|
Badovas
Badovas or Bantovas () is a rock in the Meteora rock formation complex of Thessaly Thessaly ( ; ; ancient Aeolic Greek#Thessalian, Thessalian: , ) is a traditional geographic regions of Greece, geographic and modern administrative regions of Greece, administrative region of Greece, comprising most of the ancient Thessaly, a ..., Greece. Monasteries The Monastery of St. Nicholas of Badova / Nikolaus Kofina (Agiou Nikolaou tou Bantova, Αγίου Νικολάου του Μπάντοβα / Agiou Nikolaou Kofina, Αγίου Νικολάου Κοφινά) () was founded 1400 in a rock cave at Badovas. In 1943, it was bombed and destroyed by the Germans. The ruins of the Monastery of St. Nicholas of Petra (St. Nicholas of Skala) (Μονή Αγίου Νικολάου της Πέτρας) () are also located on Badovas Rock, just to the west of the monastery of St. Nicholas of Badova. Access The rock can be reached via a trail that branches off from the gate of the main road le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meteora
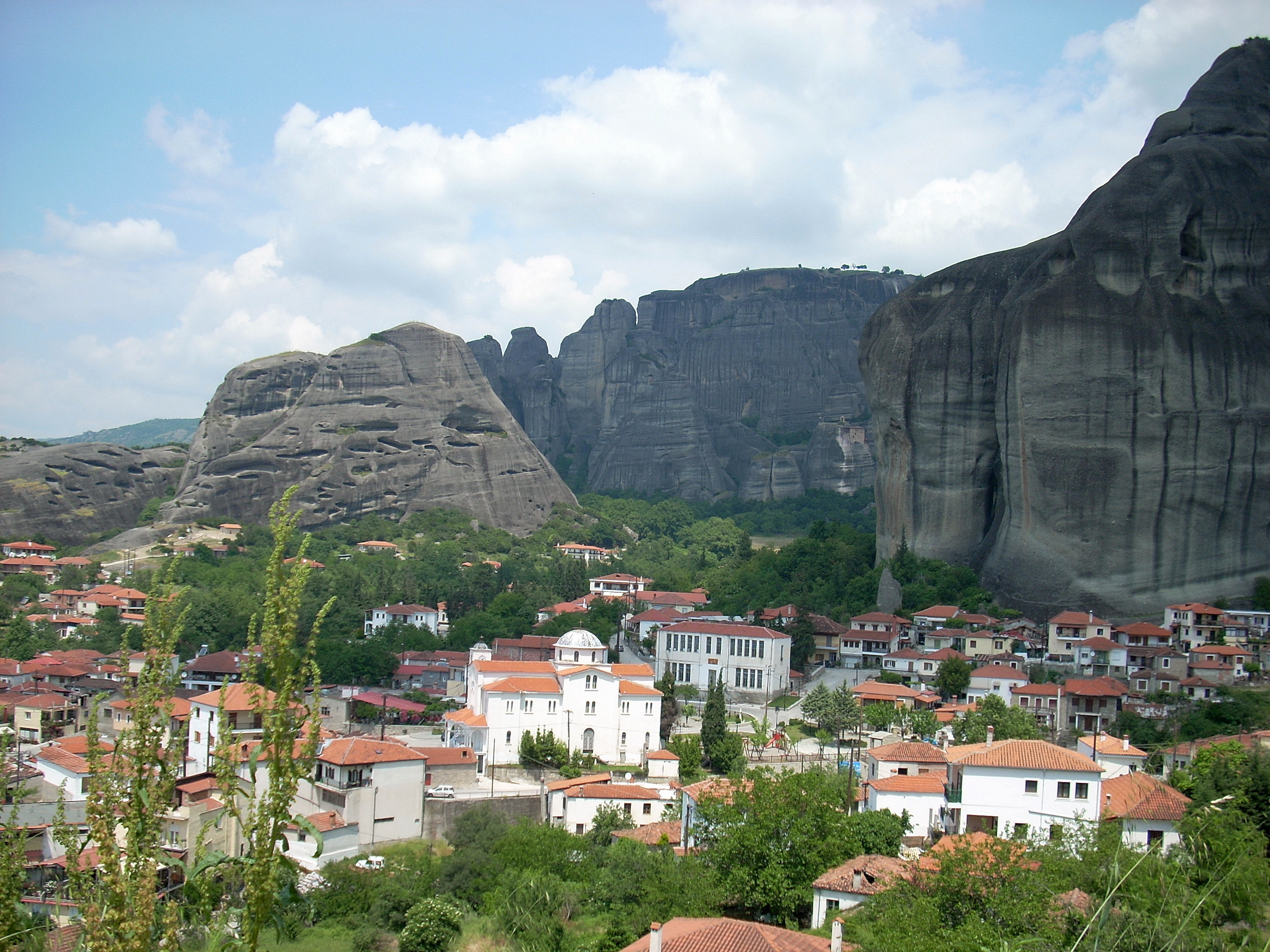
The Meteora (; , ) is a rock formation in the regional unit of Trikala, in Thessaly, in northwestern Greece, hosting one of the most prominent complexes of Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Orthodox monastery, monasteries, viewed locally as second in importance only to Mount Athos.Sofianos, D.Z.: "Metéora". Holy Monastery of Great Meteoro, 1991. Twenty-four monasteries were established atop the giant natural pillars and hill-like rounded boulders that dominate the local area, mainly from the second half of the 14th century under the local rule of Simeon Uroš. Six of these are still active and open to visitors: the monasteries of Monastery of Great Meteoron, Great Meteoron (est. 1356), Monastery of Varlaam, Varlaam, Monastery of St. Nicholas Anapausas, Saint Nicholas Anapausas, Monastery of Rousanou, Rousanou, Monastery of the Holy Trinity, Meteora, Holy Trinity, and Monastery of Saint Stephen (Meteora), Saint Stephen. The latter became a community of nuns in 1961, whereas th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
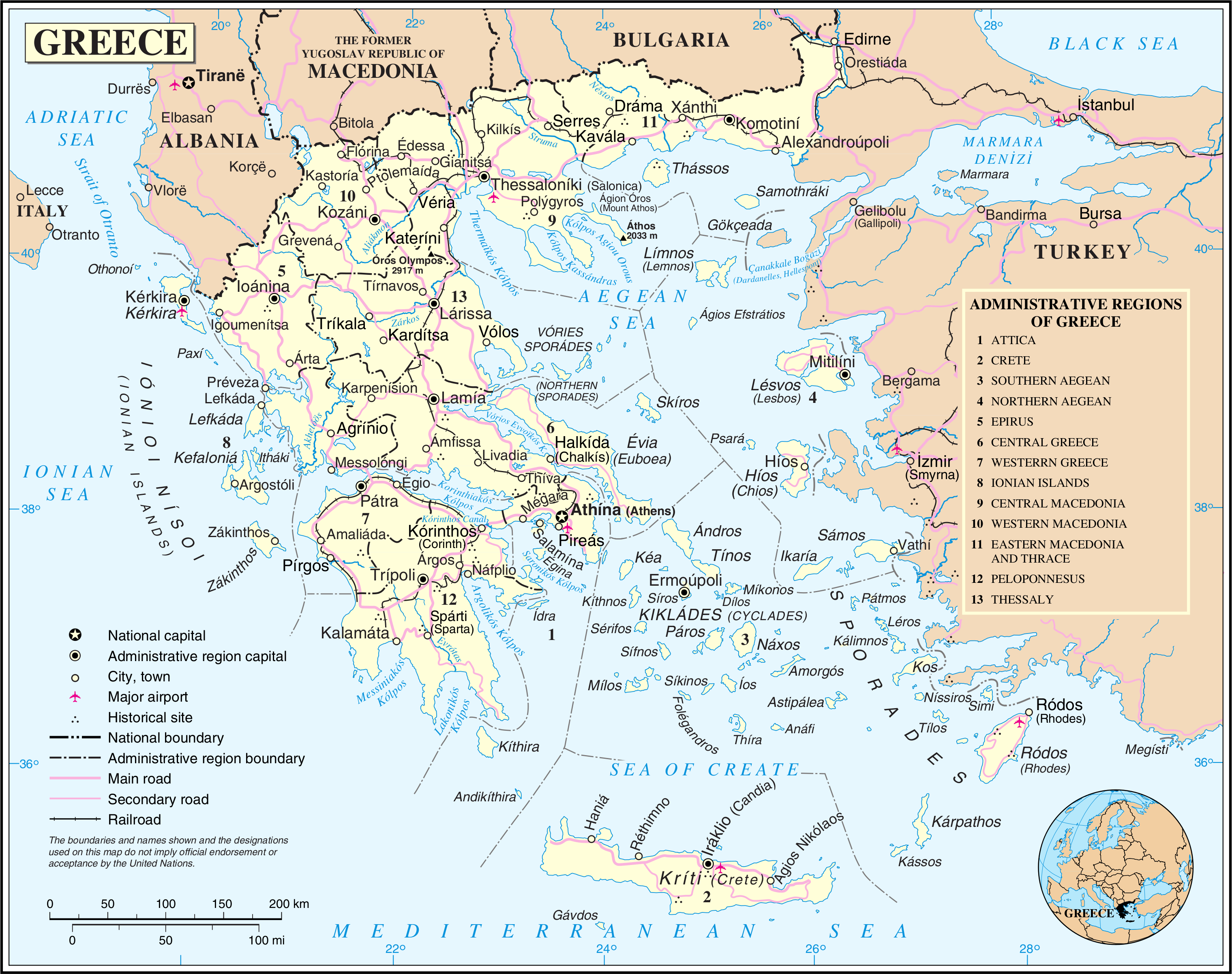
Greece
Greece, officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. Located on the southern tip of the Balkan peninsula, it shares land borders with Albania to the northwest, North Macedonia and Bulgaria to the north, and Turkey to the east. The Aegean Sea lies to the east of the Geography of Greece, mainland, the Ionian Sea to the west, and the Sea of Crete and the Mediterranean Sea to the south. Greece has the longest coastline on the Mediterranean Basin, spanning List of islands of Greece, thousands of islands and nine Geographic regions of Greece, traditional geographic regions. It has a population of over 10 million. Athens is the nation's capital and List of cities and towns in Greece, largest city, followed by Thessaloniki and Patras. Greece is considered the cradle of Western culture, Western civilisation and the birthplace of Athenian democracy, democracy, Western philosophy, Western literature, historiography, political science, major History of science in cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thessaly
Thessaly ( ; ; ancient Aeolic Greek#Thessalian, Thessalian: , ) is a traditional geographic regions of Greece, geographic and modern administrative regions of Greece, administrative region of Greece, comprising most of the ancient Thessaly, ancient region of the same name. Before the Greek Dark Ages, Thessaly was known as Aeolia (, ), and appears thus in Homer's ''Odyssey''. Thessaly Convention of Constantinople (1881), became part of the modern Greek state in 1881, after four and a half centuries of Ottoman Greece, Ottoman rule. Since 1987 it has formed one of the country's 13 Modern regions of Greece, regions and is further (since the Kallikratis reform of 2011) sub-divided into five regional units of Greece, regional units and 25 municipalities of Greece, municipalities. The capital of the region is Larissa. Thessaly lies in northern central Greece and borders the regions of Macedonia (Greece), Macedonia to the north, Epirus (region), Epirus to the west, Central Greece (geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Administrative Regions Of Greece
The regions of Greece () are the country's thirteen second-level administrative divisions of Greece, administrative entities, counting decentralized administrations of Greece as first-level. Regions are divided into regional units of Greece, regional units, known as prefectures of Greece, prefectures until 2011. History The current regions were established in July 1986 (the presidential decree officially establishing them was signed in 1987), by decision of the interior minister, Menios Koutsogiorgas, as second-level administrative entities, complementing the Prefectures of Greece, prefectures (Law 1622/1986). Ν.1622/86 "Τοπική Αυτοδιοίκηση - Περιφερειακή Ανάπτυξη - Δημοκρατικός Προγραμματισμός", (ΦΕΚ 92/τ.Α΄/14-7-1986) Before 1986, there was a traditional division into broad geographic regions of Greece, historical–geographical regions (γεωγραφικά διαμερίσματα), which, however, was of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trikala (regional Unit)
Trikala () is one of the regional units of Greece, forming the northwestern part of the modern regions of Greece, region of Thessaly. Its capital is the city of Trikala. The regional unit includes the town of Kalampaka and the Meteora monastery complex, the town of Pyli, the town of Farkadona and the mountain range of south Pindus with its destinations (i.e. Pyli's stone bridge, Basilica Church of Porta Panagia, Elati, Pertouli, Palaiokarya's stone bridge and waterfall, Pertouli Ski Center etc.) Geography Trikala borders the regional units of Karditsa (regional unit), Karditsa to the south, Arta (regional unit), Arta to the southwest, Ioannina (regional unit), Ioannina to the west, Grevena (regional unit), Grevena to the north and Larissa (regional unit), Larissa to the east. The southeastern part belongs to the Thessalian Plain. The forested Pindus mountain range dominates the western part. The northern part of Trikala is also mountainous and made up of forests and barren lands, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regional Units Of Greece
The 74 regional units of Greece (, ; singular , ) are the country's third-level administrative units (counting decentralized administrations as first-level). They are subdivisions of the country's 13 regions, and are further divided into municipalities A municipality is usually a single administrative division having municipal corporation, corporate status and powers of self-government or jurisdiction as granted by national and regional laws to which it is subordinate. The term ''municipality' .... They were introduced as part of the Kallikratis administrative reform on 1 January 2011 and are comparable in area and, on the mainland, coterminous with the "pre-Kallikratis" prefectures of Greece. List References {{Articles on second-level administrative divisions of European countries Regional units Greece transport-related lists Subdivisions of Greece ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kalabaka
Kalabaka (, ''Kalabáka'', alternative transliterations are ''Kalambaka'' and ''Kalampaka'') is a town and seat of the municipality of Meteora (municipality), Meteora in the Trikala (regional unit), Trikala regional unit, part of Thessaly in Greece. The population was 11,492 at the 2021 census, of which 8,573 in the town proper. The Meteora monasteries are located near the town. Kalabaka is the northwestern terminal of the old Thessaly Railways, now part of Hellenic Railways Organisation, OSE. History A Greek inscription on the wall of one of the town's oldest churches (Saint John the Baptist) testifies to the existence of an ancient Greek settlement under the name Aiginion. In the 10th century AD, it was known as Stagoi (Σταγοί), a Byzantine fortress and bishopric (the name is still in use for the town by the Greek Orthodox Church). Of its medieval monuments, only the cathedral, the Church of the Dormition of the Theotokos, Dormition, survives. It was a late 11th or e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rock Formation
A rock formation is an isolated, scenic, or spectacular surface rock (geology), rock outcrop. Rock formations are usually the result of weathering and erosion sculpting the existing rock. The term ''rock Geological formation, formation'' can also refer to specific sedimentary stratum, strata or other rock unit in stratigraphy, stratigraphic and petrology, petrologic studies. A rock structure can be created in any rock type or combination: * Igneous rocks are created when molten rock cools and solidifies, with or without crystallisation. They may be either plutonic bodies or volcanic extrusive. Again, erosive forces sculpt their current forms. * Metamorphic rocks are created by rocks that have been transformed into another kind of rock, usually by some combination of heat, pressure, and chemical alteration. * Sedimentary rocks are created by a variety of processes but usually involving deposition, grain by grain, layer by layer, in water or, in the case of terrestrial se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monastery Of St
A monastery is a building or complex of buildings comprising the domestic quarters and workplaces of Monasticism, monastics, monks or nuns, whether living in Cenobitic monasticism, communities or alone (hermits). A monastery generally includes a place reserved for prayer which may be a chapel, Church (building), church, or temple, and may also serve as an Oratory (worship), oratory, or in the case of Cenobium, communities anything from a single building housing only one senior and two or three junior monks or nuns, to vast complexes and estates housing tens or hundreds. A monastery complex typically comprises a number of buildings which include a church, dormitory, cloister, refectory, library, Wiktionary:balneary, balneary and Hospital, infirmary and outlying Monastic grange, granges. Depending on the location, the monastic order and the occupation of its inhabitants, the complex may also include a wide range of buildings that facilitate self-sufficiency and service to the commun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyxari
Pyxari or Pixari () is a rock in the Meteora rock formation complex of Thessaly Thessaly ( ; ; ancient Aeolic Greek#Thessalian, Thessalian: , ) is a traditional geographic regions of Greece, geographic and modern administrative regions of Greece, administrative region of Greece, comprising most of the ancient Thessaly, a ..., Greece. Pyxari is located at the southwestern edge of the Meteora rock complex. Monasteries and hermitages The rock has cave hermitages perched on cliffs, which were formerly inhabited by Christian ascetics. The Monastery of St. Anthony (Agiou Antoniou, Αγίου Αντωνίου) was built around the 14th century on the south side of Pyxari Rock. Only a small church has survived from the monastery (). It is located just to the east of the Monastery of Saint Gregory the Theologian. The historic Cell of Constantius (Κελί του Κωνστάντιου) () is located to the northeast of Pyxari Rock. Other hermitages or monasteries at Pyxari inclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rocks Of Meteora
In geology, rock (or stone) is any naturally occurring solid mass or aggregate of minerals or mineraloid matter. It is categorized by the minerals included, its chemical composition, and the way in which it is formed. Rocks form the Earth's outer solid layer, the crust, and most of its interior, except for the liquid outer core and pockets of magma in the asthenosphere. The study of rocks involves multiple subdisciplines of geology, including petrology and mineralogy. It may be limited to rocks found on Earth, or it may include planetary geology that studies the rocks of other celestial objects. Rocks are usually grouped into three main groups: igneous rocks, sedimentary rocks and metamorphic rocks. Igneous rocks are formed when magma cools in the Earth's crust, or lava cools on the ground surface or the seabed. Sedimentary rocks are formed by diagenesis and lithification of sediments, which in turn are formed by the weathering, transport, and deposition of existing rocks. M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cliff Dwellings
In archaeology, cliff dwellings are dwellings formed by using niches or caves in high cliffs, and sometimes with excavation or additions in the way of masonry. Two special types of cliff dwelling are distinguished by archaeologists: the cliff-house, which is actually built on levels in the cliff, and the cavate, which is dug out, by using natural recesses or openings. Rock-cut architecture generally refers to rather grander temples, but also tombs, cut into rock, although for example the Ajanta Caves in India, of the 2nd century BCE to 5th century CE, probably housed several hundred Buddhist monks and are cut into a cliff, as are the Mogao Caves in China. Famous cliff dwellings are found around the world. In China, the Guyaju Caves located near Dongmenying, Yanqing District, Beijing are a cave complex of many rock hewn dwellings that form a community. In the United States and Mexico, among the canyons of the southwest, in Arizona, New Mexico, Utah, Colorado, and Chihuahua, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |