|
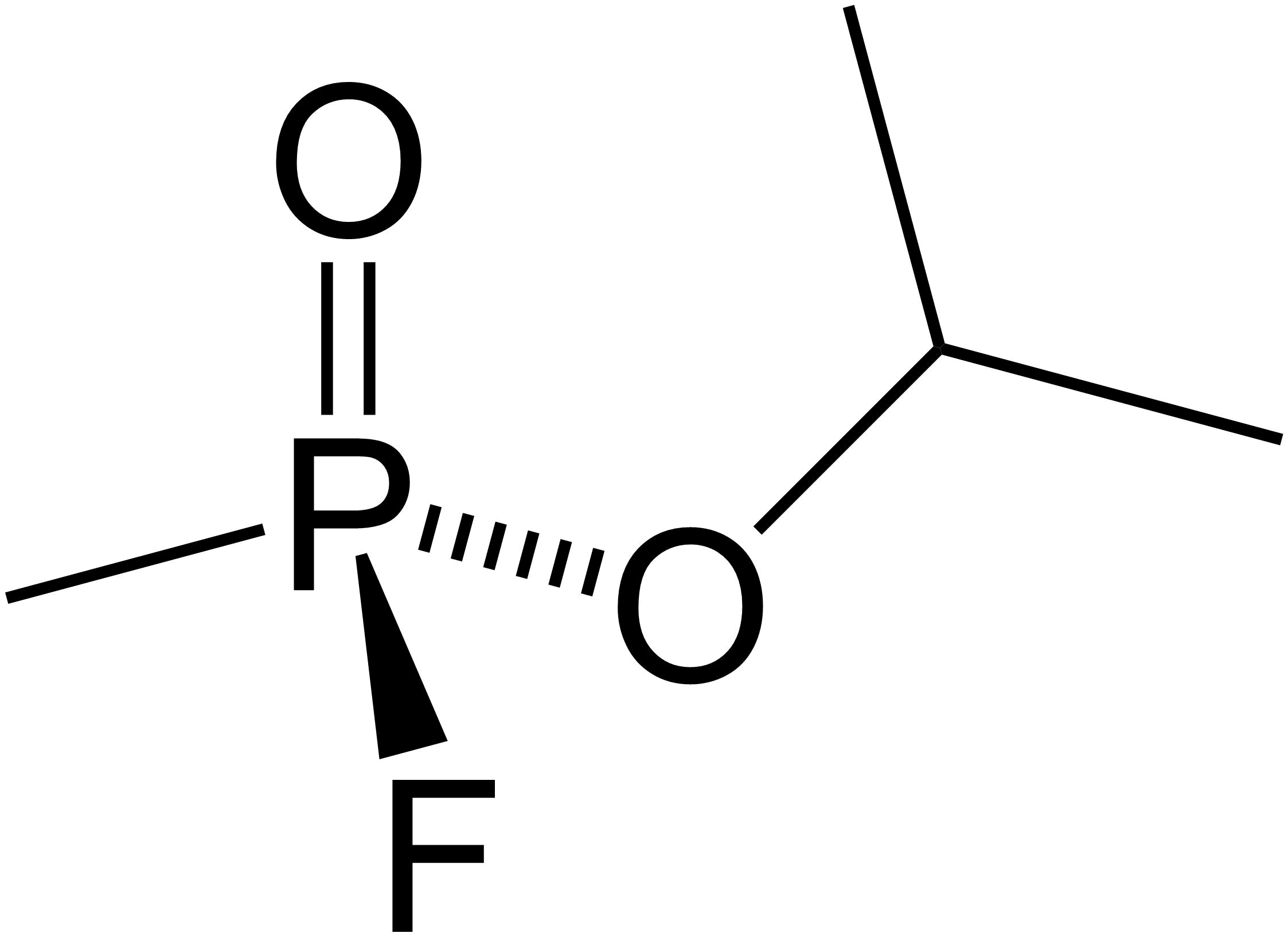
Bambuterol
Bambuterol (INN) is a long-acting β adrenoceptor agonist (LABA) used in the treatment of asthma; it also is a prodrug of terbutaline. Commercially, the AstraZeneca pharmaceutical company produces and markets bambuterol as Bambec and Oxeol. It is not available in the U.S. Indications As other LABAs, bambuterol is used in the long-term management of persistent asthma. It should not be used as a rescue medication for short-term relief of asthma symptoms. Contraindications Bambuterol is contraindicated in pregnancy and in people with seriously impaired liver function. It can be used by people with renal impairment, but dose adjustments are necessary. Adverse effects The adverse effect profile of bambuterol is similar to that of salbutamol, and may include fatigue, nausea, palpitations, headache, dizziness and tremor. Interactions Concomitant administration of bambuterol with corticosteroids, diuretics, and xanthine derivatives (such as theophylline) increases the risk of hy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palpitations
Palpitations occur when a person becomes aware of their heartbeat. The heartbeat may feel hard, fast, or uneven in their chest. Symptoms include a very fast or irregular heartbeat. Palpitations are a sensory symptom. They are often described as a skipped beat, a rapid flutter, or a pounding in the chest or neck. Palpitations are not always the result of a physical problem with the heart and can be linked to anxiety. However, they may signal a arrhythmia, fast or irregular heartbeat. Palpitations can be brief or long-lasting. They can be intermittent or continuous. Other symptoms can include dizziness, shortness of breath, sweating, headaches, and chest pain. There are a variety of causes of palpitations not limited to the following: Palpitation may be associated with coronary artery disease, coronary heart disease, perimenopause, hyperthyroidism, adult heart muscle diseases like hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, congenital heart diseases like atrial septal defects, diseases causing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vecuronium Bromide
Vecuronium bromide, sold under the brand name Norcuron among others, is a medication used as part of general anesthesia to provide skeletal muscle relaxation during surgery or mechanical ventilation. It is also used to help with endotracheal intubation; however, agents such as suxamethonium (succinylcholine) or rocuronium are generally preferred if this needs to be done quickly. It is given by injection into a vein. Effects are greatest at about 4 minutes and last for up to an hour. Side effects may include low blood pressure and prolonged paralysis. Allergic reactions are rare. It is unclear if use in pregnancy is safe for the baby. Vecuronium is in the aminosteroid neuromuscular-blocker family of medications and is of the non-depolarizing type. It works by competitively blocking the action of acetylcholine on skeletal muscles. The effects may be reversed with sugammadex or a combination of neostigmine and glycopyrrolate. To minimize residual blockade, reversal sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
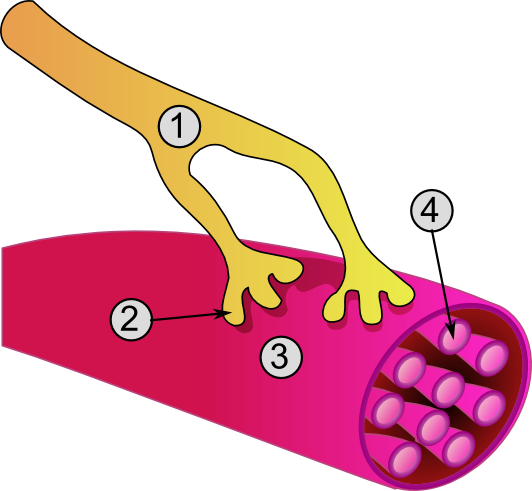
Neuromuscular-blocking Drug
Neuromuscular-blocking drugs, or Neuromuscular blocking agents (NMBAs), block transmission at the neuromuscular junction, causing paralysis of the affected skeletal muscles. This is accomplished via their action on the post-synaptic acetylcholine (Nm) receptors. In clinical use, neuromuscular block is used adjunctively to anesthesia to produce paralysis, firstly to paralyze the vocal cords, and permit endotracheal intubation, and secondly to optimize the surgical field by inhibiting spontaneous ventilation, and causing relaxation of skeletal muscles. Because the appropriate dose of neuromuscular-blocking drug may paralyze muscles required for breathing (i.e., the diaphragm), mechanical ventilation should be available to maintain adequate Respiration (physiology), respiration. This class of medications helps to reduce patient movement, breathing, or ventilator dyssynchrony and allows lower insufflation pressures during laparoscopy. It has several indication ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suxamethonium
Suxamethonium chloride (brand names Scoline and Sucostrin, among others), also known as suxamethonium or succinylcholine, or simply sux in medical abbreviation, is a medication used to cause short-term paralysis as part of general anesthesia. This is done to help with tracheal intubation or electroconvulsive therapy. It is administered by injection, either into a vein or into a muscle. When used in a vein, onset of action is generally within one minute and effects last for up to 10 minutes. Common side effects include low blood pressure, increased saliva production, muscle pain, and rash. Serious side effects include malignant hyperthermia, hyperkalemia and allergic reactions. It is not recommended in people who are at risk of high blood potassium or a history of myopathy. Use during pregnancy appears to be safe for the baby. Suxamethonium is in the neuromuscular blocker family of medications and is of the depolarizing type. It works by blocking the action of acetylcholi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cholinesterase Inhibitor
Cholinesterase inhibitors (ChEIs), also known as anti-cholinesterase, are chemicals that prevent the breakdown of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine or butyrylcholine by cholinesterase. This increases the amount of the acetylcholine or butyrylcholine in the Chemical synapse#Structure, synaptic cleft that can bind to Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor, muscarinic receptors, Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor, nicotinic receptors and others. This group of inhibitors is divided into two subgroups, acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (AChEIs) and Butyrylcholinesterase#Inhibitors, butyrylcholinesterase inhibitors (BChEIs). ChEIs may be used as drugs for Alzheimer's disease, Alzheimer's and myasthenia gravis, and also as chemical weapons and insecticides. Side effects when used as drugs may include Anorexia (symptom), loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, Diarrhea#Definition, loose stools, Dream, vivid dreams at night, dehydration, rash, bradycardia, peptic ulcer disease, seizures, weight los ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potassium
Potassium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol K (from Neo-Latin ) and atomic number19. It is a silvery white metal that is soft enough to easily cut with a knife. Potassium metal reacts rapidly with atmospheric oxygen to form flaky white potassium peroxide in only seconds of exposure. It was first isolated from potash, the ashes of plants, from which its name derives. In the periodic table, potassium is one of the alkali metals, all of which have a single valence electron in the outer electron shell, which is easily removed to create cation, an ion with a positive charge (which combines with anions to form salts). In nature, potassium occurs only in ionic salts. Elemental potassium reacts vigorously with water, generating sufficient heat to ignite hydrogen emitted in the reaction, and burning with a lilac-flame color, colored flame. It is found dissolved in seawater (which is 0.04% potassium by weight), and occurs in many minerals such as orthoclase, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypokalemia
Hypokalemia is a low level of potassium (K+) in the blood serum. Mild low potassium does not typically cause symptoms. Symptoms may include feeling tired, leg cramps, weakness, and constipation. Low potassium also increases the risk of an abnormal heart rhythm, which is often too slow and can cause cardiac arrest. Causes of hypokalemia include vomiting, diarrhea, medications like furosemide and steroids, dialysis, diabetes insipidus, hyperaldosteronism, hypomagnesemia, and not enough intake in the diet. Normal potassium levels in humans are between 3.5 and 5.0 mmol/L (3.5 and 5.0 mEq/L) with levels below 3.5 mmol/L defined as hypokalemia. It is classified as severe when levels are less than 2.5 mmol/L. Low levels may also be suspected based on an electrocardiogram (ECG). The opposite state is called hyperkalemia that means high level of potassium in the blood serum. The speed at which potassium should be replaced depends on whether or not there are symptom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theophylline
Theophylline, also known as 1,3-dimethylxanthine, is a drug that inhibits phosphodiesterase and blocks adenosine receptors. It is used to treat chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and asthma. Its pharmacology is similar to other methylxanthine drugs (e.g., theobromine and caffeine). Trace amounts of theophylline are naturally present in tea, coffee, chocolate, yerba maté, guarana, and kola nut. The name 'theophylline' derives from "Thea"—the former genus name for tea + Legacy Greek φύλλον (phúllon, "leaf") + -ine. Medical uses The main actions of theophylline involve: * relaxing bronchial smooth muscle * increasing heart muscle contractility and efficiency (positive inotrope) * increasing heart rate (positive chronotropic) * increasing blood pressure * increasing renal blood flow * anti-inflammatory effects * central nervous system stimulatory effect, mainly on the medullary respiratory center The main therapeutic uses of theophylline are for treat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xanthine
Xanthine ( or , from Ancient Greek for its yellowish-white appearance; archaically xanthic acid; systematic name 3,7-dihydropurine-2,6-dione) is a purine base found in most human body tissues and fluids, as well as in other organisms. Several stimulants are derived from xanthine, including caffeine, theophylline, and theobromine. Xanthine is a product on the pathway of purine degradation. * It is created from guanine by guanine deaminase. * It is created from hypoxanthine by xanthine oxidoreductase. * It is also created from xanthosine by purine nucleoside phosphorylase. Xanthine is subsequently converted to uric acid by the action of the xanthine oxidase enzyme. Use and production Xanthine is used as a drug precursor for human and animal medications, and is produced as a pesticide ingredient. Clinical significance Derivatives of xanthine (known collectively as xanthines) are a group of alkaloids commonly used for their effects as mild stimulants and as bronchodila ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diuretic
A diuretic () is any substance that promotes diuresis, the increased production of urine. This includes forced diuresis. A diuretic tablet is sometimes colloquially called a water tablet. There are several categories of diuretics. All diuretics increase the excretion of water from the body, through the kidneys. There exist several classes of diuretic, and each works in a distinct way. Alternatively, an antidiuretic, such as vasopressin ( antidiuretic hormone), is an agent or drug which reduces the excretion of water in urine. Medical uses In medicine, diuretics are used to treat heart failure, liver cirrhosis, hypertension, influenza, water poisoning, and certain kidney diseases. Some diuretics, such as acetazolamide, help to make the urine more alkaline, and are helpful in increasing excretion of substances such as aspirin in cases of overdose or poisoning. Diuretics are sometimes abused by people with an eating disorder, especially people with bulimia nervosa, with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are involved in a wide range of physiological processes, including stress response, immune response, and regulation of inflammation, carbohydrate metabolism, protein catabolism, blood electrolyte levels, and behavior. Some common naturally occurring steroid hormones are cortisol (), corticosterone (), cortisone () and aldosterone () (cortisone and aldosterone are isomers). The main corticosteroids produced by the adrenal cortex are cortisol and aldosterone. The etymology of the '' cortico-'' part of the name refers to the adrenal cortex, which makes these steroid hormones. Thus a corticosteroid is a "cortex steroid". Classes * Glucocorticoids such as cortisol affect carbohydrate, fat, and protein metabolism, and have anti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |