|
Bandwar
Bandwar, also called Vandwar or Banduar, is a village in Begusarai district of Bihar, a state in India. Geography It is located in the Indo-Gangetic plain region of India. The only river that flows through the village is the Burhi Gandak River. Due to the river being prone to floods, a levee, referred to as “Bandh” (Hindi: बांध) by local residents, has been constructed parallel to the Burhi Gandak River to prevent flooding of the adjoining countryside. Transport A bridge on the Burhi Gandak River The Burhi Gandak River is a tributary of the Ganges. It is also known as the Sikrahna river. The Burhi (“Old”) Gandak flows parallel to and east of the Gandak River in an old channel. Course The Burhi Gandak originates from Chautarwa Chaur n ... called the Chhatauna Bridge connects the village to other villages on the northern bank of the river. Demographics The village has 12,943 residents, 6,796 male and 6,147 female. 53 percent of the village is illiter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Begusarai District
Begusarai District is one of the thirty-eight Districts of Bihar, districts of the Indian state of Bihar. The city of Begusarai is its administrative headquarters and is part of the Munger division. History Begusarai was established in 1870 as part of Munger District. In 1972, it was given district status. Geography Begusarai district occupies an area of . The district lies on the northern bank of the river Ganges. Begusarai district is a part of Munger division. It is located at latitudes 25.15N & 25.45N and longitudes 85.45E & 86.36E. The Ganges river separates Begusarai district from Patna District and Munger District. Flora and fauna In 1989 Begusarai district became home to the Kanwar Lake Bird Sanctuary Kanwar Lake Bird Sanctuary Wildlife Sanctuary, which has an area of . It is Asia's largest freshwater oxbow lake. In November 2020, the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC) declared it the first Ramsar site in Bihar. Demographics According to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bihar
Bihar ( ) is a states and union territories of India, state in Eastern India. It is the list of states and union territories of India by population, second largest state by population, the List of states and union territories of India by area, 12th largest by area, and the List of Indian states and union territories by GDP, 14th largest by GDP in 2024. Bihar borders Uttar Pradesh to its west, Nepal to the north, the northern part of West Bengal to the east, and Jharkhand to the south. Bihar is split by the river Ganges, which flows from west to east. On 15 November 2000, a large chunk of southern Bihar was ceded to form the new state of Jharkhand. Around 11.27% of Bihar's population live in urban areas as per a 2020 report. Additionally, almost 58% of Bihari people, Biharis are below the age of 25, giving Bihar the highest proportion of young people of any Indian state. The official language is Hindi, which shares official status alongside that of Urdu. The main native languag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
States And Territories Of India
India is a federalism, federal union comprising 28 federated state, states and 8 union territory, union territories, for a total of 36 subnational entities. The states and union territories are further subdivided into 800 List of districts in India, districts and smaller administrative divisions of India, administrative divisions by the respective subnational government. The states of India are self-governing administrative divisions, each having a State governments of India, state government. The governing powers of the states are shared between the state government and the Government of India, union government. On the other hand, the union territories are directly governed by the union government. History 1876–1919 The British Raj was a very complex political entity consisting of various imperial divisions and states and territories of varying autonomy. At the time of its establishment in 1876, it was made up of 584 princely state, constituent states and the prov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Districts Of India
A district (''Zila (country subdivision), zila''), also known as revenue district, is an Administrative divisions of India, administrative division of an States and union territories of India, Indian state or territory. In some cases, districts are further subdivided into Revenue division, sub-divisions, and in others directly into tehsil, ''tehsils'' or ''talukas''. , there are a total of 780 districts in India. This count includes Mahe and Yanam which are Census districts and not Administrative districts and also includes the temporary Maha Kumbh Mela district but excludes Itanagar Capital Complex which has a Deputy Commissioner but is not an official district. District Administration ;The District officials include: *District Judge (India), District & Sessions Judge (Principal & additional), an officer belonging to the Judiciary of India, Indian Judicial Service (state), responsible for justice and passing orders of imprisonment, including the Capital punishment, death pena ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Regions Of India
The administrative divisions of India are subnational administrative units of India; they are composed of a nested hierarchy of administrative divisions. Indian states and territories frequently use different local titles for the same level of subdivision (e.g., the '' mandals'' of Andhra Pradesh and Telangana correspond to ''tehsils'' of Uttar Pradesh and other Hindi-speaking states but to ''talukas'' or ''taluks'' of Gujarat, Goa, Karnataka, Kerala, Maharashtra, and Tamil Nadu). The smaller subdivisions (villages and blocks) exist only in rural areas. In urban areas, urban local bodies exist instead of these rural subdivisions. Tiers of India The diagram below outlines the six tiers of administrative divisions: Notes: * Divisions under State: In some states, divisions do not exist, and the administrative units are split directly into districts. In these states, the division concept is either absent or only for administrative purposes. * Within a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mithila (region)
Mithila (), also known as Tirhut, Tirabhukti and Mithilanchal, is a geographical and cultural region of the Indian subcontinent bounded by the Mahananda River in the east, the Ganges in the south, the Gandaki River in the west and by the foothills of the Himalayas in the north. It comprises certain parts of Bihar and Jharkhand states of India and adjoining districts of the Koshi Province, Bagmati Pradesh and Madhesh Province of Nepal. The native language in Mithila is Maithili language, Maithili, and its speakers are referred to as Maithils. Mithila is commonly used to refer to the Videha Kingdom, as well as to the modern-day territories that fall within the ancient boundaries of Videha. Until the 20th century, Mithila was still ruled in part by the Raj Darbhanga. History In Jainism Mithilā is one of the most significant pilgrimage sites in Jainism. Apart from its association with ''Mahavira'', the 24th Tirthankara, it is also known for its association with ''Mallinatha'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
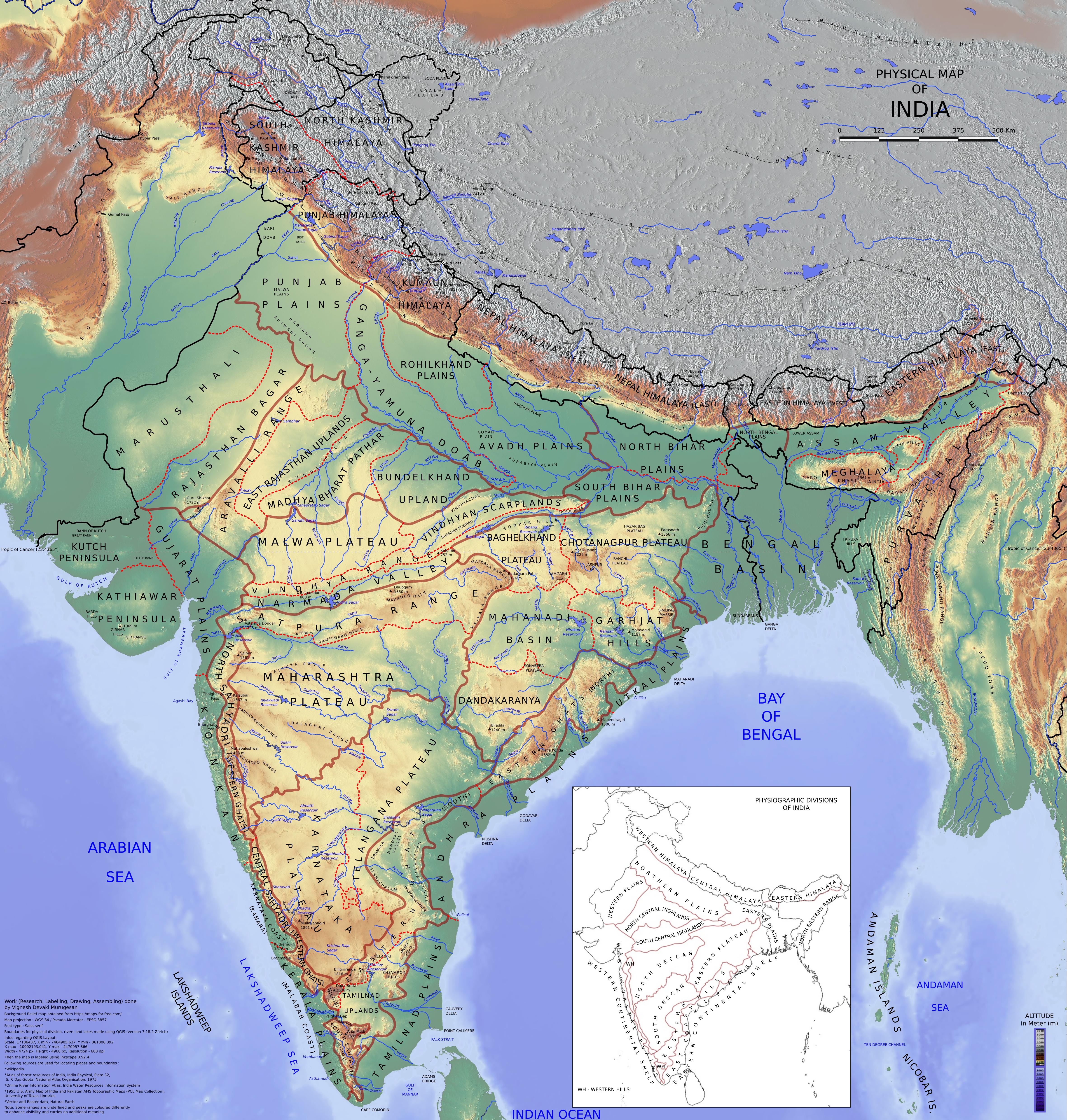
Indo-Gangetic Plain
The Indo-Gangetic Plain, also known as the Northern Plain or North Indian River Plain, is a fertile plain spanning across the northern and north-eastern part of the Indian subcontinent. It encompasses North India, northern and East India, eastern India, eastern Pakistan, southern Nepal, and almost all of Bangladesh. It is named after the two major river systems that drain the region–Indus River, Indus and Ganges. It stretches from the Himalayas in the north to the northern edge of the Deccan plateau in the south, and extends from North East India in the east to the Iranian border in the west. The region is home to many major cities and nearly one-seventh of the world's population. As the region was formed by the deposits of the three major rivers–Indus, Ganges and Brahmaputra, the plains consists of the world's largest expanse of uninterrupted alluvial soil, alluvium. Due to its rich water resources, it is one of the world's most densely populated and intensely farmed areas. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burhi Gandak River
The Burhi Gandak River is a tributary of the Ganges. It is also known as the Sikrahna river. The Burhi (“Old”) Gandak flows parallel to and east of the Gandak River in an old channel. Course The Burhi Gandak originates from Chautarwa Chaur near Bisambharpur in the district of West Champaran in Bihar. It initially flows through the East Champaran district. After flowing for a distance of about , the river takes a southerly turn where two rivers - the Dubhara and the Tour – join it. Thereafter, the river flows in a south-easterly direction through the Muzaffarpur district for about . In this portion, the river spills over its banks and a number of spill channels take off and rejoin it later. The Burhi Gandak runs a zig-zag course through the districts of Samastipur and Begusarai before covering a short distance in Khagaria district, running by the side of the town of Khagaria, and flows into the Ganges The Ganges ( ; in India: Ganga, ; in Bangladesh: Padma, ). " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Levee
A levee ( or ), dike (American English), dyke (British English; see American and British English spelling differences#Miscellaneous spelling differences, spelling differences), embankment, floodbank, or stop bank is an elevated ridge, natural or artificial, alongside the river banks, banks of a river, often intended to flood control, protect against flooding of the area adjoining the river. It is usually soil, earthen and often runs parallel (geometry), parallel to the course of a river in its floodplain or along low-lying coastlines. Naturally occurring levees form on river floodplains following flooding. Sediment and alluvium are deposition (geology), deposited on the banks and settle, forming a ridge that increases the river channel's capacity. Alternatively, levees can be artificially constructed from fill dirt, fill, designed to regulate water levels. In some circumstances, artificial levees can be environmental degradation, environmentally damaging. Ancient civilization ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |