|
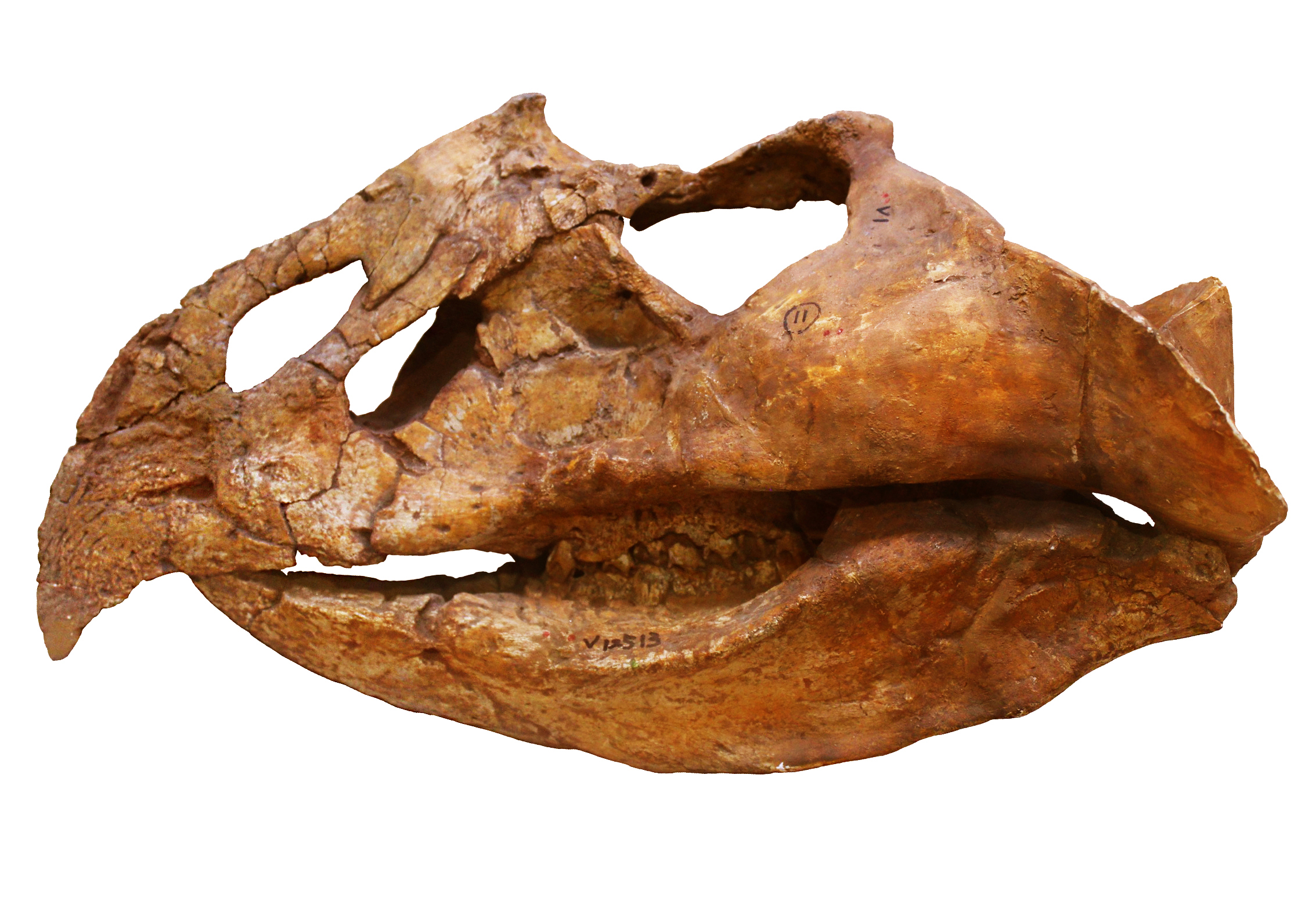
Bagaceratops Rozhdestvenskyi
''Bagaceratops'' (meaning "small-horned face") is a genus of small protoceratopsid dinosaurs that lived in Asia during the Late Cretaceous, around 72 to 71 million years ago. ''Bagaceratops'' remains have been reported from the Barun Goyot Formation and Bayan Mandahu Formation. One specimen may argue the possible presence of ''Bagaceratops'' in the Djadochta Formation. ''Bagaceratops'' was among the smallest ceratopsians, growing up to in length, with a weight about . Although emerging late in the reign of the dinosaurs, ''Bagaceratops'' had a fairly primitive anatomy—when compared to the much derived ceratopsids—and kept the small body size that characterized early ceratopsians. Unlike its close relative, ''Protoceratops'', ''Bagaceratops'' lacked premaxillary teeth (cylindrical, blunt teeth near the tip of the upper jaw). History of discovery During the large field work of the Polish-Mongolian Palaeontological Expeditions in the 1970s, abundant protoceratopsid speci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the more recent of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''creta'', the Latin word for the white limestone known as chalk. The chalk of northern France and the white cliffs of south-eastern England date from the Cretaceous Period. Climate During the Late Cretaceous, the climate was warmer than present, although throughout the period a cooling trend is evident. The tropics became restricted to equatorial regions and northern latitudes experienced markedly more seasonal climatic conditions. Geography Due to plate tectonics, the Americas were gradually moving westward, causing the Atlantic Ocean to expand. The Western Interior Seaway divided North America into eastern and western halves; Appalachia and Laramidia. India maintained a northward course towards Asia. In the Southern Hemisphere, Aus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monograph
A monograph is generally a long-form work on one (usually scholarly) subject, or one aspect of a subject, typically created by a single author or artist (or, sometimes, by two or more authors). Traditionally it is in written form and published as a book, but it may be an artwork, audiovisual work, or exhibition made up of visual artworks. In library cataloguing, the word has a specific and broader meaning, while in the United States, the Food and Drug Administration uses the term to mean a set of published standards. Written works Academic works The English term ''monograph'' is derived from modern Latin , which has its root in Greek. In the English word, ''mono-'' means and ''-graph'' means . Unlike a textbook, which surveys the state of knowledge in a field, the main purpose of a monograph is to present primary research and original scholarship. This research is presented at length, distinguishing a monograph from an article. For these reasons, publication of a monograph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Beds
Red beds (or redbeds) are sedimentary rocks, typically consisting of sandstone, siltstone, and shale, that are predominantly red in color due to the presence of ferric oxides. Frequently, these red-colored sedimentary strata locally contain thin beds of Conglomerate (geology), conglomerate, marl, limestone, or some combination of these sedimentary rocks. The ferric oxides, which are responsible for the red color of red beds, typically occur as a coating on the grains of sediments comprising red beds. Classic examples of red beds are the Permian and Triassic strata of the western United States and the Devonian Old Red Sandstone facies of Europe. Primary red beds Primary red beds may be formed by the erosion and redeposition of red soils or older red beds, but a fundamental problem with this hypothesis is the relative scarcity of red-colored source sediments of suitable age close to an area of red-bed sediments in Geology of Cheshire, Cheshire, England. Primary red beds may al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Sereno
Paul Callistus Sereno (born October 11, 1957) is a professor of paleontology at the University of Chicago who has discovered several new dinosaur species on several continents, including at sites in Inner Mongolia, Argentina, Morocco and Niger. One of his widely publicized discoveries includes a nearly complete specimen of '' Sarcosuchus imperator'' — commonly referred to as SuperCroc — found in Gadoufaoua, located in the Tenere desert of Niger. Biography Youth and education The son of a mail carrier and an art teacher at Prairie Elementary, Sereno grew up in Naperville, Illinois and graduated from Naperville Central High School. He completed his B.S., Biological Sciences from Northern Illinois University in 1979, M.A. in Vertebrate Paleontology, from Columbia University in 1981, M. Phil. in Geological Sciences in 1981, and Ph.D. in Geological Sciences, in 1987. Career Sereno was named one of ''People'' magazine's 50 Most Beautiful People (1997). Sereno co-fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breviceratops Kozlowskii
''Breviceratops'' (meaning "short horned face") is a genus of protoceratopsid dinosaur that lived during the Late Cretaceous in what is now the Barun Goyot Formation, Mongolia. Discovery and naming The first fossils were discovered during the 1960s by the Polish expedition to the Nemegt Basin of Gobi Desert. The specimens were originally described by Teresa Maryańska and Halszka Osmólska in 1975 and named as a second species of ''Protoceratops'', ''Protoceratops kozlowskii'', the specific name honouring Polish paleontologist Roman Kozłowski. The holotype, ZPAL MgD-I/117, was found in the Khulsan locality of the Barun Goyot Formation dating from the Late Campanian. It consists of a partial juvenile postcranial skeleton with skull. Other specimens were referred from the Hermiin Tsav and Khulsan localities: MgD-I/116, a skull and lower jaws of a small juvenile; MgD-I/118, fragmentary postcrania and lower jaws of a juvenile; MgD-I/119, a dentary and three neural arches; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnirostris Holotype
''Bagaceratops'' (meaning "small-horned face") is a genus of small protoceratopsid dinosaurs that lived in Asia during the Late Cretaceous, around 72 to 71 million years ago. ''Bagaceratops'' remains have been reported from the Barun Goyot Formation and Bayan Mandahu Formation. One specimen may argue the possible presence of ''Bagaceratops'' in the Djadochta Formation. ''Bagaceratops'' was among the smallest ceratopsians, growing up to in length, with a weight about . Although emerging late in the reign of the dinosaurs, ''Bagaceratops'' had a fairly primitive anatomy—when compared to the much derived ceratopsids—and kept the small body size that characterized early ceratopsians. Unlike its close relative, ''Protoceratops'', ''Bagaceratops'' lacked premaxillary teeth (cylindrical, blunt teeth near the tip of the upper jaw). History of discovery During the large field work of the Polish-Mongolian Palaeontological Expeditions in the 1970s, abundant protoceratopsid speci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anagenetic
Anagenesis is the gradual evolution of a species that continues to exist as an interbreeding population. This contrasts with cladogenesis, which occurs when branching or splitting occurs, leading to two or more lineages and resulting in separate species. Anagenesis does not always lead to the formation of a new species from an ancestral species. When speciation does occur as different lineages branch off and cease to interbreed, a core group may continue to be defined as the original species. The evolution of this group, without extinction or species selection, is anagenesis. Hypotheses One hypothesis is that during the speciation event in anagenetic evolution, the original populations increases quickly, and then racks up genetic variation over long periods of time by mutation and recombination in a stable environment. Other factors, such as selection or genetic drift will have such a significant effect on genetic material and physical traits that a species can be acknowled ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
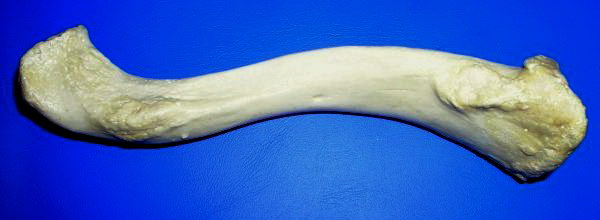
Clavicle
The clavicle, collarbone, or keybone is a slender, S-shaped long bone approximately long that serves as a strut between the scapula, shoulder blade and the sternum (breastbone). There are two clavicles, one on each side of the body. The clavicle is the only long bone in the body that lies horizontally. Together with the shoulder blade, it makes up the shoulder girdle. It is a palpable bone and, in people who have less fat in this region, the location of the bone is clearly visible. It receives its name from Latin ''clavicula'' 'little key' because the bone rotates along its axis like a key when the shoulder is Abduction (kinesiology), abducted. The clavicle is the most commonly fractured bone. It can easily be fractured by impacts to the shoulder from the force of falling on outstretched arms or by a direct hit. Structure The collarbone is a thin doubly curved long bone that connects the human arm, arm to the torso, trunk of the body. Located directly above the first rib, it ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bagaceratops Specimen MPC-D 100 551B
''Bagaceratops'' (meaning "small-horned face") is a genus of small protoceratopsid dinosaurs that lived in Asia during the Late Cretaceous, around 72 to 71 million years ago. ''Bagaceratops'' remains have been reported from the Barun Goyot Formation and Bayan Mandahu Formation. One specimen may argue the possible presence of ''Bagaceratops'' in the Djadochta Formation. ''Bagaceratops'' was among the smallest ceratopsians, growing up to in length, with a weight about . Although emerging late in the reign of the dinosaurs, ''Bagaceratops'' had a fairly primitive anatomy—when compared to the much derived ceratopsids—and kept the small body size that characterized early ceratopsians. Unlike its close relative, ''Protoceratops'', ''Bagaceratops'' lacked premaxillary teeth (cylindrical, blunt teeth near the tip of the upper jaw). History of discovery During the large field work of the Polish-Mongolian Palaeontological Expeditions in the 1970s, abundant protoceratopsid specimens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bagaceratops KID 196 Specimen
''Bagaceratops'' (meaning "small-horned face") is a genus of small protoceratopsid dinosaurs that lived in Asia during the Late Cretaceous, around 72 to 71 million years ago. ''Bagaceratops'' remains have been reported from the Barun Goyot Formation and Bayan Mandahu Formation. One specimen may argue the possible presence of ''Bagaceratops'' in the Djadochta Formation. ''Bagaceratops'' was among the smallest ceratopsians, growing up to in length, with a weight about . Although emerging late in the reign of the dinosaurs, ''Bagaceratops'' had a fairly primitive anatomy—when compared to the much derived ceratopsids—and kept the small body size that characterized early ceratopsians. Unlike its close relative, ''Protoceratops'', ''Bagaceratops'' lacked premaxillary teeth (cylindrical, blunt teeth near the tip of the upper jaw). History of discovery During the large field work of the Polish-Mongolian Palaeontological Expeditions in the 1970s, abundant protoceratopsid speci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatoly Konstantinovich Rozhdestvensky
Anatoly Konstantinovich Rozhdestvensky (, 1920–1983) was a Soviet paleontologist responsible for naming many dinosaurs, including '' Aralosaurus'' and '' Probactrosaurus''. References Soviet paleontologists 1920 births 1983 deaths Russian scientists {{Paleontologist-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleontologist
Paleontology, also spelled as palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of the life of the past, mainly but not exclusively through the study of fossils. Paleontologists use fossils as a means to classify organisms, measure geologic time, and assess the interactions between prehistoric organisms and their natural environment. While paleontological observations are known from at least the 6th century BC, the foundation of paleontology as a science dates back to the work of Georges Cuvier in 1796. Cuvier demonstrated evidence for the concept of extinction and how life of the past was not necessarily the same as that of the present. The field developed rapidly over the course of the following decades, and the French word ''paléontologie'' was introduced for the study in 1822, which was derived from the Ancient Greek word for "ancient" and words describing relatedness and a field of study. Further advances in the field accompanied the work of Charles Darwin who popu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |