|
Baldo Lupetina
Baldo Lupetino (also ''Lupatino'' and ''Baldo d'Albona'') (1502 – 1556) was an Istrian Italian Venetian Protestant preacher. Biography He was born in Albona (now Labin), in Istria. Lupetino's family belonged to the local old patriciate, and was related by marriage to the Luciani family. There is a Slavicized, modern Croatian form of his surname, ''Lupatina''. This form does not appear in contemporary sources from the 16th century. His sister Giovanna married Luciano Luciani, the brother of Jacobea Luciani, mother of Matthias Flacius Illyricus. He entered the Franciscan order in his hometown, and was ordained a priest. He entered the convent when he was but 14 years old, being immediately noted by his ability to preach in both Italian and Chakavian. By the end of the 1530s he had probably already embraced the Reformation, based on the fact that he urged Flacius to go study in Germany instead of Venice. At this time, Baldo reportedly introduced Flacius to the Reformation movem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Jeffries Martin
John Jeffries Martin (born August 1, 1951) is a historian of early modern Europe, with a special interest in the histories of religion and society in the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries. Early life John Jeffries Martin grew up on St. Simons Island, Georgia and attended St. Paul's School in Concord, New Hampshire. He earned a PhD from Harvard University in 1982. Career Martin is professor and former chair of History at Duke University . He also served as chair of History at Trinity University where he taught from 1982 to 2007. Martin's publications have explored the histories of sixteenth-century Venice, the invention of sincerity, Renaissance individualism, and early modern apocalypticism. He is, in addition, the editor or co-editor of four volumes. In ''Venice’s Hidden Enemies: Italian Heretics in a Renaissance City'', Martin writes about the European Protestants who moved to Venice and were falsely accused of heresy by Venetians in the sixteenth century. Reviewing it f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enciclopedia Italiana
Institute Giovanni Treccani for the publication of the Italian Encyclopedia (), also known as Treccani Institute or simply Treccani, is a cultural institution of national interest, active in the publishing field, founded by Giovanni Treccani and Giovanni Gentile in 1925. It is known for publishing the first edition and the subsequent ten supplements of the ''Italian Encyclopaedia of Science, Literature and Arts'' (). History The Institute of the Italian Encyclopaedia was founded in Rome in 1925 by Giovanni Treccani, with the philosopher Giovanni Gentile as editor-in-chief. The first publication by the Institute was the ''Enciclopedia Italiana di Scienze, Lettere e Arti'' (). This encyclopaedia, best known as ''Enciclopedia Italiana'' or the ''Great Encyclopaedia'', is an Italian-language encyclopaedia and is regarded as one of the great encyclopaedias, being international in scope, alongside ''Encyclopædia Britannica'' and others. Since the 1990s, Treccani has been playing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People From Labin
The term "the people" refers to the public or common mass of people of a polity. As such it is a concept of human rights law, international law as well as constitutional law, particularly used for claims of popular sovereignty. In contrast, a people is any plurality of persons considered as a whole. Used in politics and law, the term "a people" refers to the collective or community of an ethnic group or nation. Concepts Legal Chapter One, Article One of the Charter of the United Nations states that "peoples" have the right to self-determination. Though the mere status as peoples and the right to self-determination, as for example in the case of Indigenous peoples (''peoples'', as in all groups of indigenous people, not merely all indigenous persons as in ''indigenous people''), does not automatically provide for independent sovereignty and therefore secession. Indeed, judge Ivor Jennings identified the inherent problems in the right of "peoples" to self-determination, as i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1556 Deaths
Year 1556 ( MDLVI) was a leap year starting on Wednesday of the Julian calendar. Events January–March * January 4 – In Japan, Saitō Yoshitatsu, the eldest son of Saitō Dōsan, arranges the murders of his two younger brothers, Magoshiro and Kiheiji, and forces his father to flee from the Sagiyama Castle. * January 16 – Charles V abdicates the thrones of the Spanish Empire (including his colonies in the New World) in favor of his son, Philip II, and retires to a monastery. * January 23 – The Shaanxi earthquake, the deadliest earthquake in history, occurs with its epicenter in Shaanxi province, China; 830,000 people may have been killed. * January 24 – In India, at the Sher Mandal in Delhi, the Mughal Emperor Humayun trips while descending the stairs from his library and strikes the side of his head against a stone step, sustaining a fatal injury. He never regains consciousness and dies seven days later. * February 5 – Truce of Vau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1502 Births
Year 1502 ( MDII) was a common year starting on Saturday of the Julian calendar. Events January–March * January 1 – Portuguese explorers, led by Gonçalo Coelho, sail into Guanabara Bay, Brazil, mistaking it for the mouth of a river, which they name Rio de Janeiro. * January 24 – Commissioners from Scotland and England meet at Richmond Palace in London to finalize an agreement on the marriage between Scotland's King James IV to the daughter of England's King Henry VII, the princess Margaret Tudor, with a dowry of 35,000 Scottish Punnds and an agreement for a "treaty of perpetual peace". The marriage will be completed by proxy on January 25, 1503. * February 12 – Isabella I issues an edict outlawing Islam in the Crown of Castile, forcing virtually all her Muslim subjects to convert to Christianity. * February 13 – The new Viceroy of the New World, Nicolás de Ovando, departs Spain with a fleet of 30 ships and orders to replace Viceroy Franc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schmalkaldic League
The Schmalkaldic League (; ; or ) was a military alliance of Lutheranism, Lutheran Prince of the Holy Roman Empire, principalities and cities within the Holy Roman Empire during the mid-16th century. It received its name from the town of Schmalkalden, where the group was founded in 1531. Although created for religious motives soon after the start of the Reformation, its members later came to have the intention that the League would replace the Holy Roman Empire as their focus of political allegiance. While it was not the first alliance of its kind, unlike previous formations, such as the League of Torgau, the Schmalkaldic League had a substantial military to defend its political and religious interests. Origins The League was officially established on 27 February 1531 by Philip I, Landgrave of Hesse, and John Frederick I, Elector of Saxony, the two most powerful Protestant rulers in the Holy Roman Empire at the time. It originated as a defensive religious alliance, with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wittenberg
Wittenberg, officially Lutherstadt Wittenberg, is the fourth-largest town in the state of Saxony-Anhalt, in the Germany, Federal Republic of Germany. It is situated on the River Elbe, north of Leipzig and south-west of the reunified German federal capital city of Berlin, and has a population of 46,008 (2018). Wittenberg has close connections with Martin Luther (1483–1546) and the 16th century religious / theological movement of Protestantism begun here in the Reformation, and the large branch of Western Christianity started here of Lutheranism, Evangelical Lutheranism, for which it received the honorific title ''Lutherstadt'' and has been called the "cradle of the Reformation" and "cradle of Protestantism". Several of Wittenberg's buildings are associated with the historical / religious events, including a preserved part of the Augustinians, Augustinian monastery of the local community of the world-wide Catholic Church, Roman Catholic Order of St. Augustine in which Luth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lent
Lent (, 'Fortieth') is the solemn Christianity, Christian religious moveable feast#Lent, observance in the liturgical year in preparation for Easter. It echoes the 40 days Jesus spent fasting in the desert and enduring Temptation of Christ, temptation by Satan, according to the Gospels of Gospel of Matthew, Matthew, Gospel of Mark, Mark and Gospel of Luke, Luke, before beginning his Ministry of Jesus, public ministry. Lent is usually observed in the Catholic Church, Catholic, Lutheranism, Lutheran, Moravian Church, Moravian, Anglican Communion, Anglican, United and uniting churches, United Protestant and Eastern Orthodoxy, Orthodox Christian traditions, among others. A number of Anabaptism, Anabaptist, Baptists, Baptist, Methodism, Methodist, Calvinism, Reformed (including certain Continental Reformed Protestantism, Continental Reformed, Presbyterianism, Presbyterian and Congregational church, Congregationalist churches), and Nondenominational Christianity, nondenominational Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cres
Cres is an Adriatic island in Croatia. It is one of the northern islands in the Kvarner Gulf and can be reached via ferry from Rijeka, Krk island or from the Istrian peninsula (line Brestova-Porozina). With an area of , Cres has the same size as the neighbouring Krk island. In 2011, Cres had a population of 3,079 people. In the past, Cres and the neighbouring island of Lošinj used to be one island, but now they are divided by a channel and connected by a bridge that starts from the town of Osor, Croatia, Osor. Cres's only freshwater source is Lake Vrana (Cres), Lake Vrana. History Cres has been inhabited since the Paleolithic time period. In ancient times, Cres and Lošinj were called Absyrtides, Apsyrtides. In the past, the two islands were connected, but due to the needs of trade, these islands were separated by an Artificiality, artificially dug canal near Osor. Its name predates classical antiquity and derives from Proto-Indo-European language, Proto-Indo-European '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franciscus Patricius
Franciscus Patricius (Croatian language, Croatian: ''Franjo Petriš'' or ''Frane Petrić''; Italian language, Italian: ''Francesco Patrizi''; 25 April 1529 – 6 February 1597) was a philosopher and scientist from the Republic of Venice, originating from Cres. He was known as a defender of Platonism and an opponent of Aristotelianism. His national origin differs in sources, and he is described both as Croatian and as Italian. In Croatia he is mostly referred to as Franjo Petriš or Frane Petrić (sometimes ''Petris'', ''Petrišević'' and ''Petričević''). His family name in Cres was known as Petris. Patricius initially dedicated his studies to Aristotelianism, Aristotelian Philosophy at the University of Padua, but turned to Platonism while still a student. He became a sharp, high-profile opponent of Aristotelianism, with whom he grappled extensively in extensive writings. After many years of unsuccessful efforts to secure material livelihood, he finally received an invitat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Croatian Encyclopedia
The ''Croatian Encyclopedia'' () is a Croatian general encyclopedia An encyclopedia is a reference work or compendium providing summaries of knowledge, either general or special, in a particular field or discipline. Encyclopedias are divided into article (publishing), articles or entries that are arranged Alp ... (with the national component), published in 1999–2009 by the Miroslav Krleža Institute of Lexicography. Overview The project began in 1999, and it represents a fifth iteration of the encyclopedic tradition that was established by Mate Ujević's ''Croatian Encyclopedia'', and continued in the '' Encyclopedia of the Lexicographical Institute'', as well as the two editions of its ''General Encyclopedia''. Eleven volumes were published in the period 1999–2009, with a new volume appearing every year. It is named "Croatian" encyclopedia (colloquially ''Croatica'') in the tradition of general-knowledge encyclopedias as ''Britannica''. Online edition The f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
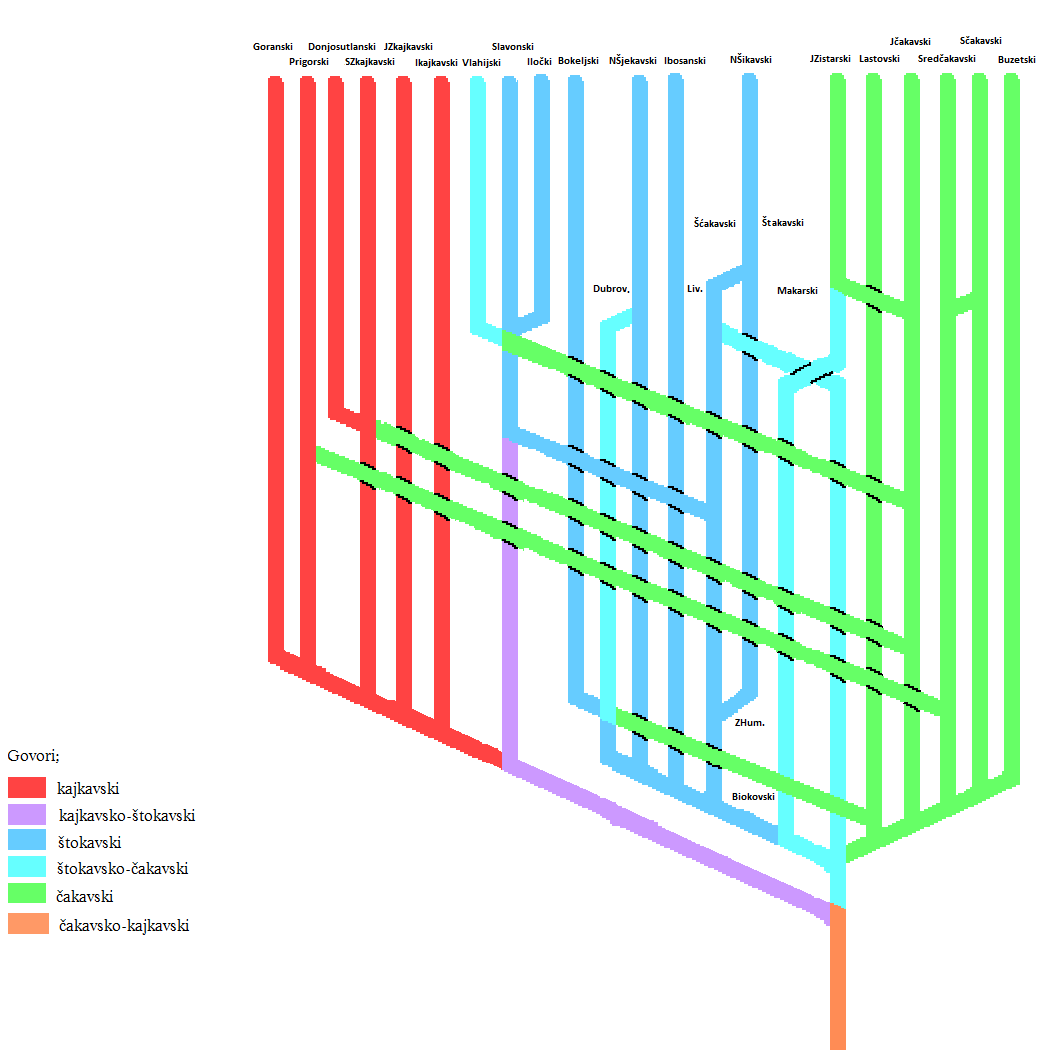
Chakavian
Chakavian or Čakavian (, , , proper name: or own name: ''čokovski, čakavski, čekavski'') is a South Slavic supradialect or language spoken by Croats along the Adriatic coast, in the historical regions of Dalmatia, Istria, Croatian Littoral and parts of coastal and southern Central Croatia (now collectively referred to as Adriatic Croatia or Littoral Croatia), as well as by the Burgenland Croats as Burgenland Croatian in southeastern Austria, northwestern Hungary and southwestern Slovakia as well as few municipalities in southern Slovenia on the border with Croatia. Chakavian represents the basis for early literary standards in Croatia, and until the modern age was simply known and understood, along with the Kajkavian and Shtokavian idioms in Croatia, as the Croatian language (''hrvatski jezik''). Legal and liturgical to literary texts until the 16th century, including literary work by "the father of Croatian literature" Marko Marulić and the first Croatian dictionar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |