|
Bamangola (community Development Block)
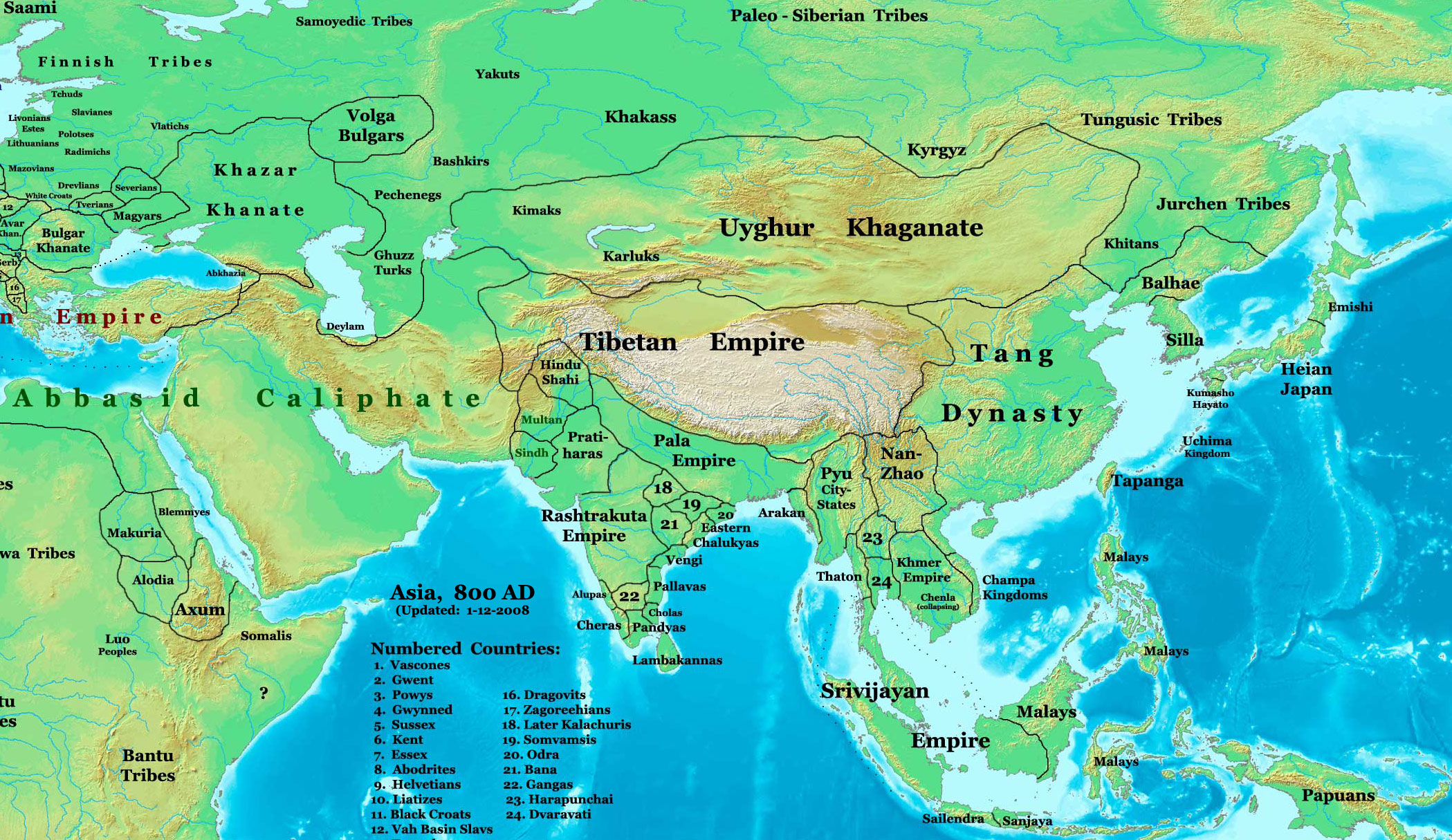
Bamangola is a community development block that forms an administrative division in Malda Sadar subdivision of Malda district in the Indian state of West Bengal. History Gauda and Pandua Gauda was once the “capital of the ancient bhukti or political division of Bengal known as Pundravardhana which lay on the eastern extremity of the Gupta Empire.” During the rule of the Sena Dynasty, in the 11th-12th century, Gauda was rebuilt and extended as Lakshmanawati (later Lakhnauti), and it became the hub of the Sena empire. Gauda was conquered by Muhammad bin Bakhtiyar Khalji in 1205. During the Turko-Afghan period, “the city of Lakhnauti or Gauda continued to function initially as their capital but was abandoned in 1342 by the Ilyas Shahi sultans in favour of Pandua because of major disturbances along the river course of the Ganga.” “Pandua then lay on the banks of the Mahananda, which was the major waterway of the sultanate at the time. However, when the Mahananda too began ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
States And Territories Of India
India is a federalism, federal union comprising 28 federated state, states and 8 union territory, union territories, for a total of 36 subnational entities. The states and union territories are further subdivided into 800 List of districts in India, districts and smaller administrative divisions of India, administrative divisions by the respective subnational government. The states of India are self-governing administrative divisions, each having a State governments of India, state government. The governing powers of the states are shared between the state government and the Government of India, union government. On the other hand, the union territories are directly governed by the union government. History 1876–1919 The British Raj was a very complex political entity consisting of various imperial divisions and states and territories of varying autonomy. At the time of its establishment in 1876, it was made up of 584 princely state, constituent states and the prov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gauḍa (city)
Gauḍa (also known as Gaur, Gour, Lakhnauti, Lakshmanavati and Jannatabad) is a historic city of Bengal in the eastern part of the Indian subcontinent, and one of the most prominent capitals of classical India, classical and medieval India, being the capital city of Bengal under several kingdoms. The Gauḍa (region), Gauḍa region was also a province of several pan-Indian empires. During the seventh century, the Gauda Kingdom was founded by King Shashanka, whose reign corresponds with the beginning of the Bengali calendar. Gour gradually became synonymous with Bengal and Bengalis. It was conquered by Bakhtiyar Khalji, a lieutenant of the Ghurid ruler Muhammad of Ghori in 1203. For a period of 112 years, between 1453 and 1565, Gauda was the capital of the Bengal Sultanate. In 1500, Gauda was the fifth-most populous city in the world, with a population of 200,000, as well as one of the most densely populated cities in the Indian subcontinent. The Portuguese people, Portuguese l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rajmahal
Rajmahal is a subdivisional town and a notified area in Rajmahal subdivision of the Sahebganj district in the Indian state of Jharkhand. It is situated at the banks of Ganges and was former capital of Bengal Subah under Mughal governor, Man Singh I. Geography Area Rajmahal has an area of . Overview The map shows a hilly area with the Rajmahal hills running from the bank of the Ganges in the extreme north to the south, beyond the area covered by the map into Dumka district. ‘Farakka’ is marked on the map and that is where Farakka Barrage is, just inside West Bengal. Rajmahal coalfield is shown in the map. The entire area is overwhelmingly rural with only small pockets of urbanisation. Note: The full screen map is interesting. All places marked on the map are linked and you can easily move on to another page of your choice. Enlarge the map to see what else is there – one gets railway links, many more road links and so on. History Rajmahal region was earlier rul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gauḍa (region)
Gauda ( ''Gauḍa''; ''Gauṛ''), was a territory located in Bengal in ancient and medieval times, as part of the Gauda Kingdom. Location and extent The ''Arthashastra'' of Chanakya (around 350–283 BC) refers to it along with Vanga, Pundra. This geographical idea continues with some of the ancient texts. Gauda and Vanga are sometimes used side by side.. Shashanka, the first important king of ancient Bengal who is believed to have ruled between 590 AD to 625 AD, had his capital at Karnasubarna, south-west of Baharampur, headquarters of Murshidabad district. The Chinese monk, Xuanzang (Hiuen Tsang) travelled from the country of Karnasubarna to a region in Orissa ruled by Shashanka. There is mention of Pundravardhana being part of Gauda in certain ancient records. Bandopadhyay, Rakhaldas, ''Bangalar Itihas'', , first published 1928, revised edition 1971, vol I, p 101, Nababharat Publishers, 72 Mahatma Gandhi Road, Kolkata. Evidence seems to be discrepant regarding link ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was an Early modern period, early modern empire in South Asia. At its peak, the empire stretched from the outer fringes of the Indus River Basin in the west, northern Afghanistan in the northwest, and Kashmir in the north, to the highlands of present-day Assam and Bangladesh in the east, and the uplands of the Deccan Plateau in South India.. Quote: "The realm so defined and governed was a vast territory of some , ranging from the frontier with Central Asia in northern Afghanistan to the northern uplands of the Deccan plateau, and from the Indus basin on the west to the Assamese highlands in the east." The Mughal Empire is conventionally said to have been founded in 1526 by Babur, a Tribal chief, chieftain from what is today Uzbekistan, who employed aid from the neighboring Safavid Iran, Safavid and Ottoman Empires Quote: "Babur then adroitly gave the Ottomans his promise not to attack them in return for their military aid, which he received in the form of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akbar
Akbar (Jalal-ud-din Muhammad Akbar, – ), popularly known as Akbar the Great, was the third Mughal emperor, who reigned from 1556 to 1605. Akbar succeeded his father, Humayun, under a regent, Bairam Khan, who helped the young emperor expand and consolidate Mughal domains in the Indian subcontinent. He is generally considered one of the greatest emperors in Indian history and led a successful campaign to unify the various kingdoms of '' Hindūstān'' or India proper. Quote: "Akbar, The greatest Mughal emperor of India." Akbar gradually enlarged the Mughal Empire to include much of the Indian subcontinent through Mughal military, political, cultural, and economic dominance. To unify the vast Mughal state, Akbar established a centralised system of administration and adopted a policy of conciliating conquered rulers through marriage and diplomacy. To preserve peace and order in a religiously and culturally diverse empire, he adopted policies that won him the support of his no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hussain Shahi Dynasty
The Hussain Shahi dynasty was a family which ruled the late medieval Sunni Muslim Sultanate of Bengal from 1494 to 1538. History The dynasty's founder, Alauddin Husain Shah was possibly of Sayyid Arab, or even Afghan origin. He is considered as the greatest of all the sultans of Bengal for bringing a cultural renaissance during his reign. Known as the Akbar of Bengal, Husain Shah was known by the Hindus of Bengal as Nripati Tilak and Jagatbhusan. He encouraged the translation of Sanskrit literature into the Bengali language and built the Chota Sona Masjid. He conquered Kamrup-Kamata and Orissa and extended the Sultanate all the way to the port of Chittagong, which witnessed the arrival of the first Portuguese merchants. His supposed heir, Shahzada Danyal, who he had appointed as the governor of Kamata, was executed by rebellious chieftains in Assam. Husain Shah's son and successor, Nasiruddin Nasrat Shah, gave refuge to the Afghans during the invasion of the Timurid wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mahananda River
The Mahananda ( ) is a trans-boundary river that flows through the Indian states of Bihar and West Bengal before crossing into Bangladesh. It is an important tributary of the Ganges. Course The Mahananda river system consists of two streams- one is locally known as Fulahar river and the other Mahananda. The Fulahar originates in the Himalayas in Nepal and traverses through the Indian state of Bihar and merges with the Ganges in left opposite to Rajmahal. The Mahananda originates in the Himalayas: Paglajhora Falls on Mahaldiram Hill near Chimli, east of Kurseong in Darjeeling district at an elevation of . It flows through Mahananda Wildlife Sanctuary and descends to the plains near Siliguri. It touches Jalpaiguri district. It enters Bangladesh near Tentulia in Panchagarh District, flows for after Tentulia and returns to India. After flowing through Uttar Dinajpur district in West Bengal and Kishanganj, Purnia and Katihar districts in Bihar, it enters Malda distric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ganges
The Ganges ( ; in India: Ganga, ; in Bangladesh: Padma, ). "The Ganges Basin, known in India as the Ganga and in Bangladesh as the Padma, is an international which goes through India, Bangladesh, Nepal and China." is a trans-boundary river of Asia which flows through India and Bangladesh. The river rises in the western Himalayas in the States and union territories of India, Indian state of Uttarakhand. It flows south and east through the Gangetic Plain, Gangetic plain of North India, receiving the right-bank tributary, the Yamuna, which also rises in the western Indian Himalayas, and several left-bank tributaries from Nepal that account for the bulk of its flow. In West Bengal state, India, a feeder canal taking off from its right bank diverts 50% of its flow southwards, artificially connecting it to the Hooghly River. The Ganges continues into Bangladesh, its name changing to the Padma River, Padma. It is then joined by the Jamuna River (Bangladesh), Jamuna, the lower str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pandua, Malda
Pandua, also historically known as Hazrat Pandua and later Firuzabad, is a ruined city in the Malda district of the Indian state of West Bengal. It served as the capital city of the independent Sultanate of Bengal for nearly a century, until the capital was moved to nearby Lakhnauti in 1450. Geography Location Pandua is located at . Overview Pandua is now almost synonymously known as Adina, a small town located about 18 km North of English Bazar (or Malda Town). Pandua is a historic city of the Indian subcontinent. It was the first capital city of the Bengal Sultanate for 114 years (1339 - 1453). It continued to be a " Mint town" until the 16th-century. The capital later shifted to Gaur. Pandua was described by travelers as a cosmopolitan administrative, commercial and military base, with a population of natives, royalty, aristocrats and foreigners from across Eurasia. Pandua was a lost city until it was rediscovered by Francis Buchanan-Hamilton in 1808. A detaile ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ilyas Shahi Dynasty
The Ilyas Shahi dynasty (, ) was the first independent dynasty to set the foundations of the late medieval Sunni Muslim Sultanate of Bengal. Their rule extended from 1342 to 1487, though interrupted with interregna by their slaves as well as the House of Ganesha. Initial dynasty The ancestors of Ilyas Shah originated from Sistan, and according to Syed A M R Haque, arrived in the subcontinent as Muslim missionaries and the family were granted jagirs in Bengal in the year 1227. Bengal was under the Delhi Sultanate at the time. During the governorship of Izz al-Din Yahya in Satgaon, Shamsuddin Ilyas Shah took service under him. Following Yahya's death in 1338, Ilyas Shah took control of Satgaon and declared himself as a Sultan, independent of Delhi. He then waged a campaign, defeating both the Sultans Alauddin Ali Shah and Ikhtiyaruddin Ghazi Shah of Lakhnauti and Sonargaon respectively by 1342. This led to the foundation of Bengal as a single political entity and the start ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
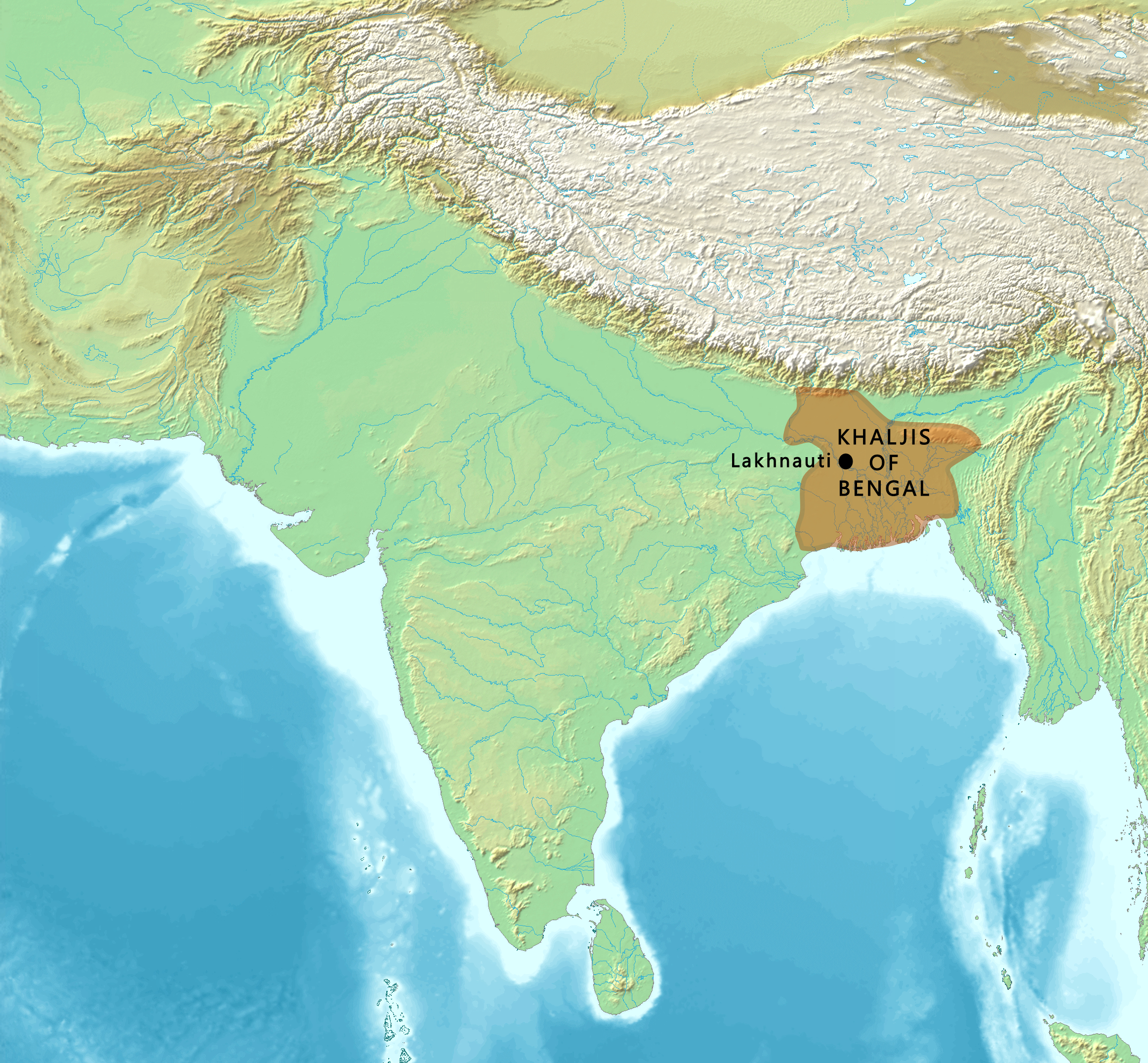
Muhammad Bin Bakhtiyar Khalji
Ikhtiyār al-Dīn Muḥammad Bin Bakhtiyār Khaljī, also known as Bakhtiyar Khalji, was a Turko-Afghan Military General of the Ghurid ruler Muhammad of Ghor, who led the Muslim conquests in the Indian subcontinent, Muslim conquests of the eastern Indian regions of Bengal and parts of Bihar and established himself as their deputy-ruler/governor, He was the founder of the Khalji dynasty of Bengal, ruling Bengal for a short period, from 1203 to 1227 CE. Khalji's invasions of the Indian subcontinent between A.D. 1197 and 1206 led to mass flight and massacres of monks, and caused damage to the traditional Buddhist institutions of higher learning in Northern India. In Bengal, Khalji's reign was responsible for the displacement of Buddhism. The leading centre of teaching for Mahayana Buddhism was Nalanda mahavihara, Nalanda. At the end of the 12th century, Bakhityar Khalji demolished the monastery in a brutal sacking . His rule is said to have begun the Muslim rule in India, Muslim r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |