|
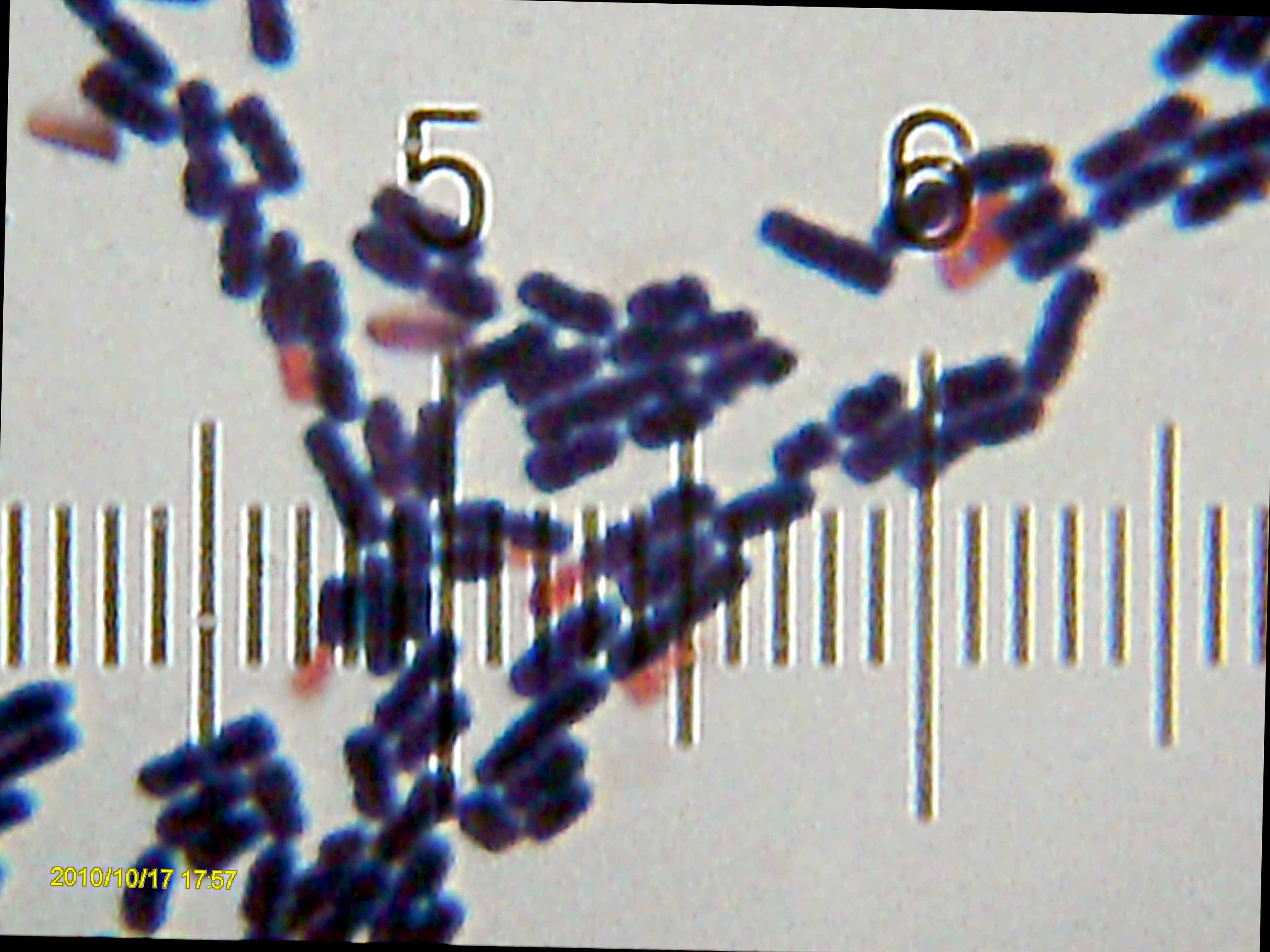
Bacillus Pasteurii
''Sporosarcina pasteurii'' formerly known as ''Bacillus pasteurii'' from older taxonomies, is a gram positive bacterium with the ability to precipitate calcite and solidify sand given a calcium source and urea; through the process of microbiologically induced calcite precipitation (MICP) or biological cementation. ''S. pasteurii'' has been proposed to be used as an ecologically sound biological construction material. Researchers studied the bacteria in conjunction with plastic and hard mineral; forming a material stronger than bone. It is a commonly used for MICP since it is non-pathogenic and is able to produce high amounts of the enzyme urease which hydrolyzes urea to carbonate and ammonia. Physiology ''S. pasteurii'' is a gram positive bacterium that is rod-like shaped in nature. It has the ability to form endospores in the right environmental conditions to enhance its survival, which is a characteristic of its bacillus class. It has dimensions of 0.5 to 1.2 microns in wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Hendricks Bergey
David Hendricks Bergey (1860-1937) was an American bacteriologist. He studied at University of Pennsylvania, where he obtained his Bachelor of Science and Doctor of Medicine degrees in 1884. He practiced medicine in North Wales, Pennsylvania, until 1893. He then joined the university's hygiene laboratory, where he taught hygiene and bacteriology. He led the laboratory from 1929 until his retirement in 1932. During WWI he was on academic leave of absence from 1917 to 1919, when he served in the United States Army Medical Reserve Corps as chief of the laboratory staff at Fort Oglethorpe (Fort Oglethorpe, Georgia), Fort Oglethorpe. His ''Principles of Hygiene'' was first published in 1901 and went through seven editions. He was chairman of the Editorial Board for the first edition of Bergey's Manual of Determinative Bacteriology, published in 1923. The Determinative Manual has subsequently been published in a further eight editions, and Bergey's Manual Trust is currently publishing th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkaliphile
Alkaliphiles are a class of extremophilic microbes capable of survival in alkaline ( pH roughly 8.5–11) environments, growing optimally around a pH of 10. These bacteria can be further categorized as obligate alkaliphiles (those that require high pH to survive), facultative alkaliphiles (those able to survive in high pH, but also grow under normal conditions) and haloalkaliphiles (those that require high salt content to survive).Horikoshi, Koki. "Alkaliphiles: Some applications of their products for biotechnology." Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews 63.4 (1999): 735-50. Print. Background information Microbial growth in alkaline conditions presents several complications to normal biochemical activity and reproduction, as high pH is detrimental to normal cellular processes. For example, alkalinity can lead to denaturation of DNA, instability of the plasma membrane and inactivation of cytosolic enzymes, as well as other unfavorable physiological changes.Higashibata, Akira, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thiamin
Thiamine, also known as thiamin and vitamin B1, is a vitamin – an essential micronutrient for humans and animals. It is found in food and commercially synthesized to be a dietary supplement or medication. Phosphorylated forms of thiamine are required for some metabolic reactions, including the breakdown of glucose and amino acids. Food sources of thiamine include whole grains, legumes, and some meats and fish. Grain processing removes much of the vitamin content, so in many countries cereals and flours are enriched with thiamine. Supplements and medications are available to treat and prevent thiamine deficiency and the disorders that result from it such as beriberi and Wernicke encephalopathy. They are also used to treat maple syrup urine disease and Leigh syndrome. Supplements and medications are typically taken by mouth, but may also be given by intravenous or intramuscular injection. Thiamine supplements are generally well tolerated. Allergic reactions, includin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cysteine
Cysteine (; symbol Cys or C) is a semiessential proteinogenic amino acid with the chemical formula, formula . The thiol side chain in cysteine enables the formation of Disulfide, disulfide bonds, and often participates in enzymatic reactions as a nucleophile. Cysteine is chiral, but both D and L-cysteine are found in nature. LCysteine is a protein monomer in all biota, and D-cysteine acts as a signaling molecule in mammalian nervous systems. Cysteine is named after its discovery in urine, which comes from the urinary bladder or cyst, from Ancient Greek, Greek κύστις ''kýstis'', "bladder". The thiol is susceptible to oxidation to give the disulfide bond, disulfide derivative cystine, which serves an important structural role in many proteins. In this case, the symbol Cyx is sometimes used. The deprotonated form can generally be described by the symbol Cym as well. When used as a food additive, cysteine has the E number E920. Cysteine is Genetic code, encoded by the codo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methionine
Methionine (symbol Met or M) () is an essential amino acid in humans. As the precursor of other non-essential amino acids such as cysteine and taurine, versatile compounds such as SAM-e, and the important antioxidant glutathione, methionine plays a critical role in the metabolism and health of many species, including humans. Methionine is also involved in angiogenesis and various processes related to DNA transcription, epigenetic expression, and gene regulation. Methionine was first isolated in 1921 by John Howard Mueller. It is Genetic code, encoded by the codon AUG. It was named by Satoru Odake in 1925, as an abbreviation of its structural description 2-amino-4-(methylthio)butanoic acid. Biochemical details Methionine (abbreviated as Met or M; encoded by the codon AUG) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated −COO− form under biological pH conditions), an amino group (which is in the proton ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auxotrophy
Auxotrophy ( "to increase"; ''τροφή'' "nourishment") is the inability of an organism to synthesize a particular organic compound required for its growth (as defined by IUPAC). An auxotroph is an organism that displays this characteristic; ''auxotrophic'' is the corresponding adjective. Auxotrophy is the opposite of prototrophy, which is characterized by the ability to synthesize all the compounds needed for growth. Prototrophic cells are self-sufficient producers of all required metabolites (e.g. amino acids, lipids, cofactors), while auxotrophs require to be on medium with the metabolite that they cannot produce. For example, a methionine auxotrophic cell could only grow on a medium that contained methionine; otherwise, it would starve. In this example, this is because it is unable to produce its own methionine. However, a methionine prototrophic cell would be able to function and replicate on a medium with or without methionine. Replica plating is a technique that transfer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microbiologically Induced Calcite Precipitation
Microbiologically induced calcium carbonate precipitation (MICP) is a bio-geochemical process that induces calcium carbonate precipitation within the soil matrix. Biomineralization in the form of calcium carbonate precipitation can be traced back to the Precambrian period. Calcium carbonate can be precipitated in three polymorphic forms, which in the order of their usual stabilities are calcite, aragonite and vaterite. The main groups of microorganisms that can induce the carbonate precipitation are photosynthetic microorganisms such as cyanobacteria and microalgae; sulfate-reducing bacteria; and some species of microorganisms involved in nitrogen cycle. Several mechanisms have been identified by which bacteria can induce the calcium carbonate precipitation, including urea hydrolysis, denitrification, sulfate production, and iron reduction. Two different pathways, or autotrophic and heterotrophic pathways, through which calcium carbonate is produced have been identified. There are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halotolerance
Halotolerance is the adaptation of living organisms to conditions of high salinity. Halotolerant species tend to live in areas such as hypersaline lakes, coastal dunes, saline deserts, salt marshes, and inland salt seas and springs. Halophiles are also organisms that not only live in highly saline environments but also ''require'' the salinity to survive. Halotolerant organisms on the other hand (belonging to different domains of life) can grow under saline conditions, but do not require elevated concentrations of salt for growth. Halophytes are salt-tolerant higher plants. Halotolerant microorganisms are of considerable biotechnological interest. Applications Fields of scientific research relevant to halotolerance include biochemistry, molecular biology, cell biology, physiology, ecology, and genetics. An understanding of halotolerance can be applicable to areas such as arid-zone agriculture, xeriscaping, aquaculture (of fish or algae), bioproduction of desirable compounds (su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bicarbonate
In inorganic chemistry, bicarbonate (IUPAC-recommended nomenclature: hydrogencarbonate) is an intermediate form in the deprotonation of carbonic acid. It is a polyatomic anion with the chemical formula . Bicarbonate serves a crucial biochemical role in the physiological pH buffering system. The term "bicarbonate" was coined in 1814 by the English chemist William Hyde Wollaston. The name lives on as a trivial name. Chemical properties The bicarbonate ion (hydrogencarbonate ion) is an anion with the empirical formula and a molecular mass of 61.01 daltons; it consists of one central carbon atom surrounded by three oxygen atoms in a trigonal planar arrangement, with a hydrogen atom attached to one of the oxygens. It is isoelectronic with nitric acid (). The bicarbonate ion carries a negative one formal charge and is an amphiprotic species which has both acidic and basic properties. It is both the conjugate base of carbonic acid (); and the conjugate acid of , t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbonic Acid
Carbonic acid is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . The molecule rapidly converts to water and carbon dioxide in the presence of water. However, in the absence of water, it is quite stable at room temperature. The interconversion of carbon dioxide and carbonic acid is related to the breathing cycle of animals and the acidification of natural waters. In biochemistry and physiology, the name "carbonic acid" is sometimes applied to aqueous solutions of carbon dioxide. These chemical species play an important role in the bicarbonate buffer system, used to maintain acid–base homeostasis. Terminology in biochemical literature In chemistry, the term "carbonic acid" strictly refers to the chemical compound with the formula . Some biochemistry literature effaces the distinction between carbonic acid and carbon dioxide dissolved in extracellular fluid. In physiology, carbon dioxide excreted by the lungs may be called ''volatile acid'' or ''respiratory acid''. Anh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
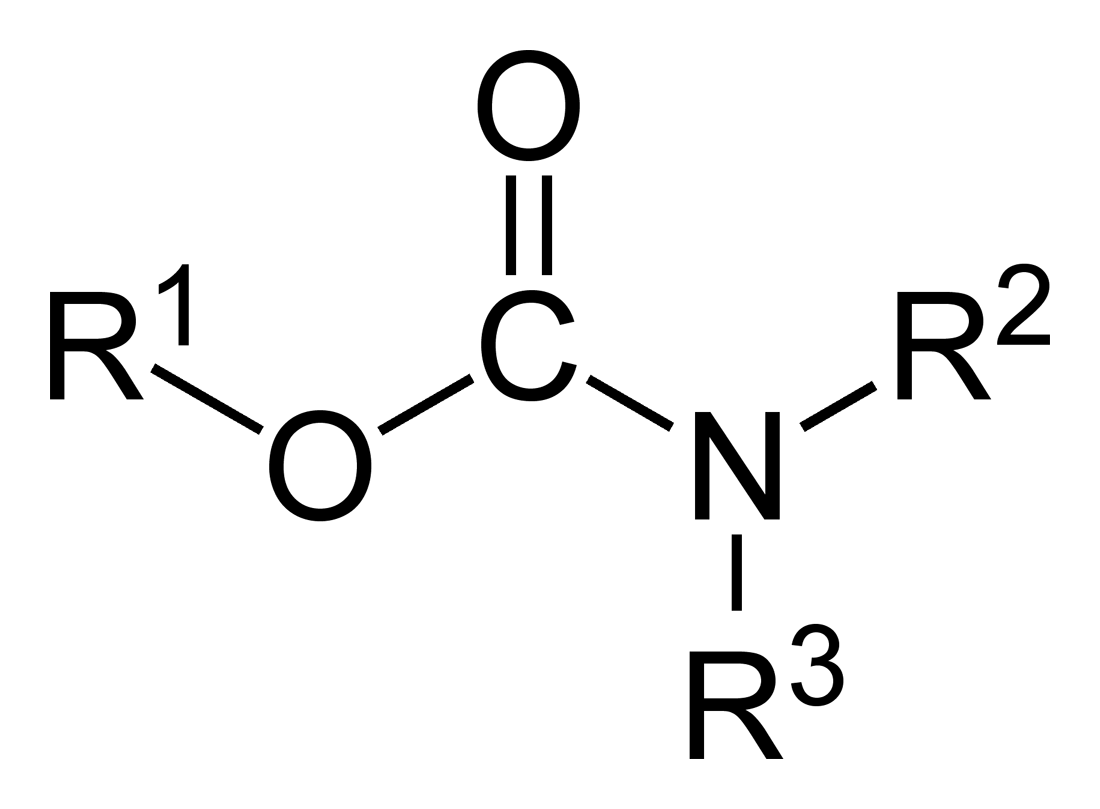
Carbamate
In organic chemistry, a carbamate is a category of organic compounds with the general Chemical formula, formula and Chemical structure, structure , which are formally Derivative (chemistry), derived from carbamic acid (). The term includes organic compounds (e.g., the ester ethyl carbamate), formally obtained by replacing one or more of the hydrogen atoms by other organic functional groups; as well as salt (chemistry), salts with the carbamate anion (e.g. ammonium carbamate). Polymers whose repeat units are joined by carbamate like groups are an important family of plastics, the polyurethanes. See for clarification. Properties While carbamic acids are unstable, many carbamate esters and salt (chemistry), salts are stable and well known. Equilibrium with carbonate and bicarbonate In water solutions, the carbamate anion slowly equilibrates with the ammonium cation and the carbonate or bicarbonate anions: : : Calcium carbamate is soluble in water, whereas calcium carbona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrolysis
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution reaction, substitution, elimination reaction, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water is the nucleophile. Biological hydrolysis is the cleavage of Biomolecule, biomolecules where a water molecule is consumed to effect the separation of a larger molecule into component parts. When a carbohydrate is broken into its component sugar molecules by hydrolysis (e.g., sucrose being broken down into glucose and fructose), this is recognized as saccharification. Hydrolysis reactions can be the reverse of a condensation reaction in which two molecules join into a larger one and eject a water molecule. Thus hydrolysis adds water to break down, whereas condensation builds up by removing water. Types Usually hydrolysis is a chemical process in which a molecule of water is added to a substance. Sometimes this addition causes both the su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |