|
Bagmati, Lalitpur
Bagmati is a Rural Municipality in Lalitpur District in Bagmati Province of Nepal that was established in 2017 by merging the former Village development committees Ashrang, Ghusel, Malta, Bhattedanda, Pyutar, Ikudol and Gimdi in March 2017. The center of this rural municipality is located in Old-Bhattedanda. Demographics At the time of the 2011 Nepal census, Bagmati Rural Municipality had a population of 13,049. Of these, 58.3% spoke Tamang, 40.2% Nepali, 0.9% Magar, 0.2% Maithili, 0.1% Bhojpuri and 0.3% other languages as their first language. In terms of ethnicity/caste, 58.6% were Tamang, 23.2% Hill Brahmin, 7.3% Chhetri, 5.9% Magar, 1.9% Kami, 1.4% Ghale, 0.5% Damai/Dholi, 0.3% Brahmu/Baramo, 0.2% other Dalit, 0.2% Newar, 0.1% other Terai and 0.4% others. In terms of religion, 59.3% were Buddhist, 39.5% Hindu, 1.1% Christian A Christian () is a person who follows or adheres to Christianity, a Monotheism, monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nepal
Nepal, officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal, is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is mainly situated in the Himalayas, but also includes parts of the Indo-Gangetic Plain. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China China–Nepal border, to the north, and India India–Nepal border, to the south, east, and west, while it is narrowly separated from Bangladesh by the Siliguri Corridor, and from Bhutan by the States and union territories of India, Indian state of Sikkim. Nepal has a Geography of Nepal, diverse geography, including Terai, fertile plains, subalpine forested hills, and eight of the world's ten List of highest mountains#List, tallest mountains, including Mount Everest, the highest point on Earth. Kathmandu is the nation's capital and List of cities in Nepal, its largest city. Nepal is a multi-ethnic, multi-lingual, multi-religious, and multi-cultural state, with Nepali language, Nepali as the official language. The name "Nepal" is first record ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nepali Language
Nepali (; , ), or ''Gorkhali'' is an Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan language native to the Himalayas region of South Asia. It is the official and most widely spoken Languages of Nepal, language of Nepal, where it also serves as a ''lingua franca''. Nepali has Languages with official status in India, official status in the Indian state of Sikkim and in the Gorkhaland Territorial Administration of West Bengal. It is spoken by about a quarter of Bhutan's population. Nepali also has a significant number of speakers in the Indian states of Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Himachal Pradesh, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram and Uttarakhand. In Myanmar it is spoken by the Burmese Gurkhas. The Nepali diaspora in the Middle East, Brunei, Australia and worldwide also use the language. Nepali is spoken by approximately 19 million native speakers and another 14 million as a second language. Nepali is commonly classified within the Eastern Pahari group of the Northern Indo-Aryan languages, Northern zo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddhism In Nepal
Buddhism in Nepal started spreading since the reign of Ashoka through Indian and Tibetan missionaries. The Kiratas were the first people in Nepal who embraced the Buddha’s teachings, followed by the Licchavi (kingdom), Licchavis and Newar people. Buddhism is Nepal's second-largest religion, with 8.2% of the country's population, or approximately 2.4 million people, identifying as adherents of Buddhism in a 2021 census. Shakyamuni Buddha was born in Lumbini in the Shakya Kingdom. Besides Shakyamuni Buddha, there are Buddhahood, many Buddha(s) before him who are worshipped in different parts of Nepal. Lumbini lies in present-day Rupandehi District, Lumbini zone of Nepal. Buddhism is the second-largest religion in Nepal. According to 2001 census, 10.74% of Nepal's population practiced Buddhism, consisting mainly of Tibeto-Burman languages, Tibeto-Burman speaking ethnicities and the Newar. However, in the 2011 census, Buddhists made up just 9% of the country's population. It has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newar People
Newar (; , endonym: Newa; , Pracalit script: ), or Nepami, are primarily inhabitants in Kathmandu Valley of Nepal and its surrounding areas, and the creators of its historic heritage and civilisation. Page 15. Newars are a distinct linguistic and cultural group, primarily Indo-Aryan peoples, Indo-Aryan and Tibeto-Burman migration to Indian subcontinent, Tibeto-Burman ethnicities, who share a common language, Newar language, Nepal Bhasa, and predominantly practice Newar Hinduism and Newar Buddhism. Newars have developed a division of labour and a sophisticated urban civilisation not seen elsewhere in the Himalayas, Himalayan foothills. Newars have continued their age-old traditions and practices and pride themselves as the true custodians of the religion, culture and civilisation of Nepal. Newars are known for their contributions to culture, Newa art, art and Newari literature, literature, Lhasa Newar, trade, Agriculture in Nepal, agriculture and Newa cuisine, cuisine. Today, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
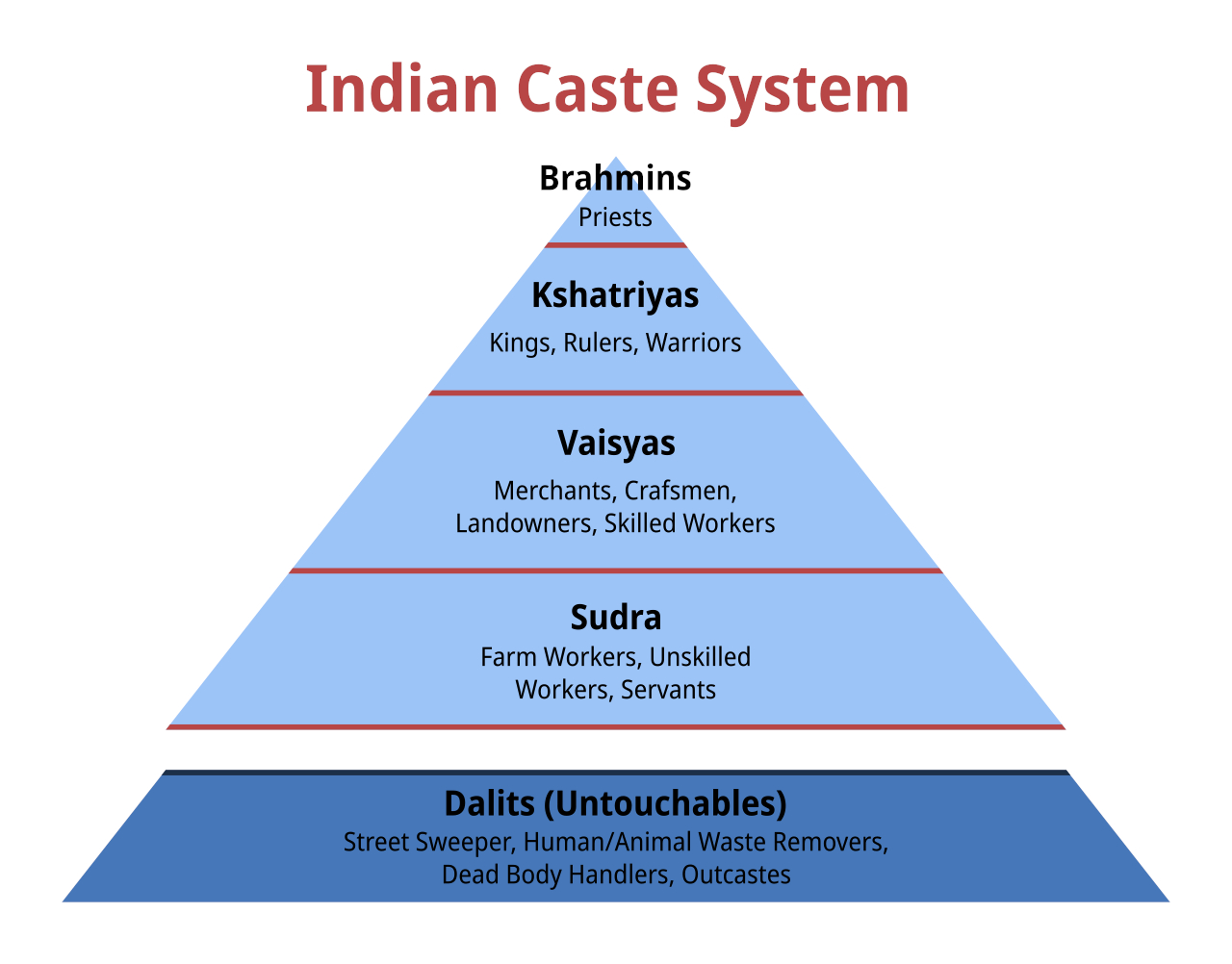
Dalit
Dalit ( from meaning "broken/scattered") is a term used for untouchables and outcasts, who represented the lowest stratum of the castes in the Indian subcontinent. They are also called Harijans. Dalits were excluded from the fourfold varna of the caste hierarchy and were seen as forming a fifth varna, also known by the name of ''Panchama''. Several scholars have drawn parallels between Dalits and the '' Burakumin'' of Japan, the '' Baekjeong'' of Korea and the peasant class of the medieval European feudal system. Dalits predominantly follow Hinduism with significant populations following Buddhism, Sikhism, Christianity, and Islam. The constitution of India includes Dalits as one of the Scheduled Castes; this gives Dalits the right to protection, positive discrimination (known as reservation in India), and official development resources. Terminology The term ''Dalit'' is for those called the "untouchables" and others that were outside of the traditional Hindu caste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Damai
Damai ( ; IAST: ''Damāĩ'') is an occupational caste found among indigenous people comprising 45 subgroups. Their surnames take after the subgroup they belong to. People belonging to this caste are traditionally tailors and musicians capable of using the naumati baja - an ensemble of nine traditional musical instruments. The term Damai is coined from the musical instrument Damaha. The 1854 Nepalese Muluki Ain (Legal Code) categorized Damai as "Lower caste” category. The Government of Nepal abolished the caste-system and criminalized any caste-based discrimination, including "untouchability" in 1963. The country, previously ruled by a Hindu monarchy was a Hindu nation which has now become a secular state. It was declared a republic in 2008, thereby ending it as the Hindu kingdom with its caste-based discriminations and the untouchability roots. According to the 2021 Nepal census, Damai make up 1.94% of Nepal's population (or 565,932 people). Damai are categorized under "H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ghale
Ghale is an ethnic group in Nepal with a unique cultural heritage and language, which serves as a significant aspect of their identity and social cohesion within the community. The preservation of their language and cultural traditions is crucial in understanding and celebrating the rich diversity that contributes to the tapestry of Nepal's ethnic landscape. Geographic distribution The Central Bureau of Statistics of Nepal classifies the Ghale within the broader social group of Mountain/Hill Janajati. At the time of the 2011 Nepal census, 22,881 people (0.1% of the population of Nepal) were Ghale. The frequency of Ghale by province was as follows: * Bagmati Province (0.3%) * Gandaki Province (0.3%) * Koshi Province (0.0%) * Lumbini Province (0.0%) * Madhesh Province (0.0%) * Sudurpashchim Province (0.0%) * Karnali Province (0.0%) The frequency of Ghale was higher than national average (0.1%) in the following districts: * Manang (7.1%) * Rasuwa (2.4%) * Dhading (2.0%) * Gorkha ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kami (caste)
Kami is an Indo-Aryan Nepali speaking group that primarily worked as metalsmiths. Later Nepal abolished its grading system. The tribal designation of Khas is given in some contexts. the Government of Nepal legally abolished the caste-system and criminalized any caste-based discrimination, including " untouchability" (the ostracism of a specific caste) - in the year 1963 A.D. With Nepal's step towards freedom and equality, Nepal, previously ruled by a Hindu monarchy was a Hindu nation which has now become a secular state, and on 28 May 2008, it was declared a republic, ending it as the Hindu kingdom. In spite of being the important occupational caste and ethnic group whose metal carving arts are globally recognized but still struggling to be recognized as it is considered as the serving occupation. The most people of this caste group are in absolute poverty to raise the voice and educate themselves to be in a good position to find the history. So they are compelled to face ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magars
The Magars, also spelled Mangar and Mongar, are the largest ethnic group native to Nepal and Northeast India, representing 6.9% of Nepal's total population according to the 2021 Nepal census. They are one of the main Gurkha tribes. The first home of the Magars was to the west of the Gandaki River and, roughly speaking, consisted of that portion of Nepal which lies between and around about Gulmi District, Gulmi, Arghakhanchi District, Arghakhanchi, and Palpa District, Palpa. This part of the country was divided into twelve districts known as ''Bahra Magarat'' (Confederation of Twelve Magar villages), which included the following regions of that period: Argha, Arghakhanchi District, Khanchi, Bhirkot, Dhor, Garhung, Ghiring, Gulmi, Isma, Musikot, Rising, Satungal, Satung, and Pyung. During the medieval period, the whole area from Palpa District, Palpa to Rukum Rolpa was called the Magarat, a place settled and inhabited by Magars. Another confederation of eighteen Magar kingdoms, k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chhetri
Chhetri (Kshetri, Kshettri, Kshetry or Chhettri), ( ; IAST: ''Kṣetrī'') historically called Kshettriya or Kshetriya or Khas are Nepali language, Nepali speaking people historically associated with the warrior class and administration, some of whom trace their origin to migration from medieval India. Chhetri was a caste of administrators, governors, Bir Bhadra Thapa, warriors and military elites in the medieval Khasa kingdom, Khas Kingdom and Gorkha Kingdom (later unified Kingdom of Nepal). The nobility of the Gorkha Kingdom mainly originated from Chhetri families. They also had a strong presence in civil administration affairs. The bulk of Prime Minister of Nepal, prime ministers of Nepal before the Revolution of 1951, democratization of Nepal belonged to this caste as a result of the old Gorkhali aristocracy. Gorkha-based aristocratic Chhetri families included the Pande dynasty, the Basnyat dynasty, the Kunwar family (and their offspring branch, the autocratic Rana dynasty) an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bahun
Bahun (), also known as Hill Brahmins, are a Brahmin varna among the Khas of Nepal. They are a sub-caste of the Kanyakubja Brahmin while their origins are from Kannauj and the Himalayan belt of South Asia. According to the 2011 Nepal census, Bahun is the second most populous group after Chhetri. According to 1854 ''Muluki Ain'', the first Nepalese civil code, Bahuns were regarded as caste among sacred thread bearers ( Tagadhari) and twice-born Hindus. Origin Traditionally, Bahuns were members of the Khas community together Chhetris. Possibly due to political power of the Khasa Malla kingdom, Khas Brahmins and Khas Kshatriyas had high social status in the present-day western Nepal. Bahuns, regarded as upper class Khas group together with Chhetris, were associated mostly with the Gorkha Kingdom and its expansion. There appears to be general agreement in historical records and family genealogy that Hill Brahmins (both Purbia and Kumai Bahuns) migrated from the G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tamang People
The Tamang people (; Devanagari: तामाङ; ''tāmāṅ'') are an ethnic group living in Nepal, Northeast India and southern Bhutan. In Nepal, they are concentrated in the central hilly and Himalayan regions and constituted over 1.6 million people in the 2021 census. In India, Tamang people live in the state of Sikkim, in the Darjeeling district, Darjeeling and Kalimpong districts of West Bengal and in Assam. In Bhutan, they live foremost in the southern foothills including Tsirang District, Dagana District, Samtse District, Chukha District, Sarpang District and Samdrup Jongkhar District. The Tamang language is the fifth most-spoken language in Nepal. History Research indicates that the Tamang people are a hybrid ethnic group with an estimated 59% genetic contribution from Tibetan and 41% from Nepalese ancestries. The Tamangs have been mentioned in various Nepalese and colonial historical records under a variety of names, such as ''Bhote'', ''Bodh'', ''Lama'', ''Murmi' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |