|
Barbara O'Neill
Barbara O'Neill (born 28 July 1953) is an Australian alternative health care promoter who advertises unsupported health practices described as misinformation and a risk to health and safety by the New South Wales Health Care Complaints Commission. She does not have any recognised qualifications and did not finish nursing training. She has presented her claims at alternative medicine organisations, wellness retreats, and Seventh-day Adventist Churches. She is married to Michael O'Neill, the founder of the now-defunct Informed Medical Options Party, an anti-vaccination and anti-fluoride political group. In 2019, the Health Care Complaints Commission in New South Wales ruled that she is prohibited from providing any health-related services following several complaints from the public and health professionals. An investigation found that she provided dangerous advice to vulnerable patients, such as telling those with cancer to forgo prescribed chemotherapy for bicarbonate of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alternative Medicine
Alternative medicine refers to practices that aim to achieve the healing effects of conventional medicine, but that typically lack biological plausibility, testability, repeatability, or supporting evidence of effectiveness. Such practices are generally not part of evidence-based medicine. Unlike modern medicine, which employs the scientific method to test plausible therapies by way of Guidelines for human subject research, responsible and ethical clinical trials, producing repeatable evidence of either effect or of no effect, alternative therapies reside outside of mainstream medicine and do not originate from using the scientific method, but instead rely on testimonials, anecdotes, religion, tradition, superstition, belief in supernatural "Energy (esotericism), energies", pseudoscience, fallacy, errors in reasoning, propaganda, fraud, or other unscientific sources. Frequently used terms for relevant practices are New Age medicine, wikt:pseudo-medicine, pseudo-medicine, unortho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Detoxification (alternative Medicine)
Detoxification (often shortened to detox and sometimes called body cleansing) is a type of alternative-medicine treatment which aims to rid the body of unspecified "toxins" – substances that proponents claim accumulate in the body over time and have undesirable short-term or long-term effects on individual health. It is not to be confused with detoxification carried out by the liver and kidneys, which filter the blood and remove harmful substances to be processed and eliminated from the body. Activities commonly associated with detoxification include dieting, fasting, consuming exclusively or avoiding specific foods (such as fats, carbohydrates, fruits, vegetables, juices, herbs), colon cleansing, chelation therapy, certain kinds of IV therapy and the removal of dental fillings containing amalgam. Scientists and health organizations have criticized the concept of detoxification for its unsound scientific basis and for the lack of evidence for claims made. The "tox ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungus
A fungus (: fungi , , , or ; or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as one of the kingdom (biology)#Six kingdoms (1998), traditional eukaryotic kingdoms, along with Animalia, Plantae, and either Protista or Protozoa and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of motility, mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible Signs and symptoms of cancer, signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal bleeding, prolonged cough, unexplained weight loss, and a change in defecation, bowel movements. While these symptoms may indicate cancer, they can also have other causes. List of cancer types, Over 100 types of cancers affect humans. Tobacco use is the cause of about 22% of cancer deaths. Another 10% are due to obesity, poor Diet (nutrition), diet, sedentary lifestyle, lack of physical activity or Alcohol abuse, excessive alcohol consumption. Other factors include certain infections, exposure to ionizing radiation, and environmental pollutants. infectious causes of cancer, Infection with specific viruses, bacteria and parasites is an environmental factor cau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cook Islands
The Cook Islands is an island country in Polynesia, part of Oceania in the South Pacific Ocean. It consists of 15 islands whose total land area is approximately . The Cook Islands' Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) covers of ocean. Avarua is its capital. The Cook Islands is self-governing while in free association with New Zealand. Since the start of the 21st century, the Cook Islands conducts its own independent foreign and defence policy, and also has its own customs regulations. Like most members of the Pacific Islands Forum, it has no armed forces, but the Cook Islands Police Service owns a Guardian Class Patrol Boat, , provided by Australia, in order to police its waters. In recent decades, the Cook Islands have adopted an increasingly assertive and distinct foreign policy, and a Cook Islander, Henry Puna, served as Secretary General of the Pacific Islands Forum from 2021 to 2024. Most Cook Islanders are also citizens of New Zealand, but they also have the status of Coo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand
New Zealand () is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and List of islands of New Zealand, over 600 smaller islands. It is the List of island countries, sixth-largest island country by area and lies east of Australia across the Tasman Sea and south of the islands of New Caledonia, Fiji, and Tonga. The Geography of New Zealand, country's varied topography and sharp mountain peaks, including the Southern Alps (), owe much to tectonic uplift and volcanic eruptions. Capital of New Zealand, New Zealand's capital city is Wellington, and its most populous city is Auckland. The islands of New Zealand were the last large habitable land to be settled by humans. Between about 1280 and 1350, Polynesians began to settle in the islands and subsequently developed a distinctive Māori culture. In 1642, the Dutch explorer Abel Tasman became the first European to sight and record New Zealand. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller islands. It has a total area of , making it the list of countries and dependencies by area, sixth-largest country in the world and the largest in Oceania. Australia is the world's flattest and driest inhabited continent. It is a megadiverse countries, megadiverse country, and its size gives it a wide variety of landscapes and Climate of Australia, climates including deserts of Australia, deserts in the Outback, interior and forests of Australia, tropical rainforests along the Eastern states of Australia, coast. The ancestors of Aboriginal Australians began arriving from south-east Asia 50,000 to 65,000 years ago, during the Last Glacial Period, last glacial period. By the time of British settlement, Aboriginal Australians spoke 250 distinct l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obesity
Obesity is a medical condition, considered by multiple organizations to be a disease, in which excess Adipose tissue, body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it can potentially have negative effects on health. People are classified as obese when their body mass index (BMI)—a person's weight divided by the square of the person's height—is over ; the range is defined as overweight. Some East Asian countries use lower values to calculate obesity. Obesity is a major cause of disability and is Obesity-associated morbidity, correlated with various diseases and conditions, particularly cardiovascular diseases, type 2 diabetes, obstructive sleep apnea, certain types of cancer, and osteoarthritis. Obesity has individual, socioeconomic, and environmental causes. Some known causes are Western pattern diet, diet, low physical activity, automation, urbanization, quantitative trait locus, genetic susceptibility, medications, mental disorders, Economic policy, economic pol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heartburn
Heartburn is a burning sensation felt behind the breastbone. It is a symptom that is commonly linked to acid reflux and is often triggered by food, particularly fatty, sugary, spicy, chocolate, citrus, onion-based and tomato-based products. Lying down, bending, lifting, and performing certain exercises can exacerbate heartburn. Causes include acid reflux, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), damage to the esophageal lining, bile acid, mechanical stimulation to the esophagus, and esophageal hypersensitivity. Heartburn affects 25% of the population at least once a month. Endoscopy and esophageal pH monitoring can be used to evaluate heartburn. Some causes of heartburn, such as GERD, may be diagnosed based on symptoms alone. Potential Differential diagnosis, differential diagnoses for heartburn include motility disorders, ulcers, Esophagitis, inflammation of the esophagus, and medication side effects. Lifestyle changes, such as weight loss, losing weight and avoiding fatty food ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Addiction
Addiction is a neuropsychological disorder characterized by a persistent and intense urge to use a drug or engage in a behavior that produces natural reward, despite substantial harm and other negative consequences. Repetitive drug use can alter brain function in synapses similar to natural rewards like food or falling in love in ways that perpetuate craving and weakens self-control for people with pre-existing vulnerabilities. This phenomenon – drugs reshaping brain function – has led to an understanding of addiction as a brain disorder with a complex variety of psychosocial as well as neurobiological factors that are implicated in the development of addiction. While mice given cocaine showed the compulsive and involuntary nature of addiction, for humans this is more complex, related to behavior or personality traits. Classic signs of addiction include compulsive engagement in rewarding stimuli, ''preoccupation'' with substances or behavior, and continued use des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Candida Albicans
''Candida albicans'' is an opportunistic pathogenic yeast that is a common member of the human gut flora. It can also survive outside the human body. It is detected in the gastrointestinal tract and mouth in 40–60% of healthy adults. It is usually a commensal organism, but it can become pathogenic in immunocompromised individuals under a variety of conditions. It is one of the few species of the genus '' Candida'' that cause the human infection candidiasis, which results from an overgrowth of the fungus. Candidiasis is, for example, often observed in HIV-infected patients. ''C. albicans'' is the most common fungal species isolated from biofilms either formed on (permanent) implanted medical devices or on human tissue. ''C. albicans'', ''C. tropicalis'', ''C. parapsilosis'', and ''C. glabrata'' are together responsible for 50–90% of all cases of candidiasis in humans. A mortality rate of 40% has been reported for patients with systemic candidiasis due to ''C. albicans''. B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
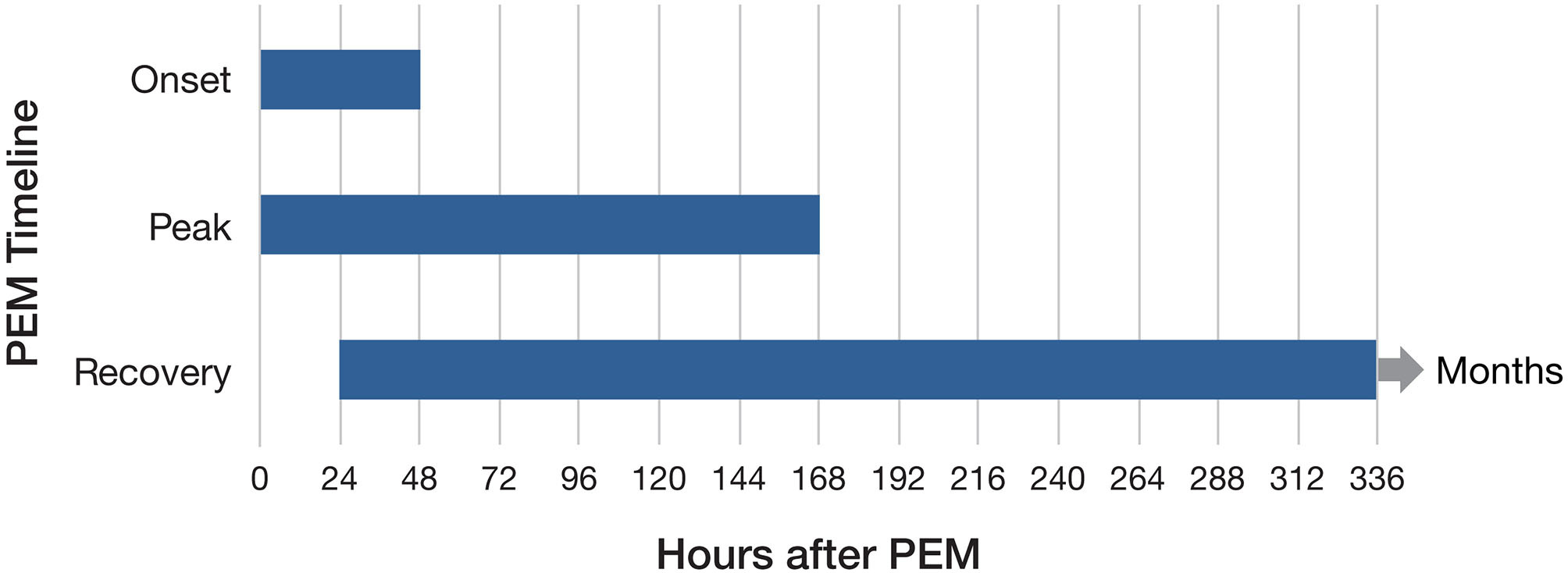
Chronic Fatigue Syndrome
Myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS) is a disabling Chronic condition, chronic illness. People with ME/CFS experience profound fatigue that does not go away with rest, as well as sleep issues and problems with memory or concentration. The Pathognomonic, hallmark symptom is post-exertional malaise (PEM), a worsening of the illness which can start immediately or hours to days after even minor physical or mental activity. This "crash" can last from hours or days to several months. Further common symptoms include orthostatic intolerance, dizziness or faintness when upright and pain. The cause of the disease is unknown. ME/CFS often starts after an infection, such as infectious mononucleosis, mononucleosis. It can run in families, but no genes that contribute to ME/CFS have been confirmed. ME/CFS is associated with changes in the nervous and immune systems, as well as in energy production. Diagnosis is based on distinctive symptoms, and a differential diag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |