|
Banginapalli
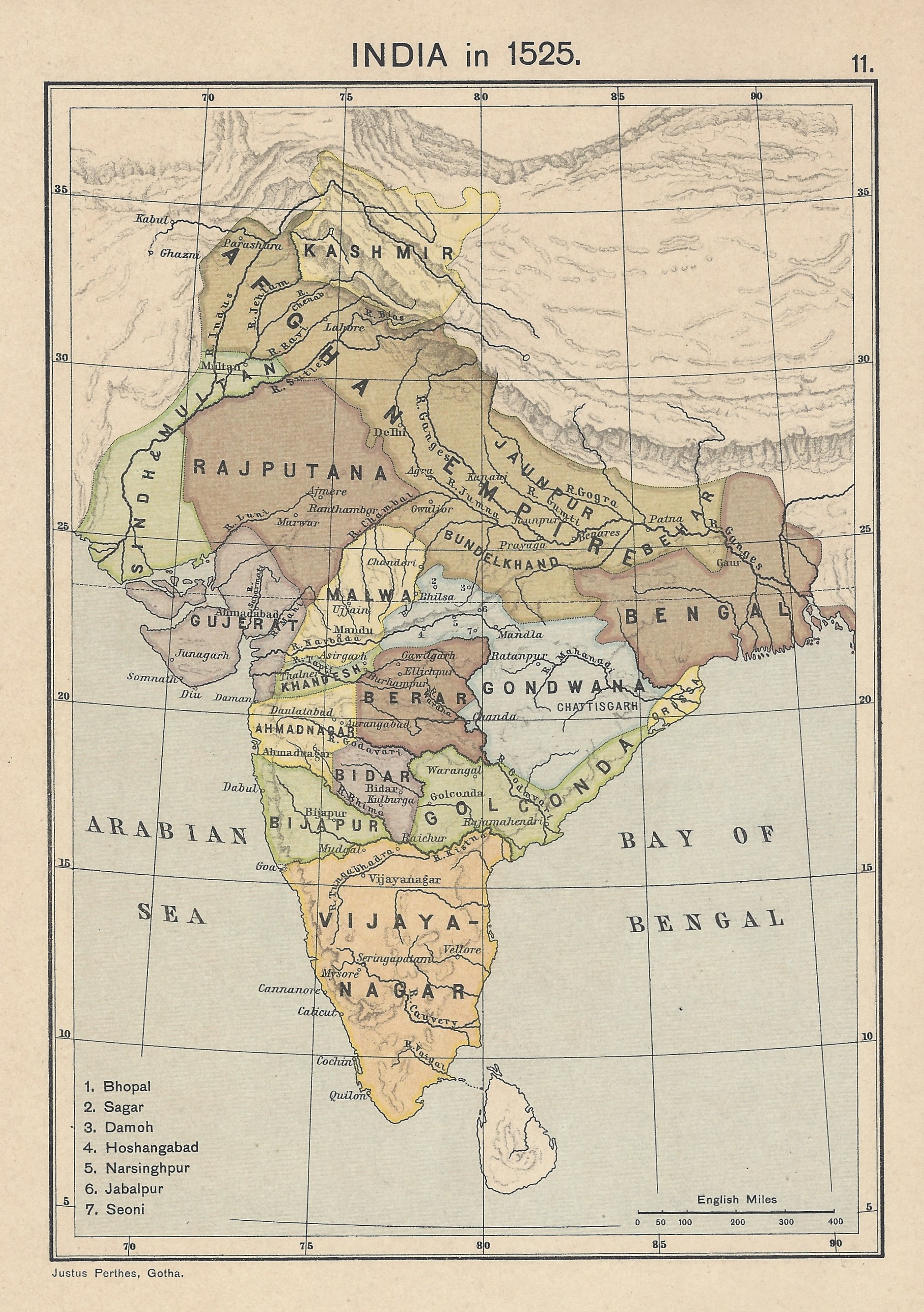
Banaganapalli is a town in the state of Andhra Pradesh, India. It lies in Nandyal district, 38 km west of the city of Nandyal. Banaganapalli is famous for its mangoes and has a cultivar, ''Banaganapalli'', named after it. Between 1790 and 1948, Banaganapalli was the capital of the princely state of the same name, Banganapalle State. Geography Banaganapalli is located at . It has an average elevation of 209 metres (688 ft). Bethamcherla, Betamcherla, Banaganapalli and Koilakuntla are called Twin towns. Right Canal of Srisailam Dam SRBC passes near Banaganapalli Town. History Banaganapalle Nawabs In 1601, Sultan Ismail Adil Shah of Bijapur Sultanate, Bijapur conquered the fortress of Banaganapalli from Raja Nanda Chakravathy. The fort and surrounding districts were placed under the control of his victorious general, Siddhu Sumbal, who held them until 1665. Muhammad Beg Khan-e Rosebahani was granted Banaganapalli and the surrounding jagir in perpetual fiefdom bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banganapalle (mango)
Banganapalle mangoes (also known as Benishan and Bernisha) is a mango variety produced in Banganapalle of Nandyal district, Nandyal District in the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It alone occupies 70% percent of total mango cultivable area of the state and was first introduced by the farmers of Banaganapalli. It was registered as one of the geographical indication from Andhra Pradesh on 3 May 2017, under Horticulture, horticultural products by Geographical Indication Registry (India), Geographical Indication Registry. It is also grown in the other parts of India and Pakistan. The fruit is described as obliquely oval in shape, around 20cm in length, with yellow flesh and a thin, smooth yellow skin. The flesh is of a firm, meaty texture and is sweet and lacks fibre. The cultivar is the most sought after in Andhra Pradesh. It is a very late-season variety that is good for canning. This cultivar is a source of vitamin A & C and is also called king of Mangoes. Etymology It is als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bethamcherla
Bethamcherla is a town with Nagar panchayat civic status and mandal headquarters located in Nandyal district of the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It comes under Dhone assembly constituency and Nandyal Parliament Constituency. Bethalpuram is the oldest name of this village which is known as Bethamcharla. A few centuries ago there was a big pond in this area. The reason is that it is a rocky area where water does not stand. It was in the sixth century that people used to quench their thirst here, grow dairy crops, and provide water to horses, thus the area was known as Betham pond. The Chalukyas who ruled the region dug a big pond here. Later in the course of time it was transformed into Bethamcherla. For some time, the body of water here has merged into the womb of time. There are hundreds of centuries old temples around this Bethamcherla area. When the name of Bethamcherla town is mentioned, the world famous Chalwa Rati( Lime Stone) comes to mind. Once upon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banganapalli 12x9
Banaganapalli is a town in the state of Andhra Pradesh, India. It lies in Nandyal district, 38 km west of the city of Nandyal. Banaganapalli is famous for its mangoes and has a cultivar, ''Banaganapalli'', named after it. Between 1790 and 1948, Banaganapalli was the capital of the princely state of the same name, Banganapalle State. Geography Banaganapalli is located at . It has an average elevation of 209 metres (688 ft). Betamcherla, Banaganapalli and Koilakuntla are called Twin towns. Right Canal of Srisailam Dam SRBC passes near Banaganapalli Town. History Banaganapalle Nawabs In 1601, Sultan Ismail Adil Shah of Bijapur conquered the fortress of Banaganapalli from Raja Nanda Chakravathy. The fort and surrounding districts were placed under the control of his victorious general, Siddhu Sumbal, who held them until 1665. Muhammad Beg Khan-e Rosebahani was granted Banaganapalli and the surrounding jagir in perpetual fiefdom but died without a male heir, le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muslims
Muslims () are people who adhere to Islam, a Monotheism, monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God in Abrahamic religions, God of Abraham (or ''Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the last Islamic prophet. Alongside the Quran, Muslims also believe in previous Islamic holy books, revelations, such as the Tawrat (Torah), the Zabur (Psalms), and the Injeel (Gospel). These earlier revelations are associated with Judaism and Christianity, which are regarded by Muslims as earlier versions of Islam. The majority of Muslims also follow the teachings and practices attributed to Muhammad (''sunnah'') as recorded in traditional accounts (hadith). With an estimated population of almost 2 billion followers, Muslims comprise around 26% of the world's total population. In descending order, the percentage of people who identify as Muslims on each ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindus
Hindus (; ; also known as Sanātanīs) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism, also known by its endonym Sanātana Dharma. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pp. 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for people living in the Indian subcontinent. It is assumed that the term ''"Hindu"'' traces back to Avestan scripture Vendidad which refers to land of seven rivers as Hapta Hendu which itself is a cognate to Sanskrit term ''Sapta Sindhuḥ''. (The term ''Sapta Sindhuḥ'' is mentioned in Rig Veda and refers to a North western Indian region of seven rivers and to India as a whole.) The Greek cognates of the same terms are "''Indus''" (for the river) and "''India''" (for the land of the river). Likewise the Hebrew cognate ''hōd-dū'' refers to India mentioned in Hebrew BibleEsther 1:1. The term "''Hindu''" also implied a geographic, ethnic or cultural identifier for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deccan Plateau
The Deccan is a plateau extending over an area of and occupies the majority of the Indian peninsula. It stretches from the Satpura Range, Satpura and Vindhya Ranges in the north to the northern fringes of Tamil Nadu in the south. It is bound by the mountain ranges of the Western Ghats and the Eastern Ghats on the sides, which separate the region from the Western Coastal Plains, Western and Eastern Coastal Plains respectively. It covers most of the Indian States of Maharashtra, Karnataka, Telangana and Andhra Pradesh excluding the coastal regions, and minor portions of Tamil Nadu and Kerala. The plateau is marked by rocky terrain with an average elevation of about . It is subdivided into Maharashtra Plateau, Karnataka Plateau, and Rayalaseema & Telangana Plateau. The Deccan Traps in the north west were formed by multiple layers of igneous rocks laid down by basaltic lava flows following a massive volcanic eruption that occurred during the end of the Cretaceous period (66 Millio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aurangzeb
Alamgir I (Muhi al-Din Muhammad; 3 November 1618 – 3 March 1707), commonly known by the title Aurangzeb, also called Aurangzeb the Conqueror, was the sixth Mughal emperors, Mughal emperor, reigning from 1658 until his death in 1707, becoming the second longest-ruling emperor of Hindustan (48 years and 7 months). Under his reign, the Mughal Empire reached its greatest extent, with territory spanning nearly the entirety of the Indian subcontinent. Aurangzeb and the Mughals belonged to a branch of the Timurid dynasty. He held administrative and military posts under his father Shah Jahan () and gained recognition as an accomplished military commander. Aurangzeb served as the viceroy of the Viceroy of the Deccan, Deccan in 1636–1637 and the governor of Gujarat under Mughal Empire, Gujarat in 1645–1647. He jointly administered the provinces of Subah of Multan, Multan and Sind State, Sindh in 1648–1652 and continued expeditions into the neighboring Safavid Iran, Safavid ter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syed Faiz Ali Khan (Banganapalle)
Syed may refer to: * Seyd, alternative for Sayyid (name) * Alternative for Sayyid, an honorific title * Ahsan Ali Syed (born 1973), Indian businessman * Ghulam Murtaza Syed (1904-1995), prominent Sindhi politician * Ibrahim Bijli Syed (born 1939), American radiological scientist, medical physicist, health physicist * Matthew Syed (born 1970), British journalist * Nabeela Syed (born 1999), American politician * Nabiha Syed, American technology lawyer and executive * Zulfi Syed, Indian model and actor * Nayyar Ali Dada, (Born 1943) also known as Syed Nayyar Ali Zaid, Famous Architect in Pakistan See also *Said (other) *Seyd (other) Seyd may refer to: * Seyd, alternative for Sayyid * Ernest Seyd (1830 – 1881), German-born British author, banker, and economist See also *Said (other) Said can refer to: * Speech, or the act of speaking * Saʽid, a male Arabic ... * Seyd Kola {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jagir
A jagir (), ( Hindustani: जागीर/جاگیر, ''Jāgīr''), ( Marathi: जहागीर, ''Jahāgīrá'') also spelled as jageer, was a type of feudal land grant in the Indian subcontinent at the foundation of its Jagirdar ( Zamindar) system. It developed during the Islamic era of the Indian subcontinent, starting in the early 13th century, wherein the powers to govern and collect tax from an estate was granted to an appointee of the state. 13th-century origin and successors This feudal system of land ownership is referred to as the ''jagirdar'' system. The system was introduced by the Sultans of Delhi from the 13th century onwards, was later adopted by the Mughal Empire, the Maratha Empire and continued under the British East India Company. Some Hindu jagirdars were converted into Muslim vassal states under Mughal imperial sway, such as the nawabs of Kurnool. Most princely states of India during the colonial British Raj era were jagirdars such as Mohrampur Jagi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bijapur Sultanate
The Sultanate of Bijapur was an early modern kingdom in the western Deccan and South India, ruled by the Muslim Adil Shahi (or Adilshahi) dynasty. Bijapur had been a '' taraf'' (province) of the Bahmani Kingdom prior to its independence in 1490 and before the kingdom's political decline in the last quarter of the 15th century. It was one of the Deccan sultanates, the collective name of the kingdom's five successor states. The Sultanate of Bijapur was one of the most powerful states on the Indian Subcontinent at its peak, second to the Mughal Empire which conquered it in 1686 under Aurangzeb. After emigrating to the Bahmani Sultanate, Yusuf Adil Shah rose through the ranks to be appointed governor of the province of Bijapur. In 1490, he created a ''de facto'' independent Bijapur state which became formally independent with the Bahmani collapse in 1518. The Bijapur Sultanate's borders changed considerably throughout its history. Its northern boundary remained relatively stabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |