|
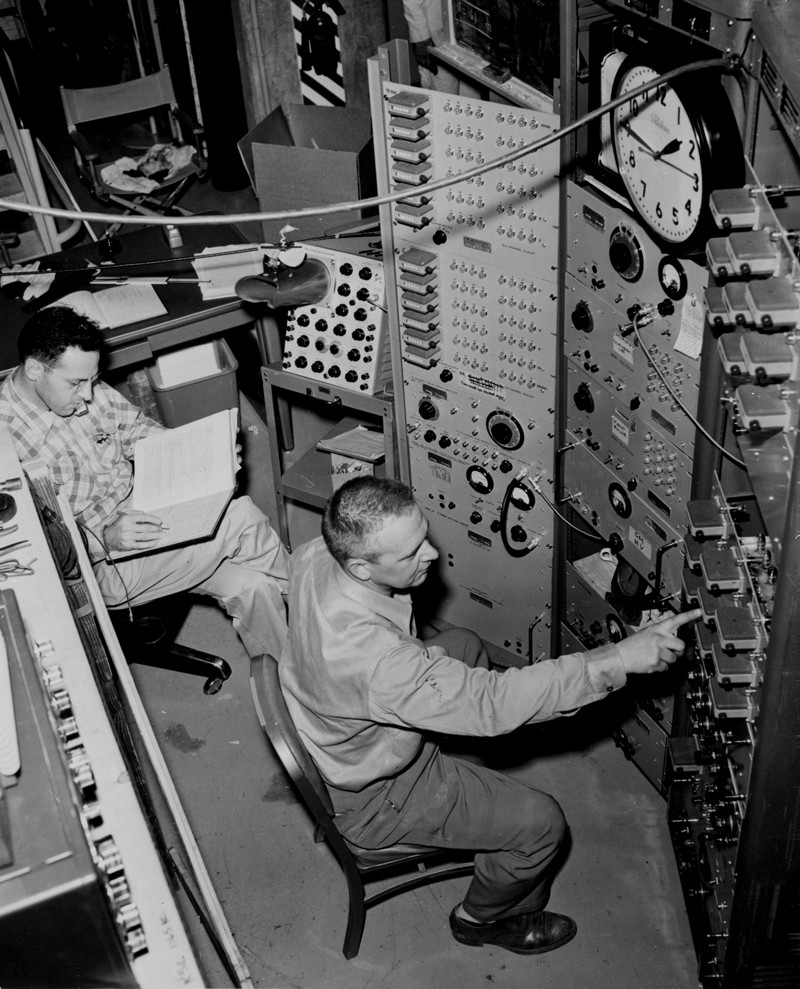
Baksan Underground Scintillator Telescope
The Baksan Neutrino Observatory (BNO; Baksan is sometimes spelled Baxan) is a scientific laboratory of Institute for Nuclear Research, INR RAS located in the Baksan River gorge in the Caucasus mountains in Russia. Cleared for building in 1967, it started operations in 1977, becoming the first such neutrino observatory in the USSR. It consists of the Baksan Underground Scintillation Telescope (BUST), located below the surface, the gallium–germanium neutrino telescope (Soviet–American Gallium Experiment, SAGE (Soviet–American Gallium Experiment), SAGE) located 4,700 Meter water equivalent, m.w.e. deep (2,100 meters) as well as a number of ground facilities. The Baksan Experiment on Sterile Transitions (SAGE (Soviet–American Gallium Experiment), BEST) is currently (2019) being conducted at Baksan with aims of understanding sterile neutrinos. The laboratory itself is located in a 4,000 meter long horizontal tunnel mined specifically for this purpose; this is in contrast to mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Institute For Nuclear Research
Institute for Nuclear Research of the Russian Academy of Sciences (INR RAS, russian: Институт ядерных исследований) is a Russian scientific research center "for further development of the experimental base and fundamental research activities in the field of atomic nucleus, elementary particle and cosmic ray physics and neutrino astrophysics". It was founded in 1970 by the Decree of the USSR Council of Ministers. Located in Moscow, Russia near the Moscow State University and in Troitsk, Moscow Oblast, Troitsk. The institute is a founder of the Baksan Neutrino Observatory, the Baikal Deep Underwater Neutrino Telescope (Lake Baikal) and the former Artemovskaya Scientific Station (Soledar, Ukraine). About 1,300 specialists including 5 academicians and 2 corresponding members of the RAS, 42 doctors and 160 candidates of science work in the institute. Directors * Albert Tavkhelidze, Albert Nikiforovich Tavkhelidze, academician of RAS (1970–1986) * Vikto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SAGE (Soviet–American Gallium Experiment)
Sage or SAGE may refer to: Plants * ''Salvia officinalis'', common sage, a small evergreen subshrub used as a culinary herb ** Lamiaceae, a family of flowering plants commonly known as the mint or deadnettle or sage family ** ''Salvia'', a large genus commonly referred to as sage, containing the common sage * ''Leucophyllum'', a genus of evergreen shrubs in the figwort family, often called sages * ''Artemisia'' (plant), a genus of shrubs in the composite family, includes several members referred to as sage or sagebrush Arts, entertainment and media Fictional characters * Sage (comics), in Marvel comics * Sage (''Dark Oracle''), in the Canadian TV series * Sage, in the TV show '' Hot Wheels Battle Force 5'' * Sage, a ''Shuffle!'' character * Sage, in ''The Vampire Diaries'' (season 3) * Sage the Owl, in '' The Herbs'' * The Sage, in the '' Groo the Wanderer'' comics * Sages, characters of ''The Legend of Zelda'' * Toad Sage and the Sage of the Six Paths, ''Naruto'' characte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomical Observatories Built In The Soviet Union
Astronomy () is a natural science that studies celestial objects and phenomena. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and evolution. Objects of interest include planets, moons, stars, nebulae, galaxies, and comets. Relevant phenomena include supernova explosions, gamma ray bursts, quasars, blazars, pulsars, and cosmic microwave background radiation. More generally, astronomy studies everything that originates beyond Earth's atmosphere. Cosmology is a branch of astronomy that studies the universe as a whole. Astronomy is one of the oldest natural sciences. The early civilizations in recorded history made methodical observations of the night sky. These include the Babylonians, Greeks, Indians, Egyptians, Chinese, Maya, and many ancient indigenous peoples of the Americas. In the past, astronomy included disciplines as diverse as astrometry, celestial navigation, observational astronomy, and the making of calendars. Nowadays, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Research Institutes In Russia
Research is "creative and systematic work undertaken to increase the stock of knowledge". It involves the collection, organization and analysis of evidence to increase understanding of a topic, characterized by a particular attentiveness to controlling sources of bias and error. These activities are characterized by accounting and controlling for biases. A research project may be an expansion on past work in the field. To test the validity of instruments, procedures, or experiments, research may replicate elements of prior projects or the project as a whole. The primary purposes of basic research (as opposed to applied research) are documentation, discovery, interpretation, and the research and development (R&D) of methods and systems for the advancement of human knowledge. Approaches to research depend on epistemologies, which vary considerably both within and between humanities and sciences. There are several forms of research: scientific, humanities, artistic, econ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutrino Observatories
A neutrino ( ; denoted by the Greek letter ) is a fermion (an elementary particle with spin of ) that interacts only via the weak interaction and gravity. The neutrino is so named because it is electrically neutral and because its rest mass is so small ('' -ino'') that it was long thought to be zero. The rest mass of the neutrino is much smaller than that of the other known elementary particles excluding massless particles. The weak force has a very short range, the gravitational interaction is extremely weak due to the very small mass of the neutrino, and neutrinos do not participate in the strong interaction. Thus, neutrinos typically pass through normal matter unimpeded and undetected. Weak interactions create neutrinos in one of three leptonic flavors: electron neutrinos muon neutrinos (), or tau neutrinos (), in association with the corresponding charged lepton. Although neutrinos were long believed to be massless, it is now known that there are three discrete neut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1977 Establishments In Russia
Events January * January 8 – Three bombs explode in Moscow within 37 minutes, killing seven. The bombings are attributed to an Armenian separatist group. * January 10 – Mount Nyiragongo erupts in eastern Zaire (now the Democratic Republic of the Congo). * January 17 ** 49 marines from the and are killed as a result of a collision in Barcelona harbour, Spain. * January 18 ** Scientists identify a previously unknown bacterium as the cause of the mysterious Legionnaires' disease. ** Australia's worst railway disaster at Granville, a suburb of Sydney, leaves 83 people dead. ** SFR Yugoslavia Prime minister Džemal Bijedić, his wife and 6 others are killed in a plane crash in Bosnia and Herzegovina. * January 19 – An Ejército del Aire CASA C-207C Azor (registration T.7-15) plane crashes into the side of a mountain near Chiva, on approach to Valencia Airport in Spain, killing all 11 people on board. * January 20 – Jimmy Carter is sworn in as the 39th President o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IceCube Neutrino Observatory
The IceCube Neutrino Observatory (or simply IceCube) is a neutrino observatory constructed at the Amundsen–Scott South Pole Station in Antarctica. The project is a recognized CERN experiment (RE10). Its thousands of sensors are located under the Antarctic ice, distributed over a cubic kilometre. Similar to its predecessor, the Antarctic Muon And Neutrino Detector Array (AMANDA), IceCube consists of spherical optical sensors called Digital Optical Modules (DOMs), each with a photomultiplier tube (PMT) and a single-board data acquisition computer which sends digital data to the counting house on the surface above the array. IceCube was completed on 18 December 2010. DOMs are deployed on strings of 60 modules each at depths between 1,450 and 2,450 meters into holes melted in the ice using a hot water drill. IceCube is designed to look for point sources of neutrinos in the teraelectronvolt (TeV) range to explore the highest-energy astrophysical processes. In November 2013 i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baikal Deep Underwater Neutrino Telescope
The Baikal Deep Underwater Neutrino Telescope (BDUNT) (russian: Байкальский подводный нейтринный телескоп) is a neutrino detector conducting research below the surface of Lake Baikal (Russia Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eigh ...) since 2003. The first detector was started in 1990 and completed in 1998. It was upgraded in 2005 and again starting in 2015 to build the Baikal Gigaton Volume Detector (Baikal-GVD.) BDUNT has studied neutrinos coming through the Earth with results on atmospheric muon flux. BDUNT picks up many atmospheric neutrinos created by cosmic rays interacting with the atmosphere – as opposed to cosmic neutrinos which give clues to cosmic events and are therefore of greater interest to physicists. Detector history ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supernova Neutrinos
Supernova neutrinos are weakly interactive elementary particles produced during a core-collapse supernova explosion. A massive star collapses at the end of its life, emitting of the order of 1058 neutrinos and antineutrinos in all lepton flavors. The luminosity of different neutrino and antineutrino species are roughly the same. They carry away about 99% of the gravitational energy of the dying star as a burst lasting tens of seconds. The typical supernova neutrino energies are 10–20 MeV. Supernovae are considered the strongest and most frequent source of cosmic neutrinos in the MeV energy range. Since neutrinos are generated in the core of a supernova, they play a crucial role in the star's collapse and explosion. Neutrino heating is believed to be a critical factor in supernova explosions. Therefore, observation of neutrinos from supernova provides detailed information about core collapse and the explosion mechanism. Further, neutrinos undergoing collective flavor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sterile Neutrinos
Sterile neutrinos (or inert neutrinos) are hypothetical particles (neutral leptons – neutrinos) that are believed to interact only via gravity and not via any of the other fundamental interactions of the Standard Model. The term ''sterile neutrino'' is used to distinguish them from the known, ordinary ''active neutrinos'' in the Standard Model, which carry an isospin charge of and engage in the weak interaction. The term typically refers to neutrinos with right-handed chirality (see right-handed neutrino), which may be inserted into the Standard Model. Particles that possess the quantum numbers of sterile neutrinos and masses great enough such that they do not interfere with the current theory of Big Bang Nucleosynthesis are often called neutral heavy leptons (NHLs) or heavy neutral leptons (HNLs). The existence of right-handed neutrinos is theoretically well-motivated, because the known active neutrinos are left-handed and all other known fermions have been observed with bot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meter Water Equivalent
In physics, the meter water equivalent (often ''m.w.e.'' or ''mwe'') is a standard measure of cosmic ray attenuation in underground laboratories. A laboratory at a depth of 1000 m.w.e is shielded from cosmic rays equivalently to a lab below the surface of a body of water. Because laboratories at the same depth (in meters) can have greatly varied levels of cosmic ray penetration, the m.w.e. provides a convenient and consistent way of comparing cosmic ray levels in different underground locations. Cosmic ray attenuation is dependent on the density of the material of the overburden, so the m.w.e. is defined as the product of depth and density (also known as an interaction depth). Because the density of water is , of water gives an interaction depth of . Some publications use hg/cm² instead of m.w.e., although the two units are equivalent. For example, the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant, located deep in a salt formation, achieves 1585 m.w.e. shielding. Soudan Mine, at depth is o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germanium
Germanium is a chemical element with the symbol Ge and atomic number 32. It is lustrous, hard-brittle, grayish-white and similar in appearance to silicon. It is a metalloid in the carbon group that is chemically similar to its group neighbors silicon and tin. Like silicon, germanium naturally reacts and forms complexes with oxygen in nature. Because it seldom appears in high concentration, germanium was discovered comparatively late in the discovery of the elements. Germanium ranks near fiftieth in relative abundance of the elements in the Earth's crust. In 1869, Dmitri Mendeleev predicted its existence and some of its properties from its position on his periodic table, and called the element ekasilicon. In 1886, Clemens Winkler at Freiberg University found the new element, along with silver and sulfur, in the mineral argyrodite. Winkler named the element after his country, Germany. Germanium is mined primarily from sphalerite (the primary ore of zinc), though ger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |