|
Baikonur Cosmodrome Site 109
Site 109/95 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome The Baikonur Cosmodrome ( kk, Байқоңыр ғарыш айлағы, translit=Baiqoñyr ğaryş ailağy, ; russian: Космодром Байконур, translit=Kosmodrom Baykonur, ) is a spaceport in an area of southern Kazakhstan leased to R ... is a missile silo built for use by the R-36 missile, which has been converted into a launch site for the Dnepr carrier rocket. Nineteen R-36 ICBMs were launched on test flights from Site 109 between its activation in 1974, and deactivation in 1983. It was subsequently reactivated for the Dnepr programme, which uses a modified R-36 missile to place satellites into orbit. The Dnepr made its maiden flight from Site 109 on 21 April 1999. The most recent launch from Site 109 was a Dnepr, with the German TanDEM-X satellite, which was launched on 21 June 2010. References * Baikonur Cosmodrome {{rocketry-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dnepr (rocket)
The Dnepr rocket (russian: Днепр, translit=Dnepr; uk, Дніпро, translit=Dnipró) was a space launch vehicle named after the Dnieper River. It was a converted ICBM used for launching artificial satellites into orbit, operated by launch service provider ISC Kosmotras. The first launch, on April 21, 1999, successfully placed UoSAT-12, a 350 kg demonstration mini-satellite, into a 650 km circular Low Earth orbit. History The Dnepr was based on the R-36MUTTH Intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM)called the ''SS-18 Satan'' by NATOdesigned in the 1970s by the Yuzhnoe Design Bureau in Dnepropetrovsk, Ukrainian SSR. The Dnepr control system was developed and produced by the JSC "Khartron", Kharkiv. The Dnepr was a three-stage rocket using storable hypergolic liquid propellants. The launch vehicles used for satellite launches have been withdrawn from ballistic missile service with the Russian Strategic Rocket Forces and stored for commercial use. A group of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baikonur Cosmodrome
''Baiqoñyr ğaryş ailağy'' rus, Космодром Байконур''Kosmodrom Baykonur'' , image = Baikonur Cosmodrome Soyuz launch pad.jpg , caption = The Baikonur Cosmodrome's " Gagarin's Start" Soyuz launch pad prior to the rollout of Soyuz TMA-13, 10 October 2008. , LID = GC0015 , type = Spaceport , owner-oper = Roscosmos Russian Aerospace Forces , location = Kazakhstan (leased to Russia) , opened = , built = , timezone = UTC+06:00 , utc = +06:00 , elevation-m = 90 , metric-elev = y , coordinates = , website = , image_map = , image_mapsize = , image_map_alt = , image_map_caption = , pushpin_map = Kazakhstan#Russia#Soviet Union , push ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RVSN
The Strategic Rocket Forces of the Russian Federation or the Strategic Missile Forces of the Russian Federation (RVSN RF; russian: Ракетные войска стратегического назначения Российской Федерации (РВСН РФ), Raketnye voyska strategicheskogo naznacheniya Rossiyskoy Federatsii, lit. 'Strategic Purpose Rocketry Troops') are a separate-troops branch of the Russian Armed Forces that control Russia's land-based intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs). The Strategic Rocket Forces was created on 17 December 1959 as part of the Soviet Armed Forces as the main force intended for attacking an enemy's offensive nuclear weapons, military facilities, and industrial infrastructure. They operated all Soviet nuclear ground-based intercontinental, intermediate-range ballistic missile, and medium-range ballistic missile with ranges over 1,000 kilometers. After the Soviet Union collapsed in 1991, assets of the Strategic Rocket F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Aerospace Forces
The Russian Aerospace Forces or Russian Air and Space Forces ( rus, Воздушно-космические силы, r=Vozdushno-kosmicheskiye sily) or VKS ( rus, ВКС}) comprise the air and space Space is the boundless three-dimensional extent in which objects and events have relative position and direction. In classical physics, physical space is often conceived in three linear dimensions, although modern physicists usually con ... Military branch, branch of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation. Russia established the VKS as a new branch of its military on 1 August 2015 with the merging of the Russian Air Force (VVS) and the Russian Aerospace Defence Forces (VVKO) - as recommended by the Ministry of Defence (Russia), Ministry of Defence. The VKS has its headquarters in Moscow. Russia's Ministry of Defence (Russia), Defense Minister Sergei Shoigu explained the merger as improving efficiency and logistical support. Organisation Sub-branches According to Ja ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ISC Kosmotras
The International Space Company Kosmotras or ISC Kosmotras (russian: ЗАО Международная космическая компания “Космотрас”) is a joint project, between Russia, Ukraine, and Kazakhstan, established in 1997. It developed and now operates a commercial expendable launch system using the Dnepr rocket. The Dnepr is a converted decommissioned SS-18 ICBM. ISC Kosmotras conducts Dnepr launches from Baikonur Cosmodrome and Yasny launch base in Dombarovskiy, Russia. In February 2015, following a year of strained relations as a result of a Russian military intervention into Ukraine, Russia announced that it would sever its "joint program with Ukraine to launch Dnepr rockets". ISC Kosmotras said it would honor its remaining launch contracts. Of the three launches planned for 2015, only one took place. As of 2016, it appears ISC Kosmotras no longer has customers, and thus whether the company is operational or not is uncertain. In May 2017, ISC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
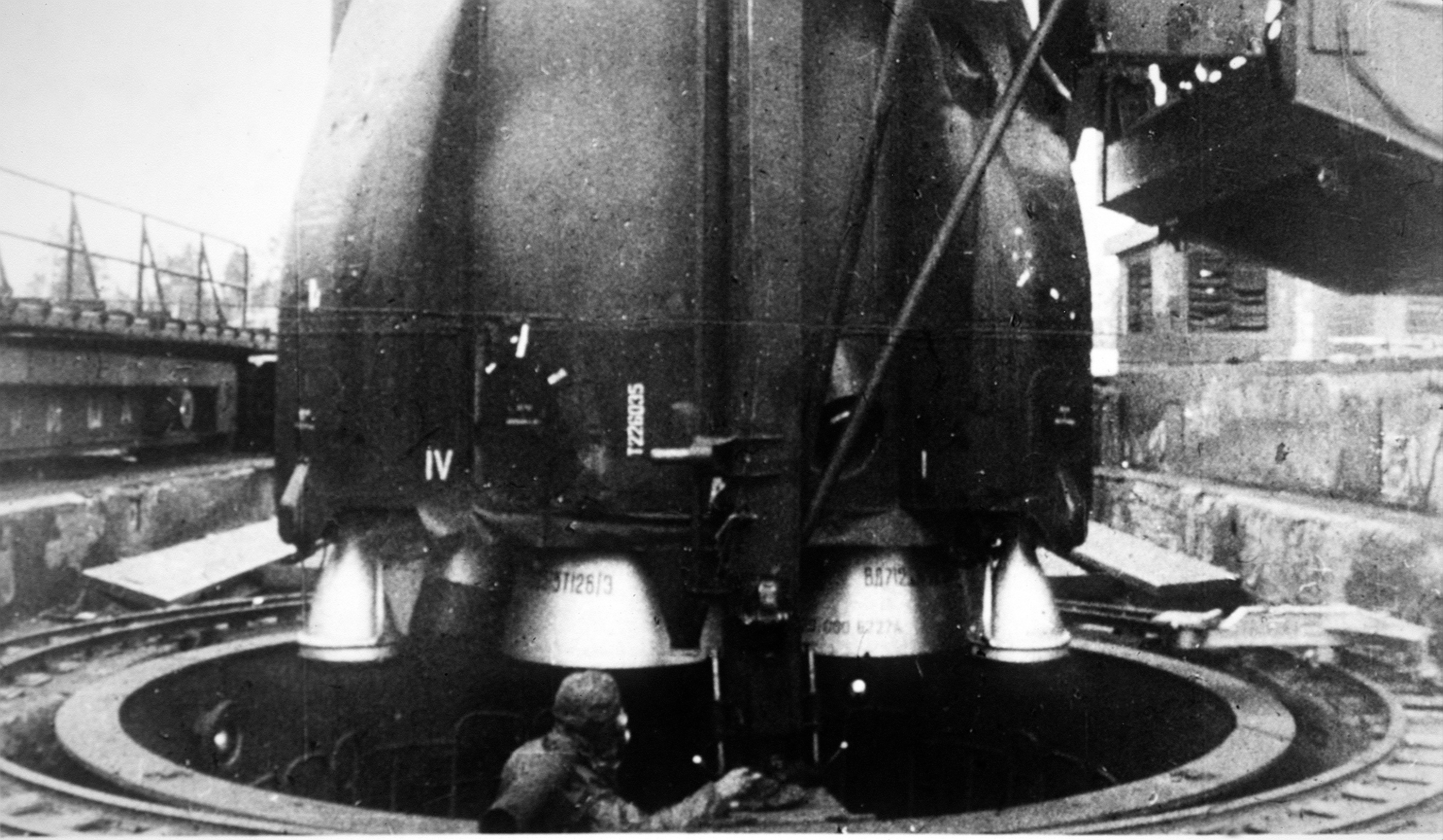
R-36 (missile)
The R-36 (russian: Р-36) is a family of intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs) and space launch vehicles (Tsyklon) designed by the Soviet Union during the Cold War. The original R-36 was deployed under the GRAU index 8K67 and was given the NATO reporting name SS-9 Scarp. It was able to carry three warheads and was the first Soviet MRV ( multiple re-entry vehicle) missile. The later version, the R-36M was produced under the GRAU designations 15A14 and 15A18 and was given the NATO reporting name SS-18 Satan. This missile was viewed by certain United States analysts as giving the Soviet Union first strike advantage over the U.S., particularly because of its rapid silo-reload ability, very heavy throw weight and extremely large number of re-entry vehicles. Some versions of the R-36M were deployed with 10 warheads and up to 40 penetration aids and the missile's high throw-weight made it theoretically capable of carrying more warheads or penetration aids. Contemporary U.S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Missile Silo
A missile launch facility, also known as an underground missile silo, launch facility (LF), or nuclear silo, is a vertical cylindrical structure constructed underground, for the storage and launching of intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs), intermediate-range ballistic missiles (IRBMs), medium-range ballistic missiles (MRBMs). Similar facilities can be used for anti-ballistic missiles (ABMs). The structures typically have the missile some distance below ground, protected by a large " blast door" on top. They are usually connected, physically and/or electronically, to a missile launch control center. With the introduction of the Soviet UR-100 and the U.S. Titan II missile series, underground silos changed in the 1960s. Both missile series introduced the use of hypergolic propellant, which could be stored in the missiles, allowing for rapid launches. Both countries' liquid-fueled missile systems were moved into underground silos. The introduction of solid fuel systems, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TanDEM-X
TanDEM-X (TerraSAR-X add-on for Digital Elevation Measurement) is the name of TerraSAR-X's twin satellite, a German Earth observation satellite using SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar) - a modern radar imaging technology. Implemented in a Public-Private-Partnership between the German Aerospace centre ( DLR) and EADS Astrium (now Airbus Defence and Space), it is a second, almost identical spacecraft to TerraSAR-X. TanDEM-X is also the name of the satellite mission flying the two satellites in a closely controlled formation with typical distances between 250 and 500 m.German Aerospace CenterTanDEM-X - A New High Resolution Interferometric SAR MissionVerified 2010-10-16. The twin satellite constellation allowed the generation of WorldDEM global digital elevation models starting in 2014. Mission The primary mission objective is the generation of WorldDEM, a consistent global Digital Elevation Model (DEM) with an unprecedented accuracy according to better than DTED Level 2 specificatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |