|
Baie Larose
Baie Larose, or Larose Bay in English, is a bay of Grande Terre, the main island of the subantarctic Kerguelen archipelago, a French territory in the southern Indian Ocean. It is important as a breeding site for seabirds, especially penguins. Description The bay lies on the southern coast of Grande Terre, west of Mont Ross and Gallieni Massif, and encompassing the mouth of Fjord Larose and the tilted monolith known as the ''Doigt de Sainte Anne'' (Saint Anne's Finger). Important Bird Area The bay, with part of the south-western slopes of Mont Ross, has been identified as a 20 km2 Important Bird Area (IBA) by BirdLife International because of its breeding seabirds. Of the penguins, there are some 21,500 pairs of kings, 500 pairs of gentoos, 6000 pairs of macaronis and 4000 pairs of eastern rockhoppers. Other birds nesting in the IBA include a few pairs of wandering albatrosses, Antarctic and slender-billed prions, white-chinned, northern giant and common d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
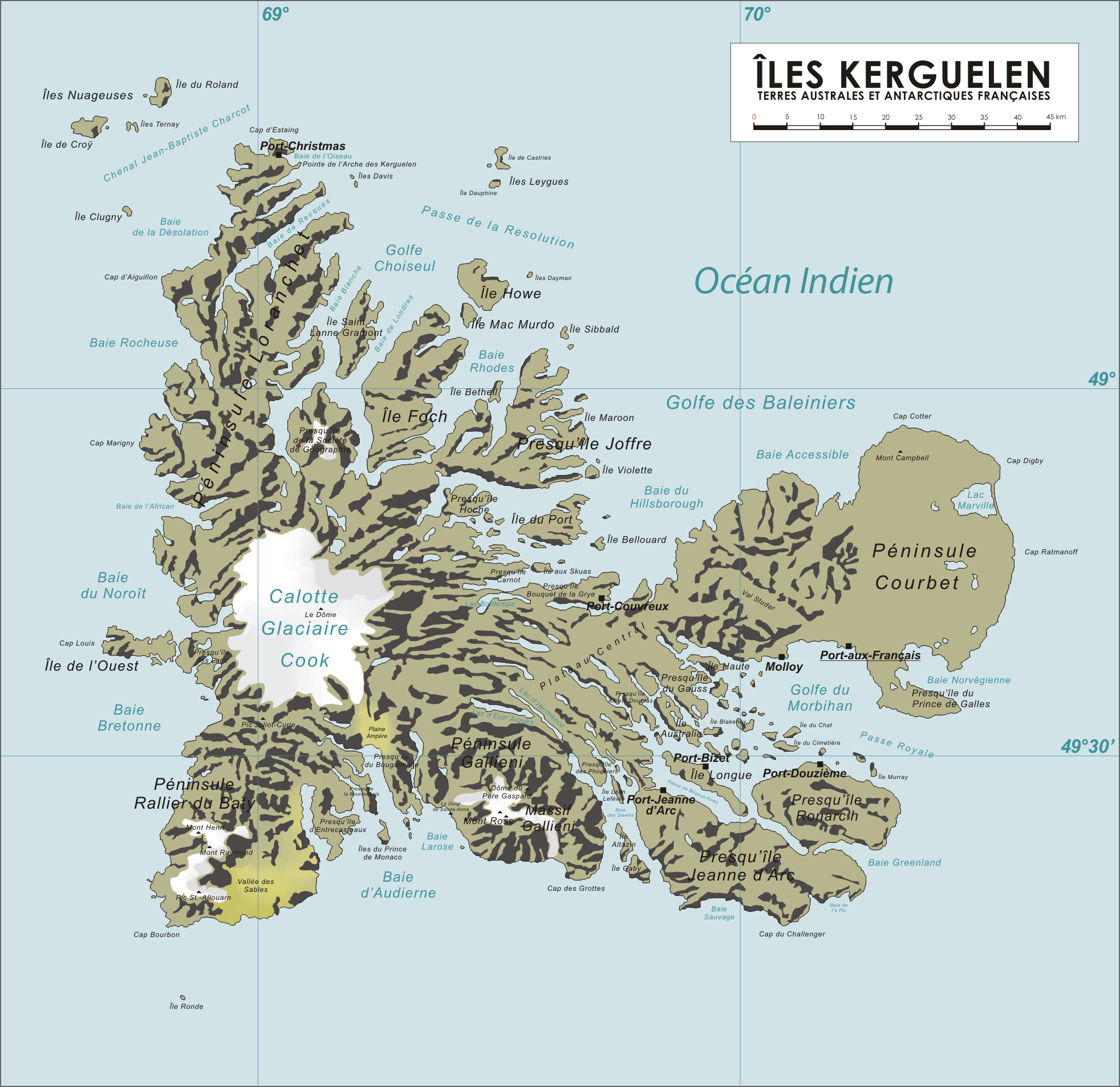
Kerguelen Map
The Kerguelen Islands ( or ; in French commonly ' but officially ', ), also known as the Desolation Islands (' in French), are a group of islands in the sub-Antarctic constituting one of the two exposed parts of the Kerguelen Plateau, a large igneous province mostly submerged in the southern Indian Ocean. They are among the most isolated places on Earth, located more than from Madagascar. The islands, along with Adélie Land, the Crozet Islands, Amsterdam and Saint Paul islands, and France's Scattered Islands in the Indian Ocean, are part of the French Southern and Antarctic Lands and are administered as a separate district. The main island, Grande Terre, is in area, about three quarters of the size of Corsica, and is surrounded by a further 300 smaller islands and islets, forming an archipelago of . The climate is harsh and chilly with frequent high winds throughout the year. The surrounding seas are generally rough and they remain ice-free year-round. There are no indigen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Rockhopper Penguin
The eastern rockhopper penguin (''Eudyptes chrysocome filholi'') is a crested penguin with yellow crest feathers. It is a subspecies of the southern rockhopper penguin (''Eudyptes chrysocome'') found in subantarctic regions and the Indian Ocean. It is one of the smallest crested penguins and has distinctive pink margins around its bill. Description The eastern rockhopper penguin is a small, crested penguin with a black back and throat, a white belly and pink feet. This seabird measures approximately 45–55 cm in length, and weighs 2.2–4.3 kg. It has a thin yellow stripe that stretches from its lower forehead, over its red eye and splits into crest feathers at the back of its head. The crest feathers are composed of long, thin, spiky yellow feathers on either side of the penguin's head and they are joined by shorter black feathers. Rockhopper penguins have an orange-brown bill and the eastern rockhopper penguin has distinctive pink margins around the bill. Males an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landforms Of The Kerguelen Islands
A landform is a natural or anthropogenic land feature on the solid surface of the Earth or other planetary body. Landforms together make up a given terrain, and their arrangement in the landscape is known as topography. Landforms include hills, mountains, canyons, and valleys, as well as shoreline features such as bays, peninsulas, and seas, including submerged features such as mid-ocean ridges, volcanoes, and the great ocean basins. Physical characteristics Landforms are categorized by characteristic physical attributes such as elevation, slope, orientation, stratification, rock exposure and soil type. Gross physical features or landforms include intuitive elements such as berms, mounds, hills, ridges, cliffs, valleys, rivers, peninsulas, volcanoes, and numerous other structural and size-scaled (e.g. ponds vs. lakes, hills vs. mountains) elements including various kinds of inland and oceanic waterbodies and sub-surface features. Mountains, hills, plateau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Elephant Seal
The southern elephant seal (''Mirounga leonina'') is one of two species of elephant seals. It is the largest member of the clade Pinnipedia and the order Carnivora, as well as the largest extant marine mammal that is not a cetacean. It gets its name from its massive size and the large proboscis of the adult male, which is used to produce very loud roars, especially during the breeding season. A bull southern elephant seal is about 40% heavier than a male northern elephant seal (''Mirounga angustirostris''), twice as heavy as a male walrus (''Odobenus rosmarus''), and 6–7 times heavier than the largest living mostly-terrestrial carnivoran, the polar bear (''Ursus maritimus'') and the Kodiak bear (''Ursus arctos middendorffi''),. Taxonomy The southern elephant seal was one of the many species originally described by Swedish zoologist Carl Linnaeus in the landmark 1758 10th edition of his ''Systema Naturae'', where it was given the binomial name of ''Phoca leonina''. John Ed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctic Fur Seal
The Antarctic fur seal (''Arctocephalus gazella''), is one of eight seals in the genus '' Arctocephalus'', and one of nine fur seals in the subfamily Arctocephalinae. Despite what its name suggests, the Antarctic fur seal is mostly distributed in Subantarctic islands and its scientific name is thought to have come from the German vessel SMS Gazelle, which was the first to collect specimens of this species from Kerguelen Islands. Taxonomy Antarctic fur seals are member of the genus ''Arctocephalus''. Recently, a proposal was made to reassign this species to the resurrected genus ''Arctophoca''. Antarctic fur seals may be confused with southern otariids that share their range, like Subantarctic (''A. tropicalis''), New Zealand (''A. forsteri''), and South American fur seals (''A. australis''), and the Juan Fernandez fur seal (''A. phillippii''), as well as the South American (''Otaria flavescens'') and New Zealand sea lions (''Phocarctos hookeri''). Genetic studies on populat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eaton's Pintail
Eaton's pintail (''Anas eatoni'') is a dabbling duck of the genus ''Anas''. It is also known as the southern pintail. The species is restricted to the island groups of Kerguelen and Crozet in the southern Indian Ocean. It resembles a small female northern pintail. It was named after the English explorer and naturalist Alfred Edmund Eaton. It is threatened by introduced species, particularly feral cats, which prey Predation is a biological interaction where one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation (which usually do not kill the ... on it. There are two subspecies: ''A. eatoni eatoni'' (Kerguelen pintail) and ''A. eatoni drygalskii'' (Crozet pintail). References External links BirdLife Species Factsheet Eaton's pintail Birds of the Indian Ocean Birds of subantarctic islands Fauna of the Crozet Islands Fauna of the Kerguelen Islands ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black-faced Sheathbill
The black-faced sheathbill (''Chionis minor''), also known as the lesser sheathbill or paddy bird, is one of only two species of sheathbills, aberrant shorebirds which are terrestrial scavengers of subantarctic islands. Description They are dumpy, short-necked, pigeon-like birds with white plumage, black bills, caruncles and facial skin. This species measures in length, in wingspan and weighs , with males being slightly larger than females.''CRC Handbook of Avian Body Masses'' by John B. Dunning Jr. (Editor). CRC Press (1992), . Distribution Restricted to subantarctic islands in the southern Indian Ocean: the South African territory of the Prince Edward Islands, the French territories of the Crozet Islands and Kerguelen Islands, and the Australian territory of Heard Island. The race ''C. m. nasicornis'' is endemic to Heard Island, while the race ''C. m. marionesis'' is endemic to the Prince Edward Islands. Habitat Coastlines and intertidal zones of subantarctic islands, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kerguelen Tern
The Kerguelen tern (''Sterna virgata'') is a tern of the southern hemisphere. This seabird mainly breeds colonially in the Kerguelen Islands, as its common name implies. However, smaller colonies are also found in the Prince Edward Islands (i.e. Prince Edward and Marion) and Crozet Islands. The total number of individuals is from 3,500 to 6,500 birds, although there is no recent data from the main colony at Kerguelen. These birds do not inhabit Kerguelen proper, instead nesting on islets free of feral cats. During bad weather, they are known to abandon their colonies. Kerguelen terns are among the least-ranging of all typical terns. They generally do not reach far into the seas near their breeding grounds. These birds eat fish and marine invertebrates, especially those found in beds of the seaweed Macrocystis spp. They sometimes also hunt insects on land and catch fish from rivers on Kerguelen. There are two subspecies: *''S. v. mercuri'' (Voisin, 1971) – Crozet a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kerguelen Shag
The Kerguelen shag (''Leucocarbo verrucosus'') is a species of cormorant endemic to the Kerguelen Islands in the southern Indian Ocean, one of the most isolated places on Earth. Many authorities consider it a subspecies of the imperial shag. Range and habitat This species nests on the coast of Grande Terre (the main island of the archipelago), on offshore islands, and on islands in the Golfe du Morbihan. It forages at sea throughout the archipelago, usually within of shore and especially in bays and inlets, though immatures have been seen rarely as far as . Reports from Heard Island and western Australia may be of ship-assisted birds. In the austral summer it feeds among kelp, sometimes at the bottom. Description The Kerguelen shag is long with a wingspan of , making it the smallest blue-eyed shag. The adult's upperparts, tail, and thighs are metallic greenish black; the underbody to the throat is white; and the wing linings are brown. Some individuals have white patches ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Diving Petrel
The common diving petrel (''Pelecanoides urinatrix''), also known as the smaller diving petrel or simply the diving petrel, is a diving petrel, one of four very similar auk-like small petrels of the southern oceans. It is native to South Atlantic islands and islands of the subantarctic southern Indian Ocean, islands and islets off New Zealand and south-eastern Australian islands. Taxonomy The common diving petrel was formally described in 1788 by the German naturalist Johann Friedrich Gmelin. He placed it with the other petrels in the genus '' Procellaria'' and coined the binomial name ''Procellaria uriatrix''. Gmelin based his description on the "diving petrel" that had been described in 1785 by the English ornithologist John Latham in the second volume of his ''A General Synopsis of Birds''. Latham reported that they were found in great numbers in Queen Charlotte Sound at the northern end of South Island, New Zealand. The common diving petrel is now one of four petrels ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Giant Petrel
The northern giant petrel (''Macronectes halli''), also known as Hall's giant petrel, is a large predatory seabird of the southern oceans. Its distribution overlaps broadly, but is slightly north of, the similar southern giant petrel (''Macronectes giganteus''). Taxonomy The northern giant petrel was formally described in 1912 by the Australian born ornithologist Gregory Mathews as a subspecies of the southern giant petrel with the trinomial name ''Macronectes giganteus halli''. The specific epithet ''halli'' was chosen to honour the Australian ornithologist Robert Hall who had described the birds breeding on the Kerguelen Islands. The northern giant petrel is now considered to be a separate species and has the binomial name ''Macronectes halli''. It is monotypic: no subspecies are recognised. The genus name combines the Ancient Greek ''makros'' meaning "great" and ''nēktēs'' meaning "swimmer". The name "petrel" refers to the Biblical account of Saint Peter walking on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
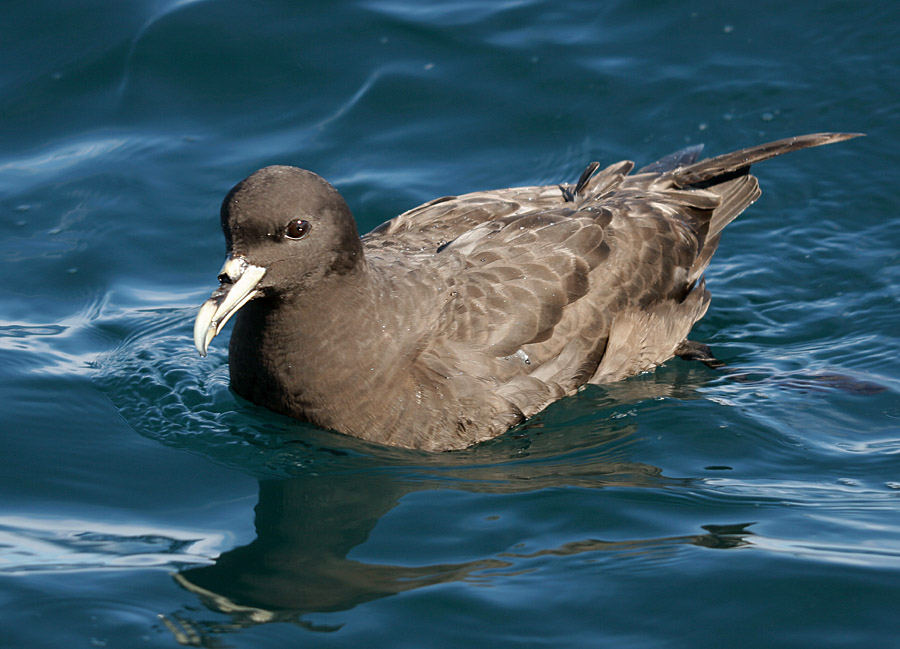
White-chinned Petrel
The white-chinned petrel (''Procellaria aequinoctialis'') also known as the Cape hen and shoemaker, is a large shearwater in the family Procellariidae. It ranges around the Southern Ocean as far north as southern Australia, Peru and Namibia, and breeds colonially on scattered islands. The white-chinned petrel was formerly considered to be conspecific with the spectacled petrel (''Procellaria conspicillata''). Taxonomy In 1747 the English naturalist George Edwards included an illustration and a description of the white-chinned petrel in the second volume of his ''A Natural History of Uncommon Birds''. He used the English name "The great Black Peteril" and based his hand-coloured etching on a preserved specimen that had been brought to London. He believed that it had been collected near the Cape of Good Hope. When in 1758 the Swedish naturalist Carl Linnaeus updated his ''Systema Naturae'' for the tenth edition, he placed the white-chinned petrel with the other petrels in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)

.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)

