|
Baião (music)
Baião () or "''baiano''"ALVARENGA, Oneyda. Música popular brasileira. Porto Alegre: Globo, 1960. pág. 157 is a Northeastern Brazilian music genre and dance style based on a syncopated duple meter rhythm, based around the pulse of the zabumba, a flat, double-headed bass drum played with a mallet in one hand and a stick in the other, each striking the opposite head of the drum for alternating high and low notes, frequently accompanied by an accordion and a triangle pattern. The baião rhythm is integral to the genres of forró, repente and coco (or embolada). Baião was popularized via radio in the 1940s, reaching peak popularity in the 1950s. Description Amerindian elements include the use of flutes, later replaced by the accordion, and wooden Shaker; African-influenced baião might be accompanied by atabaque drums and include overlapping call and response singing; and European influences include the use of the triangle, Western harmony, and dance music such as the quadril ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northeast Region, Brazil
The Northeast Region of Brazil ( ) is one of the five official and political regions of the country according to the Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics. Of Brazil's twenty-six states, it comprises nine: Maranhão, Piauí, Ceará, Rio Grande do Norte, Paraíba, Pernambuco, Alagoas, Sergipe and Bahia, along with the Fernando de Noronha archipelago (formerly a separate territory, now part of Pernambuco). Chiefly known as ''Nordeste'' ("Northeast") in Brazil, this region was the first to be colonized by the Portuguese and other European peoples, playing a crucial role in the country's history. ''Nordestes dialects and rich culture, including its folklore, cuisines, music and literature, became the most easily distinguishable across the country. To this day, ''Nordeste'' is known for its history and culture, as well as for its natural environment and its hot weather. ''Nordeste'' stretches from the Atlantic seaboard in the northeast and southeast, northwest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polka
Polka is a dance style and genre of dance music in originating in nineteenth-century Bohemia, now part of the Czech Republic. Though generally associated with Czech and Central European culture, polka is popular throughout Europe and the Americas. History Etymology The term ''polka'' referring to the dance is believed to derive from the Czech words "půlka", meaning "half-step". Czech cultural historian Čeněk Zíbrt attributes the term to the Czech word ''půlka'' (half), referring to both the half-tempo and the half-jump step of the dance.Čeněk Zíbrt, "Jak se kdy v Čechách tancovalo: dějiny tance v Čechách, na Moravě, ve Slezsku a na Slovensku z věků nejstarších až do nové doby se zvláštním zřetelem k dějinám tance vůbec", Prague, 189(Google eBook)/ref> This name has been changed to "Polka" as an expression of honour and sympathy for Poland and the Poles after the November Uprising 1830-1831. "Polka" meaning, in both the Czech and Poli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ionian Mode
The Ionian mode is a Mode (music), musical mode or, in modern usage, a diatonic scale also called the major scale. It is named after the Ionians, Ionian Greeks. It is the name assigned by Heinrich Glarean in 1547 to his new Gregorian mode#Authentic mode, authentic mode on C (mode 11 in his numbering scheme), which uses the diatonic octave species from C to the C an octave higher, divided at G (as its dominant, reciting tone/reciting note or ''tenor'') into a fourth species of perfect fifth (tone–tone–semitone–tone) plus a third species of perfect fourth (tone–tone–semitone): C D E F G + G A B C. This octave species is essentially the same as the Major scale, major mode of tonal music. Church music had been explained by theorists as being organised in eight Mode (music), musical modes: the scales on D, E, F, and G in the "greater perfect system" of "musica recta," each with their authentic mode, authentic and plagal mode, plagal counterparts. Glarean's twelfth mode was t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
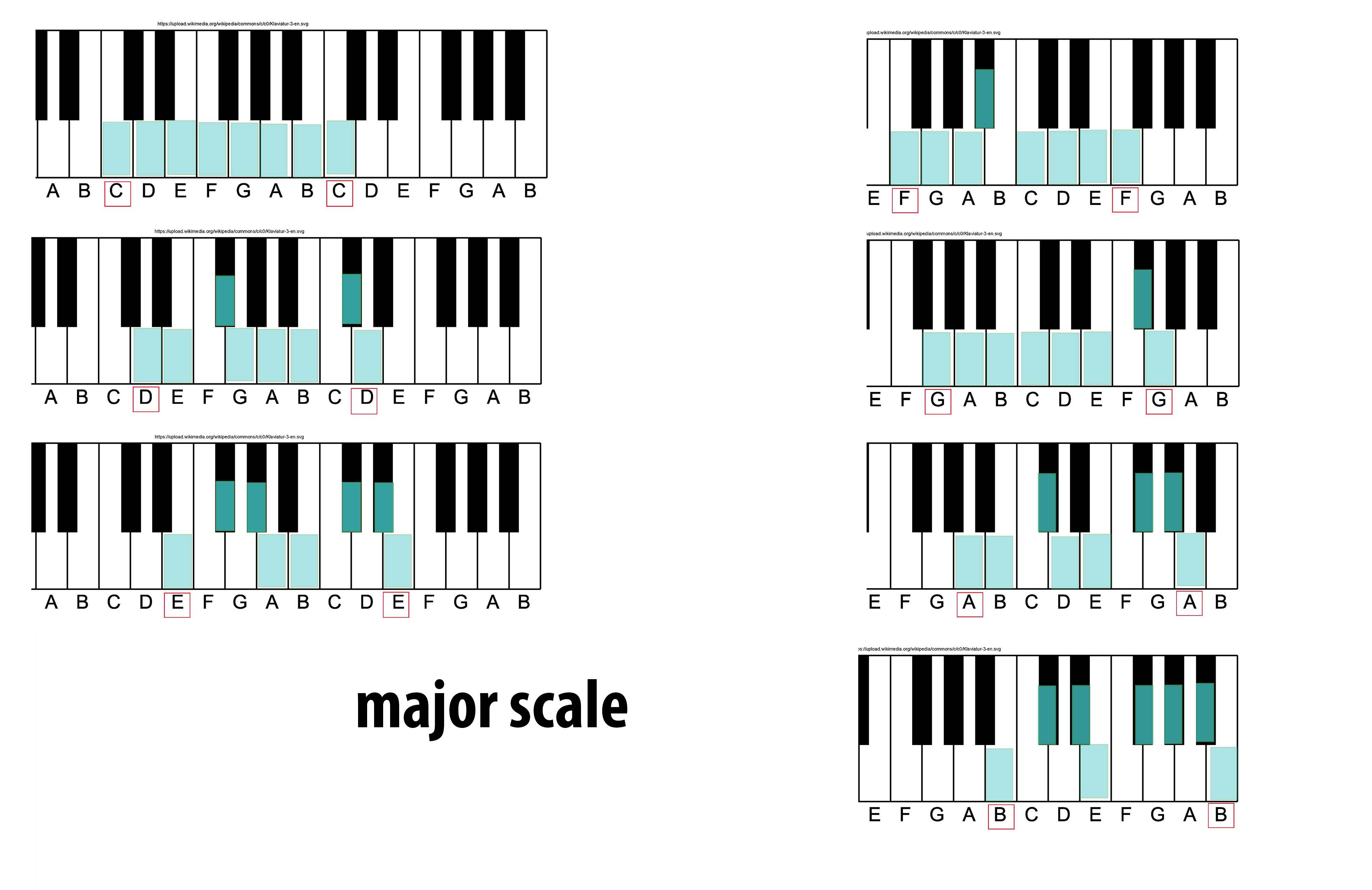
Major Scale
The major scale (or Ionian mode) is one of the most commonly used musical scales, especially in Western music. It is one of the diatonic scales. Like many musical scales, it is made up of seven notes: the eighth duplicates the first at double its frequency so that it is called a higher octave of the same note (from Latin "octavus", the eighth). The simplest major scale to write is C major, the only major scale not requiring sharps or flats: The major scale has a central importance in Western music, particularly that of the common practice period and in popular music. In Carnatic music, it is known as '' Sankarabharanam''. In Hindustani classical music, it is known as '' Bilaval''. Structure A major scale is a diatonic scale. The sequence of intervals between the notes of a major scale is: : whole, whole, half, whole, whole, whole, half where "whole" stands for a whole tone (a red u-shaped curve in the figure), and "half" stands for a semitone (a red angled ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minor Mode
In Western classical music theory, the minor scale refers to three scale patterns – the natural minor scale (or Aeolian mode), the harmonic minor scale, and the melodic minor scale (ascending or descending). These scales contain all three notes of a minor triad: the root, a minor third (rather than the major third, as in a major triad or major scale), and a perfect fifth (rather than the diminished fifth, as in a diminished scale or half diminished scale). Minor scale is also used to refer to other scales with this property, such as the Dorian mode or the minor pentatonic scale (see other minor scales below). Natural minor scale Relationship to relative major A natural minor scale (or Aeolian mode) is a diatonic scale that is built by starting on the sixth degree of its relative major scale. For instance, the A natural minor scale can be built by starting on the 6th degree of the C major scale: : Because of this, the key of A minor is called the ''relative ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Music Tradition
European, or Europeans, may refer to: In general * ''European'', an adjective referring to something of, from, or related to Europe ** Ethnic groups in Europe ** Demographics of Europe ** European cuisine, the cuisines of Europe and other Western countries * ''European'', an adjective referring to something of, from, or related to the European Union ** European Union citizenship ** Demographics of the European Union In publishing * ''The European'' (1953 magazine), a far-right cultural and political magazine published 1953–1959 * ''The European'' (newspaper), a British weekly newspaper published 1990–1998 * ''The European'' (2009 magazine), a German magazine first published in September 2009 *''The European Magazine'', a magazine published in London 1782–1826 *''The New European'', a British weekly pop-up newspaper first published in July 2016 Other uses * * Europeans (band), a British post-punk group, from Bristol See also * * * Europe (other) * The Europ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guerra Peixe
Guerra is a Portuguese, Spanish and Italian term meaning "war". Notable people with the surname Guerra include: People Arts * Aaron Guerra, American guitarist * Adam Daniel Guerra, American drag queen also known as Venus D-Lite * Ana Clara Guerra Marques, Angolan dancer * Andrea Guerra (composer), Italian composer * Aureliano Fernández-Guerra, Spanish historian, poet and playwright * Carlos Rivera Guerra, Mexican singer * Carolina Guerra, Colombian model and actress * Cástulo Guerra, Argentine actor * César Guerra-Peixe, Brazilian violinist * Ciro Guerra, Colombian film director, screenwriter * Ely Guerra, Mexican singer * Gabriel Guerra, Mexican sculptor * Giovanni Guerra, Italian painter * Gregório de Matos e Guerra, Brazilian poet * Juan Luis Guerra, Dominican singer * Marcelino Guerra, Cuban singer * María Inés Guerra, Mexican singer * Pedro Guerra, Spanish singer * Pia Guerra, Canadian comic book artist * Raquel Guerra, Portuguese singer * Rita Guerra, Portugu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orchestra
An orchestra (; ) is a large instrumental ensemble typical of classical music, which combines instruments from different families. There are typically four main sections of instruments: * String instruments, such as the violin, viola, cello, and double bass * Woodwinds, such as the flute, oboe, clarinet, bassoon, and occasional saxophone * Brass instruments, such as the French horn (commonly known as the "horn"), trumpet, trombone, cornet, and tuba, and sometimes euphonium * Percussion instruments, such as the timpani, snare drum, bass drum, cymbals, triangle, tambourine, tam-tam and mallet percussion instruments Other instruments such as the piano, harpsichord, pipe organ, and celesta may sometimes appear in a fifth keyboard section or may stand alone as soloist instruments, as may the concert harp and, for performances of some modern compositions, electronic instruments, and guitars. A full-size Western orchestra may sometimes be called a or phil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metre (poetry)
In poetry, metre ( Commonwealth spelling) or meter ( American spelling; see spelling differences) is the basic rhythmic structure of a verse or lines in verse. Many traditional verse forms prescribe a specific verse metre, or a certain set of metres alternating in a particular order. The study and the actual use of metres and forms of versification are both known as prosody. (Within linguistics, " prosody" is used in a more general sense that includes not only poetic metre but also the rhythmic aspects of prose, whether formal or informal, that vary from language to language, and sometimes between poetic traditions.) Characteristics An assortment of features can be identified when classifying poetry and its metre. Qualitative versus quantitative metre The metre of most poetry of the Western world and elsewhere is based on patterns of syllables of particular types. The familiar type of metre in English-language poetry is called qualitative metre, with stressed syllables comin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Singing
Singing is the art of creating music with the voice. It is the oldest form of musical expression, and the human voice can be considered the first musical instrument. The definition of singing varies across sources. Some sources define singing as the act of creating musical sounds with the voice. Other common definitions include "the utterance of words or sounds in tuneful succession" or "the production of musical tones by means of the human voice". A person whose profession is singing is called a singer or a vocalist (in jazz or popular music). Singers perform music (arias, recitatives, songs, etc.) that can be sung accompaniment, with or a cappella, without accompaniment by musical instruments. Singing is often done in an ensemble (music), ensemble of musicians, such as a choir. Singers may perform as Soloist (music), soloists or accompanied by anything from a single instrument (as in art songs or some Jazz, jazz styles) up to a symphony orchestra or big band. Many styles o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acoustic Guitar
An acoustic guitar is a musical instrument in the string family. When a string is plucked, its vibration is transmitted from the bridge, resonating throughout the top of the guitar. It is also transmitted to the side and back of the instrument, resonating through the air in the body, and producing sound from the sound hole. While the original, general term for this stringed instrument is ''guitar'', the retronym 'acoustic guitar' – often used to indicate the Steel-string acoustic guitar, steel stringed model – distinguishes it from an electric guitar, which relies on electronic amplification. Typically, a guitar's body is a sound box, of which the top side serves as a Sound board (music), sound board that enhances the vibration sounds of the strings. In Guitar tunings, standard tuning the guitar's six strings are tuned (low to high) E2 A2 D3 G3 B3 E4. Guitar strings may be plucked individually with a Guitar pick, pick (plectrum) or fingertip, or Strumming, strummed to play Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |