|
Bagh-o-Bahar
''The Tale of the Four Dervishes'' ( ''Qissa-ye Chahār Darvēsh'', ), known as ''Bāgh-o Bahār'' (, ) in Urdu, is a collection of allegorical stories by Amir Khusro written in Persian in the early 13th century. While legend says that Amir Khusro was the author, the tales were written long after his death. Legend has it that Amir Khusro's master and Sufi saint Nizamuddin Auliya had fallen ill. To cheer him up, Amir Khusro started telling him a series of stories in the style of the ''One Thousand and One Nights''. Style The book is in some ways similar to the ''Thousand and One Nights'' in its method of framing and linking unfinished stories within each other. The central character is a king, Azad Bakht, who falls into depression after thinking about his own mortality, and so sets out from his palace seeking wise men. He comes upon four dervishes in a cemetery, and listens to their fantastical stories. Each Dervish narrates his own story, which is basically on love and fidelit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urdu Literature
Urdu literature (, ) comprises the literary works, written in the Urdu language. While it tends to be dominated by poetry, especially the verse forms of the ''ghazal'' () and '' nazm'' (), it has expanded into other styles of writing, including the short story, or ''afsana'' (). Urdu literature is popular mostly in Pakistan, where Urdu is the national language, and in India, where it is an Eighth Schedule language. Origin Urdu developed during the 12th to 13th centuries, although the name "Urdu" did not exist at the time for the language. Amir Khusrau, who lived in the thirteenth century, wrote and gave shape to the Rekhta dialect (the Persianized combination of Hindavi), which was the early form of Modern Standard Urdu. He was thus called, the "father of Urdu literature". The continuing traditions of Islam and patronizations of foreign culture centuries earlier by Muslim rulers, usually of Turkic or Afghan descent, marked their influence on the Urdu language given that both ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
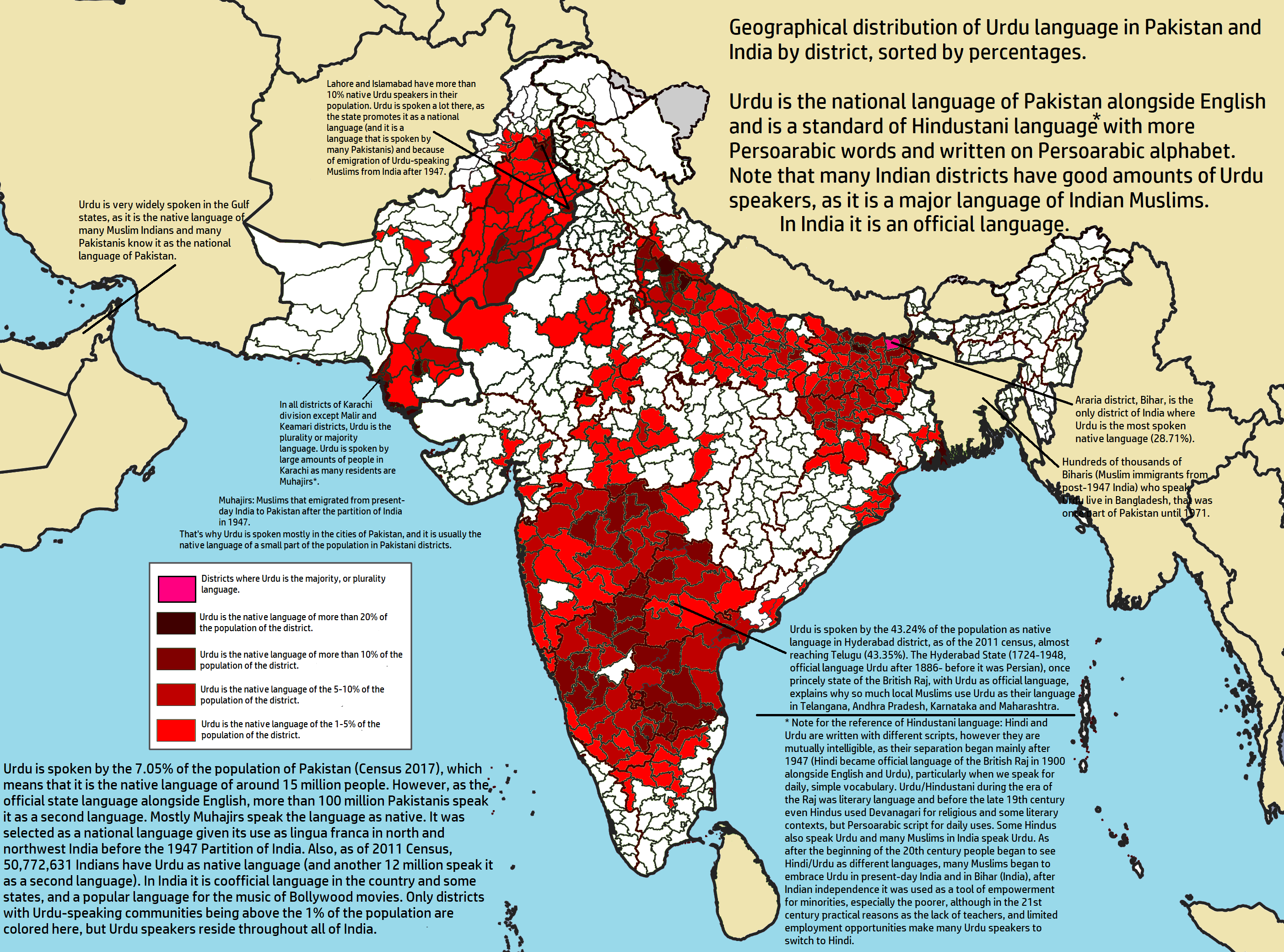
Urdu
Urdu (; , , ) is an Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan language spoken chiefly in South Asia. It is the Languages of Pakistan, national language and ''lingua franca'' of Pakistan. In India, it is an Eighth Schedule to the Constitution of India, Eighth Schedule language, the status and cultural heritage of which are recognised by the Constitution of India. Quote: "The Eighth Schedule recognizes India's national languages as including the major regional languages as well as others, such as Sanskrit and Urdu, which contribute to India's cultural heritage. ... The original list of fourteen languages in the Eighth Schedule at the time of the adoption of the Constitution in 1949 has now grown to twenty-two." Quote: "As Mahapatra says: "It is generally believed that the significance for the Eighth Schedule lies in providing a list of languages from which Hindi is directed to draw the appropriate forms, style and expressions for its enrichment" ... Being recognized in the Constitution, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encyclopaedia Iranica
An encyclopedia is a reference work or compendium providing summaries of knowledge, either general or special, in a particular field or discipline. Encyclopedias are divided into articles or entries that are arranged alphabetically by article name or by thematic categories, or else are hyperlinked and searchable. Encyclopedia entries are longer and more detailed than those in most dictionaries. Generally speaking, encyclopedia articles focus on ''factual information'' concerning the subject named in the article's title; this is unlike dictionary entries, which focus on linguistic information about words, such as their etymology, meaning, pronunciation, use, and grammatical forms.Béjoint, Henri (2000)''Modern Lexicography'', pp. 30–31. Oxford University Press. Encyclopedias have existed for around 2,000 years and have evolved considerably during that time as regards language (written in a major international or a vernacular language), size (few or many volumes), intent ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Legends
Indian or Indians may refer to: Associated with India * of or related to India ** Indian people ** Indian diaspora ** Languages of India ** Indian English, a dialect of the English language ** Indian cuisine Associated with indigenous peoples of the Americas * Indigenous peoples of the Americas ** First Nations in Canada ** Native Americans in the United States ** Indigenous peoples of the Caribbean ** Indigenous languages of the Americas Places * Indian, West Virginia, U.S. * The Indians, an archipelago of islets in the British Virgin Islands Arts and entertainment Film * ''Indian'' (film series), a Tamil-language film series ** ''Indian'' (1996 film) * ''Indian'' (2001 film), a Hindi-language film Music * Indians (musician), Danish singer Søren Løkke Juul * "The Indian", an unreleased song by Basshunter * "Indian" (song), by Sturm und Drang, 2007 * "Indians" (song), by Anthrax, 1987 * Indians, a song by Gojira from the 2003 album '' The Link'' Other uses i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Fairy Tales
The folklore of India encompasses the folklore of the Republic of India and the Indian subcontinent. India is an ethnically and religiously diverse country. Given this diversity, it is difficult to generalize the vast folklore of India as a unit. Although India is a Hindu-majority country, with more than three-fourths of the population identifying themselves as Hindus, there is no single, unified, and all-pervading concept of identity present in it. Various heterogeneous traditions, numerous regional cultures and different religions to grow and flourish here. Folk religion in Hinduism may explain the rationale behind local religious practices, and contain local myths that explain the customs or rituals. However, folklore goes beyond religious or supernatural beliefs and practices, and encompasses the entire body of social tradition whose chief vehicle of transmission is oral or outside institutional channels. Folk art of India The folk and tribal arts of India speak volumes a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urdu-language Literature
Urdu (; , , ) is an Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan language spoken chiefly in South Asia. It is the Languages of Pakistan, national language and ''lingua franca'' of Pakistan. In India, it is an Eighth Schedule to the Constitution of India, Eighth Schedule language, the status and cultural heritage of which are recognised by the Constitution of India. Quote: "The Eighth Schedule recognizes India's national languages as including the major regional languages as well as others, such as Sanskrit and Urdu, which contribute to India's cultural heritage. ... The original list of fourteen languages in the Eighth Schedule at the time of the adoption of the Constitution in 1949 has now grown to twenty-two." Quote: "As Mahapatra says: "It is generally believed that the significance for the Eighth Schedule lies in providing a list of languages from which Hindi is directed to draw the appropriate forms, style and expressions for its enrichment" ... Being recognized in the Constitution, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persian Fairy Tales
Persian may refer to: * People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language ** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples ** Persian language, an Iranian language of the Indo-European family, native language of ethnic Persians *** Persian alphabet, a writing system based on the Arabic script * People and things from the historical Persian Empire Other uses * Persian (patience), a card game * Persian (roll), a pastry native to Thunder Bay, Ontario * Persian (wine) * Persian, Indonesia, on the island of Java * Persian cat, a long-haired breed of cat characterized by its round face and shortened muzzle * The Persian, a character from Gaston Leroux's ''The Phantom of the Opera'' * The Persians, an ancient Greek tragedy play written by the Athenian playwright Aeschylus in the 5th century BC * ''Persa'' (play) or ''The Persian'', comedy by the Roman playwright Plautus * Persian, a generation I Pokémon sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persian-language Literature
Persian ( ), also known by its endonym and exonym, endonym Farsi (, Fārsī ), is a Western Iranian languages, Western Iranian language belonging to the Iranian languages, Iranian branch of the Indo-Iranian languages, Indo-Iranian subdivision of the Indo-European languages. Persian is a pluricentric language predominantly spoken and used officially within Iran, Afghanistan, and Tajikistan in three mutual intelligibility, mutually intelligible standard language, standard varieties, respectively Iranian Persian (officially known as ''Persian''), Dari, Dari Persian (officially known as ''Dari'' since 1964), and Tajik language, Tajiki Persian (officially known as ''Tajik'' since 1999).Siddikzoda, S. "Tajik Language: Farsi or not Farsi?" in ''Media Insight Central Asia #27'', August 2002. It is also spoken natively in the Tajik variety by a significant population within Uzbekistan, as well as within other regions with a Persianate society, Persianate history in the cultural sphere o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Folklore
The folklore of India encompasses the folklore of the Republic of India and the Indian subcontinent. India is an ethnically and religiously diverse country. Given this diversity, it is difficult to generalize the vast folklore of India as a unit. Although India is a Hindu-majority country, with more than three-fourths of the population identifying themselves as Hindus, there is no single, unified, and all-pervading concept of identity present in it. Various heterogeneous traditions, numerous regional cultures and different religions to grow and flourish here. Folk religion in Hinduism may explain the rationale behind local religious practices, and contain local myths that explain the customs or rituals. However, folklore goes beyond religious or supernatural beliefs and practices, and encompasses the entire body of social tradition whose chief vehicle of transmission is oral or outside institutional channels. Folk art of India The folk and tribal arts of India speak volumes a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chishti Order
The Chishti order () is a Sufi Tariqa, order of Sunni Islam named after the town of Chishti Sharif District, Chisht, Afghanistan where it was initiated by Abu Ishaq Shami. The order was brought to Herat and later spread across South Asia by Mu'in al-Din Chishti in the city of Ajmer. The Chishti order is known for its emphasis on love, tolerance, and openness. The Chishti order is primarily followed in Afghanistan and the Indian subcontinent. The Chishti order was the first of the four main Sufi orders that became well-established in South Asia, which are the Qadiriyya, Qadiri, Chishti, Naqshbandi and Suhrawardiyya, Suhrawardi Sufi orders. Moinuddin Chishti, Khwaja Muinuddin Chishti introduced the Chishti Order in Ajmer (Rajasthan, India) sometime in the middle of the 12th century. He was eighth in the line of succession from the founder of the Chishti Order, Abu Ishaq Shami. There are now several branches of the order, which has been the most prominent South Asian Sufi brother ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dervish
Dervish, Darvesh, or Darwīsh (from ) in Islam can refer broadly to members of a Sufi fraternity (''tariqah''), or more narrowly to a religious mendicant, who chose or accepted material poverty. The latter usage is found particularly in Persian and Turkish (''derviş'') as well as in Tamazight (''Aderwic''), corresponding to the Arabic term '' faqīr''. Their focus is on the universal values of love and service, deserting the illusions of ego (''nafs'') to reach God. In most Sufi orders, a dervish is known to practice ''dhikr'' through physical exertions or religious practices to attain the ecstatic trance to reach God. Their most popular practice is Sama, which is associated with the 13th-century mystic Rumi. In folklore and with adherents of Sufism, dervishes are often credited with the ability to perform miracles and ascribed supernatural powers. Historically, the term Dervish has also been used more loosely, as the designation of various Islamic political movements or mil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sufi Literature
Sufi literature consists of works in various languages that express and advocate the ideas of Sufism. Sufism had an important influence on medieval literature, especially poetry, that was written in Arabic, Persian, Punjabi, Turkic, Sindhi and Urdu. Sufi doctrines and organizations provided more freedom to literature than did the court poetry of the period. The Sufis borrowed elements of folklore in their literature. The works of Nizami, Nava'i, Hafez, Sam'ani and Jami were more or less related to Sufism. The verse of such Sufi poets as Sanai (died c. 1140), Attar (born c. 1119), and Rumi (died 1273) protested against oppression with an emphasis on divine justice and criticized evil rulers, religious fanaticism and the greed and hypocrisy of the orthodox Muslim clergy. The poetic forms used by these writers were similar to the folk song, parable and fairy tale. Authors of Sufi folk literature particularly borrowed preexisting poetic forms, songs, and narrative structure to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |