|
Ballochney Railway
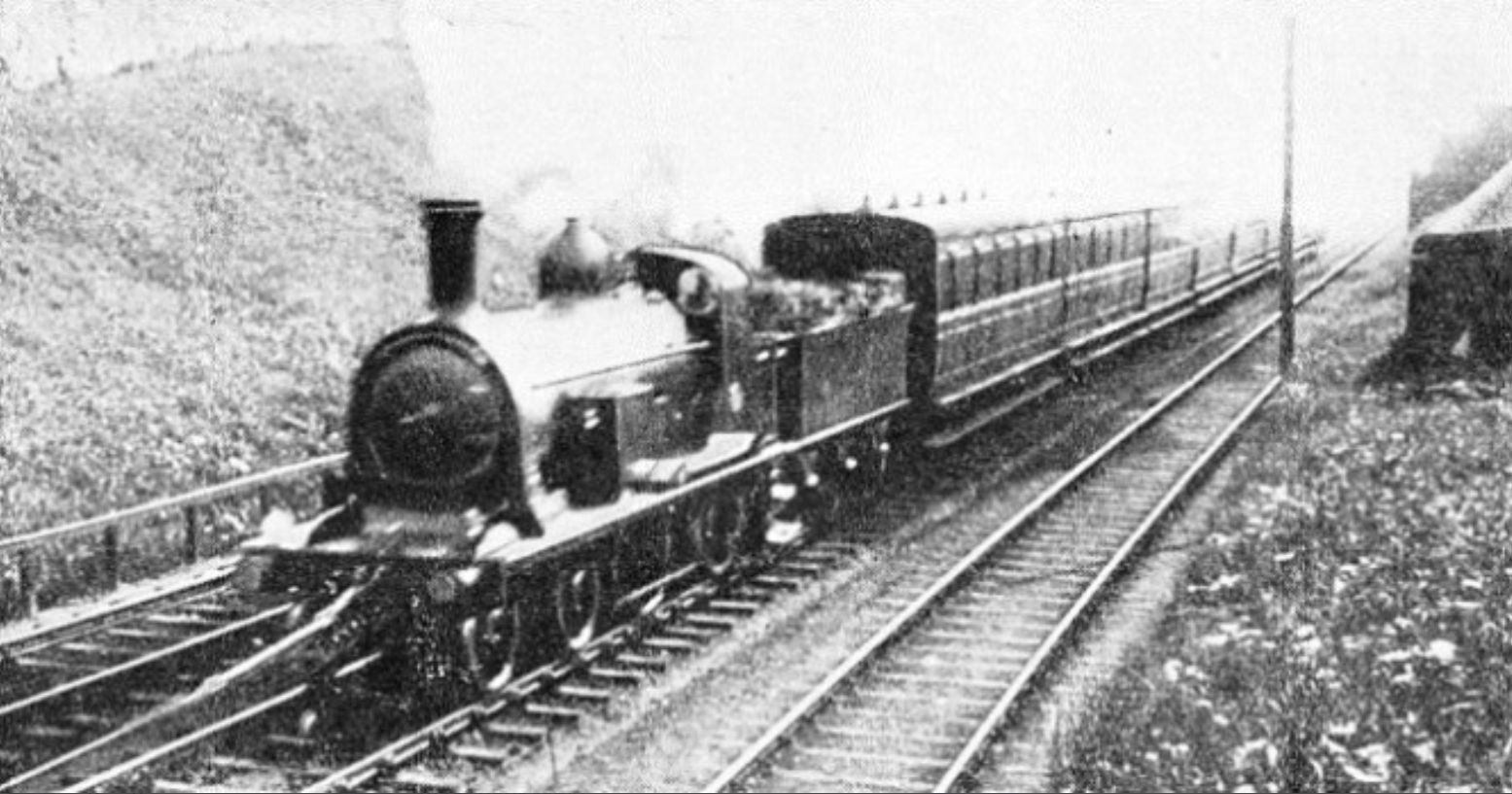
The Ballochney Railway was an early railway built near Airdrie, North Lanarkshire, Scotland. It was intended primarily to carry minerals from coal and ironstone pits, and stone quarries, in the area immediately north and east of Airdrie, to market, predominantly over the adjoining Monkland and Kirkintilloch Railway. Passengers were carried later. Trains were pulled by horses at first, although locomotives were employed later on. The mineral extraction was located in high ground and rope-worked inclines were incorporated into the line to bring loaded wagons down. The line used the track gauge of , which was already in use on the Monkland and Kirkintilloch line. It opened in 1828, and in 1848 it amalgamated with two associated railways, forming the Monkland Railways. All of the route is now closed, although much of it can still be discovered. Origins In 1794 the Monkland Canal was completed, enabling the cheap transport of coal from the Monklands coalfields, south of Airdrie, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Airdrie, North Lanarkshire
Airdrie (; ; ) is a town in North Lanarkshire, Scotland. It lies on a plateau 400 ft (130 m) above sea level, 12 miles (19 km) east of Glasgow. , it had a population of 37,130. Airdrie developed as a market town in the late 17th century following an act of Parliament allowing it to hold a weekly market. It later grew in prominence as a centre for weaving and manufacturing, as well as being the settlement near several coalmines. In the mid 19th century, the town expanded greatly as a result of immigration and the development of iron works and railway links. The first public library in Scotland was established in Airdrie in 1853. During the 20th century, industrial decline took place in Airdrie, with heavy industry closing down across much of the town. In the 21st century, Airdrie has continued as a regional centre for services and retail, as well as being a commuter settlement within the Central Belt. Historically part of Lanarkshire, Airdrie forms a conurbation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Airdrie Leaend Railway Station
Airdrie Leaend railway station served the town of Airdrie, North Lanarkshire Airdrie (; ; ) is a town in North Lanarkshire, Scotland. It lies on a plateau 400 ft (130 m) above sea level, 12 miles (19 km) east of Glasgow. , it had a population of 37,130. Airdrie developed as a market town in the late 17th ce ..., Scotland from 1828 to 1843 on the Hallcraig Street branch. History The station opened on 8 August 1828 by the Monkland Railways. It was situated on a siding. Garden Square was built in 1830, which was a local village for railway workers. The station closed in 1843. Nothing remains. References {{Reflist Disused railway stations in North Lanarkshire Railway stations in Great Britain opened in 1828 Railway stations in Great Britain closed in 1843 1828 establishments in Scotland 1843 disestablishments in Scotland ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edinburgh And Glasgow And Monkland Railways Amalgamation Act 1865
The Monkland Railways was a railway company formed in 1848 by the merger of three "coal railways" that had been built to serve coal and iron pits around Airdrie in Central Scotland, and connect them to canals for onward transport of the minerals. The newly formed company had a network stretching from Kirkintilloch to Causewayend, near Linlithgow. These coal railways had had mixed fortunes; the discovery of blackband ironstone and the development of the iron smelting industry around Coatbridge had led to phenomenal success, but hoped-for mineral discoveries in the moorland around Slamannan had been disappointing. The pioneering nature of the railways left them with a legacy of obsolete track and locomotives, and new, more modern, railways were being built around them. The new company responded with connections to other lines, and to Bo'ness Harbour, and built new lines to Bathgate, but it was taken over by the Edinburgh and Glasgow Railway in 1865. Much of the network was dependen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
11 & 12 Vict
Eleven or 11 may refer to: *11 (number) * One of the years 11 BC, AD 11, 1911, 2011 Literature * ''Eleven'' (novel), a 2006 novel by British author David Llewellyn *''Eleven'', a 1970 collection of short stories by Patricia Highsmith *''Eleven'', a 2004 children's novel in The Winnie Years by Lauren Myracle *''Eleven'', a 2008 children's novel by Patricia Reilly Giff *''Eleven'', a short story by Sandra Cisneros Music * Eleven (band), an American rock band * Eleven: A Music Company, an Australian record label *Up to eleven, an idiom from popular culture, coined in the movie ''This Is Spinal Tap'' Albums * ''11'' (The Smithereens album), 1989 * ''11'' (Ua album), 1996 * ''11'' (Bryan Adams album), 2008 * ''11'' (Sault album), 2022 * ''Eleven'' (Harry Connick, Jr. album), 1992 * ''Eleven'' (22-Pistepirkko album), 1998 * ''Eleven'' (Sugarcult album), 1999 * ''Eleven'' (B'z album), 2000 * ''Eleven'' (Reamonn album), 2010 * ''Eleven'' (Martina McBride album), 2011 * ''Eleven'' (Mr F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monkland Railways Act 1848
The Monkland Railways was a railway company formed in 1848 by the merger of three "coal railways" that had been built to serve coal and iron pits around Airdrie in Central Scotland, and connect them to canals for onward transport of the minerals. The newly formed company had a network stretching from Kirkintilloch to Causewayend, near Linlithgow. These coal railways had had mixed fortunes; the discovery of blackband ironstone and the development of the iron smelting industry around Coatbridge had led to phenomenal success, but hoped-for mineral discoveries in the moorland around Slamannan had been disappointing. The pioneering nature of the railways left them with a legacy of obsolete track and locomotives, and new, more modern, railways were being built around them. The new company responded with connections to other lines, and to Bo'ness Harbour, and built new lines to Bathgate, but it was taken over by the Edinburgh and Glasgow Railway in 1865. Much of the network was dependen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
9 & 10 Vict
9 (nine) is the natural number following and preceding . Evolution of the Hindu–Arabic digit Circa 300 BC, as part of the Brahmi numerals, various Indians wrote a digit 9 similar in shape to the modern closing question mark without the bottom dot. The Kshatrapa, Andhra and Gupta started curving the bottom vertical line coming up with a -look-alike. How the numbers got to their Gupta form is open to considerable debate. The Nagari continued the bottom stroke to make a circle and enclose the 3-look-alike, in much the same way that the sign @ encircles a lowercase ''a''. As time went on, the enclosing circle became bigger and its line continued beyond the circle downwards, as the 3-look-alike became smaller. Soon, all that was left of the 3-look-alike was a squiggle. The Arabs simply connected that squiggle to the downward stroke at the middle and subsequent European change was purely cosmetic. While the shape of the glyph for the digit 9 has an ascender in most modern typ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wishaw And Coltness Railway
The Wishaw and Coltness Railway was an early Scottish mineral railway. It ran for approximately from Chapel Colliery, at Newmains in North Lanarkshire connecting to the Monkland and Kirkintilloch Railway near Whifflet, giving a means of transport for minerals around Newmains to market in Glasgow and Edinburgh. Shortage of capital made construction slow, and the line was opened in stages from 1833, opening fully on 9 March 1844. It was built to the track gauge of , commonly used in Scotland for coal railways. It had several branches serving pits and ironworks. In 1849 it became part of the Caledonian Railway and sections of the original network form part of the modern West Coast Main Line railway. Formation of the railway In the early decades of the nineteenth century, the pace of industrialisation in central Scotland accelerated considerably, generating a huge demand for the raw materials of coal and iron ore. Transport of these heavy materials to market was a key issue. Canal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Airdrie Hallcraig Street Railway Station
Airdrie Hallcraig Street railway station served the town of Airdrie, North Lanarkshire, Scotland from 1844 to 1871 on the Hallcraig Street branch. History The station opened on 26 December 1844 by the North British Railway The North British Railway was one of the two biggest of the five major Scottish railway companies prior to the 1923 Grouping. It was established in 1844, with the intention of linking with English railways at Berwick. The line opened in 1846, .... It closed on 1 June 1871 but remained open as a goods station until 1964. Nothing remains today. References External links Disused railway stations in North Lanarkshire Former North British Railway stations Railway stations in Great Britain opened in 1844 Railway stations in Great Britain closed in 1871 1844 establishments in Scotland 1871 disestablishments in Scotland {{NorthLanarkshire-railstation-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edinburgh And Glasgow Railway
The Edinburgh and Glasgow Railway was authorised by act of Parliament on 4 July 1838. It was opened to passenger traffic on 21 February 1842, between its Glasgow Queen Street railway station (sometimes referred to at first as Dundas Street) and Haymarket railway station in Edinburgh. Construction cost £1,200,000 for 46 miles (74 km). The intermediate stations were at Corstorphine (later Saughton), Gogar, Ratho, Winchburgh, Linlithgow, Polmont, Falkirk, Castlecary, Croy, Kirkintilloch (later Lenzie) and Bishopbriggs. There was a ticket platform at Cowlairs. The line was extended eastwards from Haymarket to North Bridge in 1846, and a joint station for connection with the North British Railway was opened on what is now Edinburgh Waverley railway station in 1847. Patronage on the line quickly reached double the railway's initial estimates, and by 1850 58 locomotives and 216 coaches were needed to handle the traffic. Goods traffic started in March 1842 and slo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Union Canal (Scotland)
The Union Canal, full name the Edinburgh and Glasgow Union Canal, is a canal in Scotland, running from Falkirk to Edinburgh, constructed to bring minerals, especially coal, to the capital. It was opened in 1822 and was initially successful, but the construction of railways, particularly the Edinburgh and Glasgow Railway, which opened in 1842, diminished its value as a transport medium. It fell into slow commercial decline and was closed to commercial traffic in 1933. It was officially closed in 1965. The canal is listed as three individual scheduled monuments by Historic Scotland according to the three former counties, Midlothian, West Lothian and Stirlingshire, through which it flows. It has benefited from a general revival of interest in canals and, as a result of the Millennium Link, was reopened in 2001 and reconnected to the Forth and Clyde Canal in 2002 by the Falkirk Wheel. It is now in popular use for leisure purposes. History Proposal The canal was conceived ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stockton And Darlington Railway
The Stockton and Darlington Railway (S&DR) was a railway company that operated in north-east England from 1825 to 1863. The world's first public railway to use steam locomotives, its first line connected coal mining, collieries near with and in County Durham, and was officially opened on 27 September 1825. The movement of coal to ships rapidly became a lucrative business, and the line was soon extended to a at Middlesbrough. While coal waggons were hauled by steam locomotives from the start, passengers were carried in coaches drawn by horses until carriages hauled by steam locomotives were introduced in 1833. The S&DR was involved in building the East Coast Main Line between and Darlington, but its main expansion was at Middlesbrough Docks and west into Weardale and east to Redcar. It suffered severe financial difficulties at the end of the 1840s and was nearly taken over by the York, Newcastle and Berwick Railway, before the discovery of iron ore in Cleveland, Yorkshi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |