|
Bacterial Outer Membrane Vesicles
Outer membrane vesicles (OMVs) are vesicle (biology and chemistry), vesicles released from the bacterial outer membrane, outer membranes of Gram-negative bacteria. While Gram-positive bacteria release vesicles as well, those vesicles fall under the broader category of bacterial membrane vesicles (MVs). OMVs were the first MVs to be discovered, and are distinguished from outer inner membrane vesicles (OIMVs), which are gram-negative bacterial vesicles containing portions of both the outer and inner bacterial membrane. Outer membrane vesicles were first discovered and characterized using Transmission electron microscopy, transmission-electron microscopy by Indian people, Indian Scientist Prof. Smriti Narayan Chatterjee and J. Das in 1966-67. OMVs are ascribed the functionality to provide a manner to communicate among themselves, with other microorganisms in their environment and with the host. These vesicles are involved in membrane vesicle trafficking, trafficking bacterial cell si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Salmonella Secreting Outer Membrane Vesicles In Vivo In Chicken Ileum %28Original Work Of Dr R C YashRoy%29
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') or modern humans are the most common and widespread species of primate, and the last surviving species of the genus ''Homo''. They are Hominidae, great apes characterized by their Prehistory of nakedness and clothing#Evolution of hairlessness, hairlessness, bipedality, bipedalism, and high Human intelligence, intelligence. Humans have large Human brain, brains, enabling more advanced cognitive skills that facilitate successful adaptation to varied environments, development of sophisticated tools, and formation of complex social structures and civilizations. Humans are Sociality, highly social, with individual humans tending to belong to a Level of analysis, multi-layered network of distinct social groups — from families and peer groups to corporations and State (polity), political states. As such, social interactions between humans have established a wide variety of Value theory, values, norm (sociology), social norms, languages, and traditions (co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quorum Sensing
In biology, quorum sensing or quorum signaling (QS) is the process of cell-to-cell communication that allows bacteria to detect and respond to cell population density by gene regulation, typically as a means of acclimating to environmental disadvantages. Quorum sensing is a type of cellular signaling, and can be more specifically considered a type of paracrine signaling. However, it also contains traits of autocrine signaling: a cell produces both an autoinducer molecule and the receptor for the autoinducer. As one example, quorum sensing enables bacteria to restrict the expression of specific genes to the high cell densities at which the resulting phenotypes will be most beneficial, especially for phenotypes that would be ineffective at low cell densities and therefore too energetically costly to express. Many species of bacteria use quorum sensing to coordinate gene expression according to the density of their local population. In a similar fashion, some social insects use q ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of a cell from the outside environment (the extracellular space). The cell membrane consists of a lipid bilayer, made up of two layers of phospholipids with cholesterols (a lipid component) interspersed between them, maintaining appropriate membrane fluidity at various temperatures. The membrane also contains membrane proteins, including integral proteins that span the membrane and serve as membrane transporters, and peripheral proteins that loosely attach to the outer (peripheral) side of the cell membrane, acting as enzymes to facilitate interaction with the cell's environment. Glycolipids embedded in the outer lipid layer serve a similar purpose. The cell membrane controls the movement of substances in and out of a cell, being selectively permeable to ions and organic mole ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lipid Bilayer
The lipid bilayer (or phospholipid bilayer) is a thin polar membrane made of two layers of lipid molecules. These membranes form a continuous barrier around all cell (biology), cells. The cell membranes of almost all organisms and many viruses are made of a lipid bilayer, as are the nuclear envelope, nuclear membrane surrounding the cell nucleus, and biological membrane, membranes of the membrane-bound organelles in the cell. The lipid bilayer is the barrier that keeps ions, proteins and other molecules where they are needed and prevents them from diffusing into areas where they should not be. Lipid bilayers are ideally suited to this role, even though they are only a few nanometers in width, because they are impermeable to most water-soluble (hydrophilic) molecules. Bilayers are particularly impermeable to ions, which allows cells to regulate salt concentrations and pH by transporting ions across their membranes using proteins called Ion transporter, ion pumps. Biological bilaye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reuters
Reuters ( ) is a news agency owned by Thomson Reuters. It employs around 2,500 journalists and 600 photojournalists in about 200 locations worldwide writing in 16 languages. Reuters is one of the largest news agencies in the world. The agency was established in London in 1851 by Paul Reuter. The Thomson Corporation of Canada acquired the agency in a 2008 corporate merger, resulting in the formation of the Thomson Reuters Corporation. In December 2024, Reuters was ranked as the 27th most visited news site in the world, with over 105 million monthly readers. History 19th century Paul Julius Reuter worked at a book-publishing firm in Berlin and was involved in distributing radical pamphlets at the beginning of the Revolutions of 1848. These publications brought much attention to Reuter, who in 1850 developed a prototype news service in Aachen using homing pigeons and electric telegraphy from 1851 on, in order to transmit messages between Brussels and Aachen, in what today is Aa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gonorrhea
Gonorrhoea or gonorrhea, colloquially known as the clap, is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the bacterium ''Neisseria gonorrhoeae''. Infection may involve the genitals, mouth, or rectum. Gonorrhea is spread through sexual contact with an infected person, or from a vertical transmission, mother to a child during birth. Infected males may experience Dysuria, pain or burning with urination, discharge from the Human penis, penis, or testicular pain. Infected females may experience burning with urination, vaginal discharge, vaginal bleeding between Menstruation, periods, or pelvic pain. Complications in females include pelvic inflammatory disease and in males include epididymitis, inflammation of the epididymis. Many of those infected, however, have no symptoms. If untreated, gonorrhea can spread to septic arthritis, joints or endocarditis, heart valves. Globally, gonorrhea affects about 0.8% of women and 0.6% of men. An estimated 33 to 106 million new cases occu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meningitis
Meningitis is acute or chronic inflammation of the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord, collectively called the meninges. The most common symptoms are fever, intense headache, vomiting and neck stiffness and occasionally photophobia. Other symptoms include confusion or altered consciousness, nausea, and an inability to tolerate loud noises. Young children often exhibit only nonspecific symptoms, such as irritability, drowsiness, or poor feeding. A non-blanching rash (a rash that does not fade when a glass is rolled over it) may also be present. The inflammation may be caused by infection with viruses, bacteria, fungi or parasites. Non-infectious causes include malignancy (cancer), subarachnoid hemorrhage, chronic inflammatory disease ( sarcoidosis) and certain drugs. Meningitis can be life-threatening because of the inflammation's proximity to the brain and spinal cord; therefore, the condition is classified as a medical emergency. A lumba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meningococcal Vaccine
Meningococcal vaccine refers to any vaccine used to prevent infection by '' Neisseria meningitidis''. Different versions are effective against some or all of the following types of meningococcus: A, B, C, W-135, and Y. The vaccines are between 85 and 100% effective for at least two years. They result in a decrease in meningitis and sepsis among populations where they are widely used. They are given either by injection into a muscle or just under the skin. The World Health Organization recommends that countries with a moderate or high rate of disease or with frequent outbreaks should routinely vaccinate. In countries with a low risk of disease, they recommend that high-risk groups should be immunized. In the African meningitis belt efforts to immunize all people between the ages of one and thirty with the meningococcal A conjugate vaccine are ongoing. In Canada and the United States the vaccines are effective against four types of meningococcus (A, C, W, and Y) are recomme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infection
An infection is the invasion of tissue (biology), tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host (biology), host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable disease, is an Disease#Terminology, illness resulting from an infection. Infections can be caused by a wide range of pathogens, most prominently pathogenic bacteria, bacteria and viruses. Hosts can fight infections using their immune systems. Mammalian hosts react to infections with an Innate immune system, innate response, often involving inflammation, followed by an Adaptive immune system, adaptive response. Treatment for infections depends on the type of pathogen involved. Common medications include: * Antibiotics for bacterial infections. * Antivirals for viral infections. * Antifungals for fungal infections. * Antiprotozoals for protozoan infections. * Antihelminthics for infections caused by parasi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vaccines
A vaccine is a biological preparation that provides active acquired immunity to a particular infectious or malignant disease. The safety and effectiveness of vaccines has been widely studied and verified. A vaccine typically contains an agent that resembles a disease-causing microorganism and is often made from weakened or killed forms of the microbe, its toxins, or one of its surface proteins. The agent stimulates the body's immune system to recognize the agent as a threat, destroy it, and recognize further and destroy any of the microorganisms associated with that agent that it may encounter in the future. Vaccines can be prophylactic (to prevent or alleviate the effects of a future infection by a natural or "wild" pathogen), or therapeutic (to fight a disease that has already occurred, such as cancer). Some vaccines offer full sterilizing immunity, in which infection is prevented. The administration of vaccines is called vaccination. Vaccination is the most effective ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pathogen
In biology, a pathogen (, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of"), in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a Germ theory of disease, germ. The term ''pathogen'' came into use in the 1880s. Typically, the term ''pathogen'' is used to describe an ''infectious'' microorganism or agent, such as a virus, bacterium, protozoan, prion, viroid, or fungus. Small animals, such as helminths and insects, can also cause or Transmission (medicine), transmit disease. However, these animals are usually referred to as parasites rather than pathogens. The scientific study of microscopic organisms, including microscopic pathogenic organisms, is called microbiology, while parasitology refers to the scientific study of parasites and the organisms that host them. There are several pathways through which pathogens can invade a host. The principal pathways have different episodic time ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
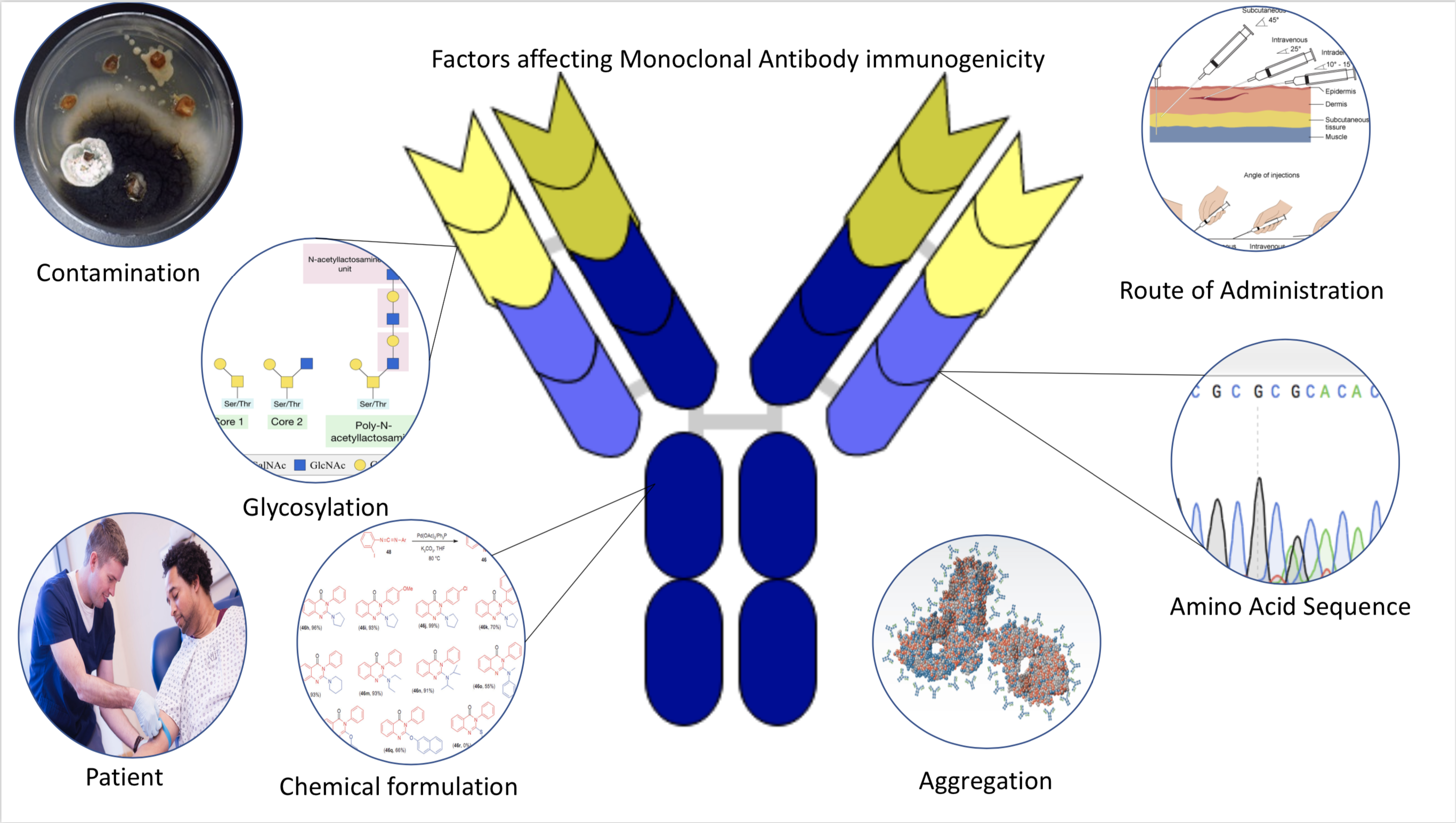
Immunogenic
Immunogenicity is the ability of a foreign substance, such as an antigen, to provoke an immune response in the body of a human or other animal. It may be wanted or unwanted: * Wanted immunogenicity typically relates to vaccines, where the injection of an antigen (the vaccine) provokes an immune response against the pathogen, protecting the organism from future exposure. Immunogenicity is a central aspect of vaccine development. * Unwanted immunogenicity is an immune response by an organism against a therapeutic antigen. This reaction leads to production of anti-drug-antibodies (ADAs), inactivating the therapeutic effects of the treatment and potentially inducing adverse effects. A challenge in biotherapy is predicting the immunogenic potential of novel protein therapeutics. For example, immunogenicity data from high-income countries are not always transferable to low-income and middle-income countries. Another challenge is considering how the immunogenicity of vaccines changes with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)