|
Bangabandhu Bridge
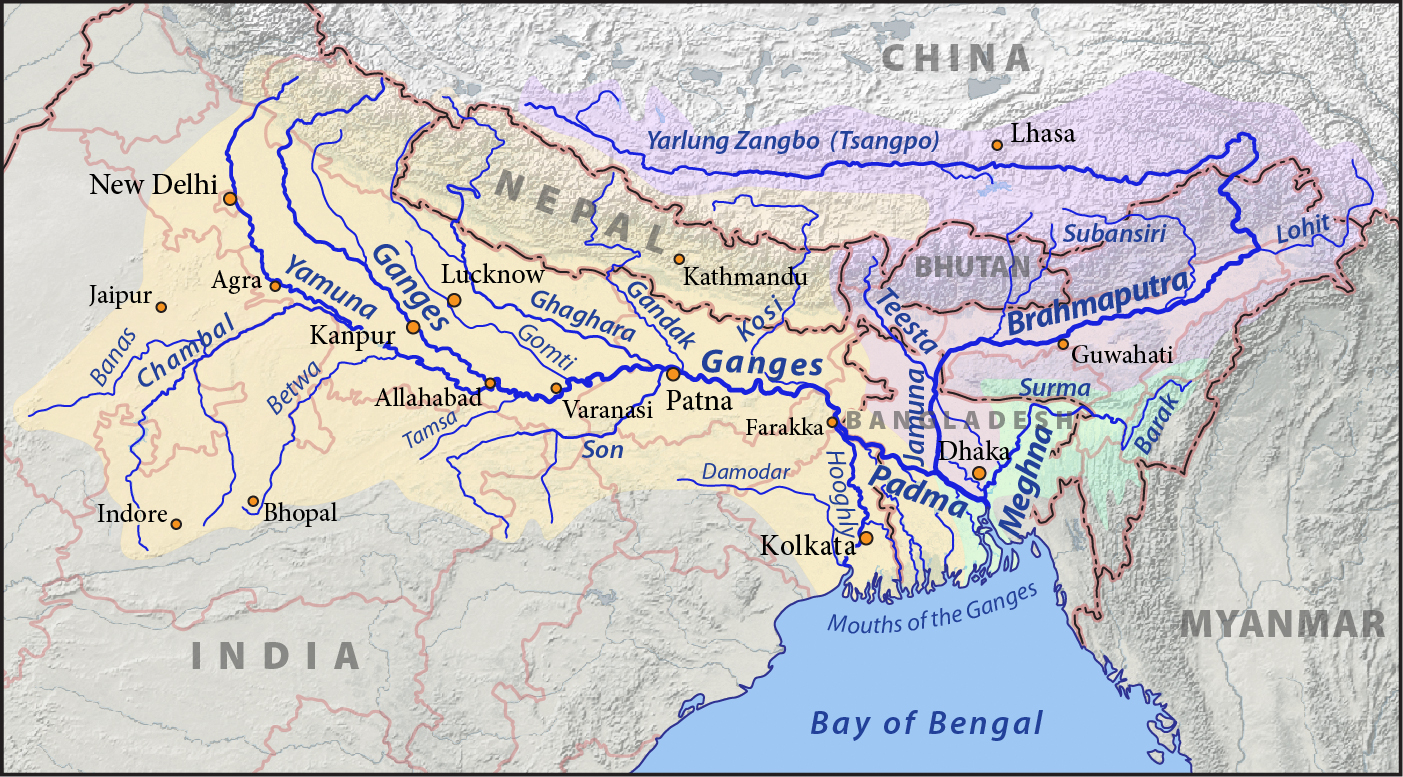
Jamuna Multi-purpose Bridge (), is a bridge built over the river Jamuna in Bangladesh. The bridge was opened in June 1998. With a length of 4.8 kilometres, it is the second longest bridge of Bangladesh, Padma Bridge being the first. It connects Bhuapur on the Jamuna River's east bank to Sirajganj on its west bank. 90% of this bridge is under Tangail district and 10% under Sirajganj district. It was the 11th longest bridge in the world when constructed in 1998 and at present is the 6th longest bridge in South Asia. The Jamuna River, which it spans, is one of the three major rivers of Bangladesh, and is fifth largest in the world in discharge volume. History of construction The river Jamuna (Brahmaputra), along with the lower stretch of the Padma (Ganges) divides Bangladesh into nearly two equal halves. Until now all road and rail communication between the two parts of the country has had to rely on time-consuming ferry services that were often disrupted because of navigabili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
N405 (Bangladesh)
Dhaka-North Bengal Highway or simply Elenga-Nalka-Hatikamrul Road is a national highway which connects Elenga, a town in Tangail district to Hatikumrul Interchange. The highway was also known as the Jamuna Bridge approach Road. This highway plays an important role for regional and national connectivity in the western region. History This road was built as a pilot project of Jamuna Bridge Jamuna Multi-purpose Bridge (), is a bridge built over the river Jamuna in Bangladesh. The bridge was opened in June 1998. With a length of 4.8 kilometres, it is the second longest bridge of Bangladesh, Padma Bridge being the first. It connect ... in 1998. For this reason the road is also known as Jamuna Bridge Approach Road. References {{Reflist National highways in Bangladesh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Bridges By Length
This is a list of the world's longest bridges that are more than in length sorted by their full length above land and water. The main span is the longest span without any ground support. ''Note: There is no standard way to measure the total length of a bridge. Some bridges are measured from the beginning of the entrance ramp to the end of the exit ramp. Some are measured from shoreline to shoreline. Yet others use the length of the total construction involved in building the bridge. Since there is no standard, no ranking of a bridge should be assumed because of its position in the list. Additionally, numbers are merely estimates and measures in United States customary units, U.S. customary units (foot (unit), feet) may be imprecise due to conversion rounding.'' Completed Under construction See also * List of spans * List of longest arch bridge spans * List of longest masonry arch bridge spans * List of longest cantilever bridge spans * List of longest cable-stayed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
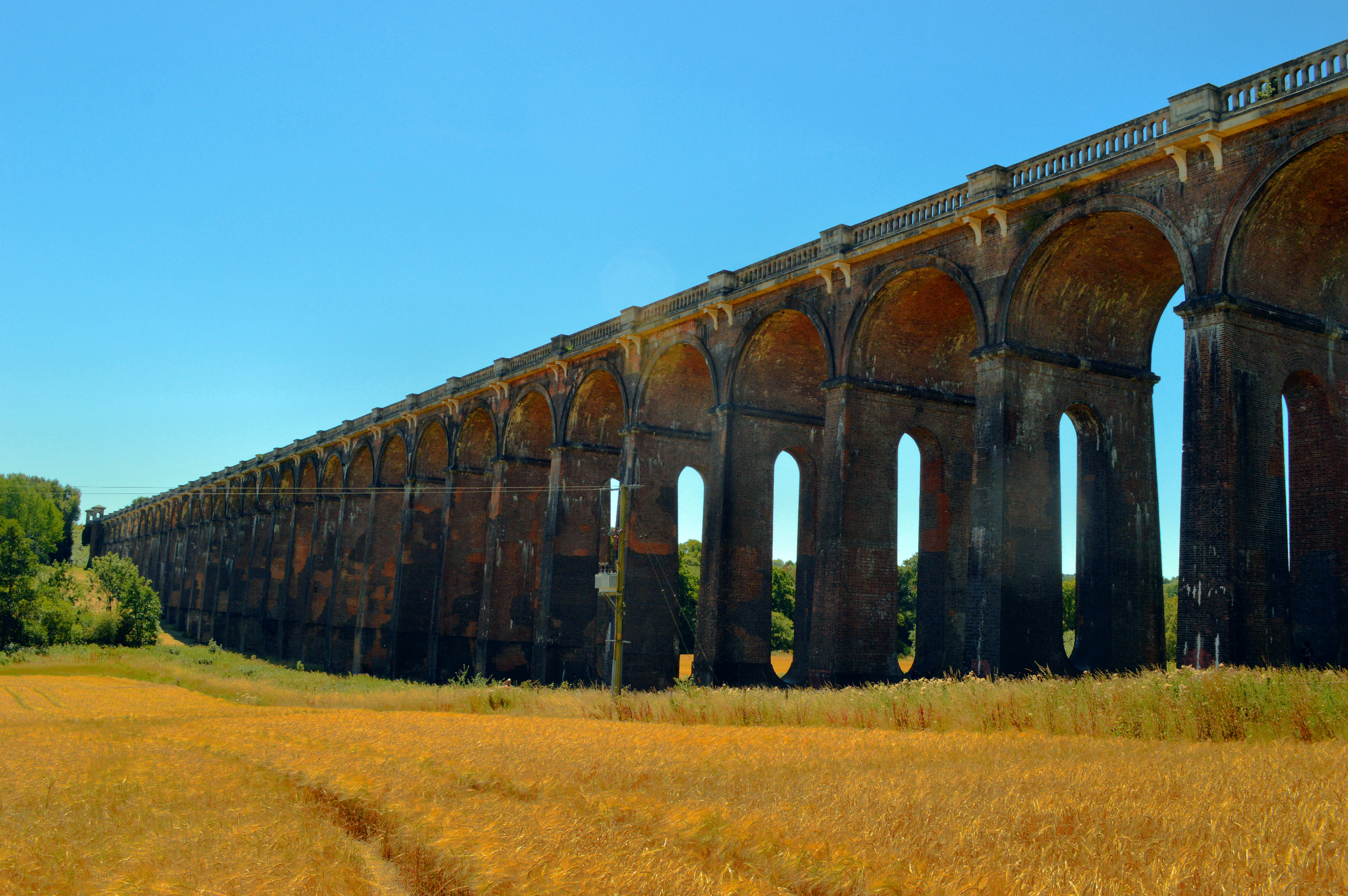
Viaducts
A viaduct is a specific type of bridge that consists of a series of arches, piers or columns supporting a long elevated railway or road. Typically a viaduct connects two points of roughly equal elevation, allowing direct overpass across a wide valley, road, river, or other low-lying terrain features and obstacles. The term ''viaduct'' is derived from the Latin ''via'' meaning "road", and ''ducere'' meaning "to lead". It is a 19th-century derivation from an analogy with ancient Roman aqueducts. Like the Roman aqueducts, many early viaducts comprised a series of arches of roughly equal length. Over land The longest viaduct in antiquity may have been the Pont Serme which crossed wide marshes in southern France. At its longest point, it measured 2,679 meters with a width of 22 meters. Viaducts are commonly used in many cities that are railroad hubs, such as Chicago, Birmingham, London and Manchester. These viaducts cross the large railroad yards that are needed for freight ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inclined Plane
An inclined plane, also known as a ramp, is a flat supporting surface tilted at an angle from the vertical direction, with one end higher than the other, used as an aid for raising or lowering a load. The inclined plane is one of the six classical simple machines defined by Renaissance scientists. Inclined planes are used to move heavy loads over vertical obstacles. Examples vary from a ramp used to load goods into a truck, to a person walking up a pedestrian ramp, to an automobile or railroad train climbing a grade. Moving an object up an inclined plane requires less force than lifting it straight up, at a cost of an increase in the distance moved. The mechanical advantage of an inclined plane, the factor by which the force is reduced, is equal to the ratio of the length of the sloped surface to the height it spans. Owing to conservation of energy, the same amount of mechanical energy (work (physics), work) is required to lift a given object by a given vertical distance, disr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Span (architecture)
In engineering, span is the distance between two adjacent structural supports (e.g., two piers) of a structural member (e.g., a beam). Span is measured in the horizontal direction either between the faces of the supports (clear span) or between the centers of the bearing surfaces (effective span): A span can be closed by a solid beam or by a rope. The first kind is used for bridges, the second one for power lines, overhead telecommunication lines, some type of antennas or for aerial tramways. Span is a significant factor in finding the strength and size of a beam as it determines the maximum bending moment and deflection. The maximum bending moment M_ and deflection \delta_in the pictured beam is found using: :M_ = \frac :\delta_ = \frac = \frac where :q = Uniformly distributed load :L = Length of the beam between two supports (span) :E = Modulus of elasticity :I = Area moment of inertia The maximum bending moment and deflection occur midway between the two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OECD
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD; , OCDE) is an international organization, intergovernmental organization with 38 member countries, founded in 1961 to stimulate economic progress and international trade, world trade. It is a forum (legal), forum whose member countries describe themselves as committed to democracy and the market economy, providing a platform to compare policy experiences, seek answers to common problems, identify good practices, and coordinate domestic and international policies of its members. The majority of OECD members are generally regarded as developed country, developed countries, with High-income economy, high-income economies, and a very high Human Development Index. their collective population is 1.38 billion people with an average life expectancy of 80 years and a median age of 40, against a global average of 30. , OECD Member countries collectively comprised 62.2% of list of countries by GDP (nominal), global nom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asian Development Bank
The Asian Development Bank (ADB) is a regional development bank to promote social and economic development in Asia. The bank is headquartered in Metro Manila, Philippines and maintains 31 field offices around the world. The bank was established on 19 December 1966 and admits the members of the UN Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (UNESCAP, formerly the Economic Commission for Asia and the Far East or ECAFE), and non-regional developed countries. Starting with 31 members at its establishment, by 2019 ADB had 69 members. The ADB was modeled closely on the World Bank and has a similar weighted voting system, where votes are distributed in proportion with members' capital subscriptions. ADB releases an annual report that summarizes its operations, budget, and other materials for review by the public. The ADB-Japan Scholarship Program (ADB-JSP) enrolls about 300 students annually in academic institutions located in 10 countries within the Region. After comple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Development Association
The International Development Association (IDA) () is a development finance institution which offers concessional loans and grant (money), grants to the world's poorest developing country, developing countries. The IDA is a member of the World Bank Group and is headquartered in Washington, D.C. in the United States. It was established in 1960 to complement the existing International Bank for Reconstruction and Development by lending to developing countries which suffer from the lowest gross national income, from troubled credit risk, creditworthiness, or from the lowest per capita income. Together, the International Development Association and International Bank for Reconstruction and Development are collectively generally known as the World Bank, as they follow the same executive leadership and operate with the same staff. The association shares the World Bank's mission of poverty reduction, reducing poverty and aims to provide affordable development financing to countries whos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Navigability
A body of water, such as a river, canal or lake, is navigable if it is deep, wide and calm enough for a water vessel (e.g. boats) to pass safely. Navigability is also referred to in the broader context of a body of water having sufficient under keel clearance for a vessel. Such a navigable water is called a ''waterway'', and is preferably with few obstructions against direct traverse that need avoiding, such as rocks, reefs or trees. Bridges built over waterways must have sufficient clearance. High flow speed may make a channel unnavigable due to risk of ship collisions. Waters may be unnavigable because of ice, particularly in winter or high-latitude regions. Navigability also depends on context: a small river may be navigable by smaller craft such as a motorboat or a kayak, but unnavigable by a larger cargo ship, freighter or cruise ship. Shallow rivers may be made navigable by the installation of locks that regulate flow and increase upstream water level, or by dredgi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferry
A ferry is a boat or ship that transports passengers, and occasionally vehicles and cargo, across a body of water. A small passenger ferry with multiple stops, like those in Venice, Italy, is sometimes referred to as a water taxi or water bus. Ferries form a part of the public transport systems of many waterside cities and islands, allowing direct transit between points at a capital cost much lower than bridges or tunnels. Ship connections of much larger distances (such as over long distances in water bodies like the Baltic Sea) may also be called ferry services, and many carry vehicles. History The profession of the ferryman is embodied in Greek mythology in Charon, the boatman who transported souls across the River Styx to the Underworld. Speculation that a pair of oxen propelled a ship having a water wheel can be found in 4th century Roman literature "''Anonymus De Rebus Bellicis''". Though impractical, there is no reason why it could not work and such a ferry, mod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ganges
The Ganges ( ; in India: Ganga, ; in Bangladesh: Padma, ). "The Ganges Basin, known in India as the Ganga and in Bangladesh as the Padma, is an international which goes through India, Bangladesh, Nepal and China." is a trans-boundary river of Asia which flows through India and Bangladesh. The river rises in the western Himalayas in the States and union territories of India, Indian state of Uttarakhand. It flows south and east through the Gangetic Plain, Gangetic plain of North India, receiving the right-bank tributary, the Yamuna, which also rises in the western Indian Himalayas, and several left-bank tributaries from Nepal that account for the bulk of its flow. In West Bengal state, India, a feeder canal taking off from its right bank diverts 50% of its flow southwards, artificially connecting it to the Hooghly River. The Ganges continues into Bangladesh, its name changing to the Padma River, Padma. It is then joined by the Jamuna River (Bangladesh), Jamuna, the lower str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Padma River
The Padma () is a major river in Bangladesh. It is the eastern and main distributary of the Ganges, flowing generally southeast for to its confluence with the Meghna River, near the Bay of Bengal. The city of Rajshahi is situated on the banks of the river.Hossain ML, Mahmud J, Islam J, Khokon ZH and Islam S (eds.) (2005) Padma, Tatthyakosh Vol. 1 and 2, Dhaka, Bangladesh, p. 182 . Since 1966, over 66,000 hectares of land have been lost to erosion of the Padma. History Etymology The Padma, Sanskrit for lotus flower, is mentioned in ancient Hindu scripts as a byname for the Goddess Lakshmi. Geographic effects Eighteenth-century geographer James Rennell referred to a former course of the Ganges north of its present channel, as follows: Murshidabad District Murshidabad District is situated on the western bank of the Padma. It flows dividing the Rajshahi and Murshidabad District of West Bengal and created a natural river border between India and Bangladesh. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |