of the 19th century. A box battery consists of a thick armour surrounding a central battery to protect the guns. It was an interim disposition between full-length broadside guns and turret-mounted artillery. Description From the first time that artillery was carried aboard warships, in the early Tudor period, until the middle of the 19th century, warships had carried their cannon in long rows along their sides. Bigger ships had carried more and bigger cannon, culminating in wooden line-of-battle ships carrying some 140 muzzle-loading smoothbore cannon, 70 on each side. With the advent of steam power, iron armour, and vastly larger guns, first-line battleships built from 1860 onwards tended to carry fewer but heavier guns. The first broadside ironclad to be commissioned into the Royal Navy The Royal Navy (RN) is the naval warfare force of the United Ki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Broadside (naval)
A broadside is the side of a ship, or more specifically the artillery battery, battery of cannon on one side of a warship or their coordinated fire in naval warfare, or a measurement of a warship's maximum simultaneous firepower which can be delivered upon a single target (because this concentration is usually obtained by firing a broadside). From the 16th century until the early decades of the steamship, vessels had rows of guns set in each side of the hull (watercraft), hull. Firing all guns on one side of the ship became known as a "broadside". The cannon of 18th-century man-of-war, men of war were accurate only at short range, and their penetrating power mediocre, which meant that the thick hulls of wooden ships could only be pierced at short ranges. These wooden ships sailed closer and closer towards each other until cannon fire would be effective. Each tried to be the first to fire a broadside, often giving one party a decisive headstart in the battle when it crippled the oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meyers B12 S0661a
Meyers is a surname of English origin; many branches of the Meyers family trace their origins to Anglo-Saxon England. The name is derived from the Old French name ''Maire'', meaning an officer in charge of legal matters. The English surname may also mean "physician" (from ''mire'', Old French), or "marsh" (from , Old Norse). The name may also be an Anglicization of the Irish surname ó Meidhir or one of the Scottish surname MacMoyers Notable people *Abby Meyers (born 1999), American basketball player * Adam Meyers (1812–1875), lawyer and political figure in Canada West * Al Meyers (1908–1976), American pioneer aviator * Albert Meyers (1932–2007), American organic chemist * Albertus L. Meyers (1890–1979), American music conductor and cornet player *Ann Meyers (born 1955), American basketball player and sportscaster *Anne Akiko Meyers (born 1970), American concert violinist *Ari Meyers (born 1969), American actress, ''Kate & Allie'' * August Meyers (1864–1951), American p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |