|
Bacillary Dysentery
Bacillary dysentery is a type of dysentery, and is a severe form of shigellosis. It is associated with species of bacteria from the family Enterobacteriaceae. The term is usually restricted to ''Shigella'' infections. Shigellosis is caused by one of several types of ''Shigella'' bacteria. Three species are associated with bacillary dysentery: ''Shigella sonnei, Shigella flexneri'' and ''Shigella dysenteriae''. A study in China indicated that ''Shigella flexneri'' 2a was the most common serotype. Salmonellosis caused by ''Salmonella enterica'' (serovar ''Typhimurium'') has also been described as a cause of bacillary dysentery, though this definition is less common. It is sometimes listed as an explicit differential diagnosis of bacillary dysentery, as opposed to a cause. Bacillary dysentery should not be confused with diarrhea caused by other bacterial infections. One characteristic of bacillary dysentery is blood in stool, which is the result of invasion of the mucosa by the path ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dysentery
Dysentery ( , ), historically known as the bloody flux, is a type of gastroenteritis that results in bloody diarrhea. Other symptoms may include fever, abdominal pain, and a feeling of incomplete defecation. Complications may include dehydration. The cause of dysentery is usually the bacteria from genus '' Shigella'', in which case it is known as shigellosis, or the amoeba '' Entamoeba histolytica''; then it is called amoebiasis. Other causes may include certain chemicals, other bacteria, other protozoa, or parasitic worms. It may spread between people. Risk factors include contamination of food and water with feces due to poor sanitation. The underlying mechanism involves inflammation of the intestine, especially of the colon. Efforts to prevent dysentery include hand washing and food safety measures while traveling in countries of high risk. While the condition generally resolves on its own within a week, drinking sufficient fluids such as oral rehydration solutio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Traveler's Diarrhea
Travelers' diarrhea (TD) is a stomach and intestinal infection. TD is defined as the passage of unformed stool (one or more by some definitions, three or more by others) while traveling. It may be accompanied by abdominal cramps, nausea, fever, headache and bloating. Occasionally dysentery may occur. Most travelers recover within three to four days with little or no treatment. About 12% of people may have symptoms for a week. Bacteria are responsible for more than half of cases, typically via foodborne illness and waterborne diseases. The bacteria enterotoxigenic ''Escherichia coli'' (ETEC) are typically the most common except in Southeast Asia, where '' Campylobacter'' is more prominent. About 10 to 20 percent of cases are due to norovirus. Protozoa such as ''Giardia'' may cause longer term disease. The risk is greatest in the first two weeks of travel and among young adults. People affected are more often from the developed world. Recommendations for prevention include eat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vaccine
A vaccine is a biological Dosage form, preparation that provides active acquired immunity to a particular infectious disease, infectious or cancer, malignant disease. The safety and effectiveness of vaccines has been widely studied and verified. A vaccine typically contains an agent that resembles a disease-causing microorganism and is often made from weakened or killed forms of the microbe, its toxins, or one of its surface proteins. The agent stimulates the body's immune system to recognize the agent as a threat, destroy it, and recognize further and destroy any of the microorganisms associated with that agent that it may encounter in the future. Vaccines can be prophylaxis, prophylactic (to prevent or alleviate the effects of a future infection by a natural or "wild" pathogen), or therapeutic vaccines, therapeutic (to fight a disease that has already occurred, such as cancer vaccine, cancer). Some vaccines offer full sterilizing immunity, in which infection is prevented. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bactrim
Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole, sold under the trade names Bactrim, Cotrim (a short form of the British Approved Name, Co-trimoxazole) and Septra, among others, is a fixed-dose combination antibiotic medication used to treat a variety of bacterial infections. It consists of one part trimethoprim to five parts sulfamethoxazole. It is used to treat urinary tract infections, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) skin infections, travelers' diarrhea, respiratory tract infections, and cholera, among others. It is used both to treat and prevent pneumocystis pneumonia and toxoplasmosis in people with HIV/AIDS and other causes of immunosuppression. It can be given orally (swallowed by mouth) or intravenous infusion (slowly injected into a vein with an IV). Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. It is available as a generic medication. In 2022, it was the 143rd most commonly prescribed medication in the United Stat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ciprofloxacin
Ciprofloxacin is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic used to treat a number of bacterial infections. This includes bone and joint infections, intra-abdominal infections, certain types of infectious diarrhea, respiratory tract infections, skin infections, typhoid fever, and urinary tract infections, among others. For some infections it is used in addition to other antibiotics. It can be taken by mouth, as eye drops, as ear drops, or intravenously. Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Severe side effects include tendon rupture, hallucinations, and nerve damage. In people with myasthenia gravis, there is worsening muscle weakness. Rates of side effects appear to be higher than some groups of antibiotics such as cephalosporins but lower than others such as clindamycin. Studies in other animals raise concerns regarding use in pregnancy. No problems were identified, however, in the children of a small number of women who took the medication. It appear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infection
An infection is the invasion of tissue (biology), tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host (biology), host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable disease, is an Disease#Terminology, illness resulting from an infection. Infections can be caused by a wide range of pathogens, most prominently pathogenic bacteria, bacteria and viruses. Hosts can fight infections using their immune systems. Mammalian hosts react to infections with an Innate immune system, innate response, often involving inflammation, followed by an Adaptive immune system, adaptive response. Treatment for infections depends on the type of pathogen involved. Common medications include: * Antibiotics for bacterial infections. * Antivirals for viral infections. * Antifungals for fungal infections. * Antiprotozoals for protozoan infections. * Antihelminthics for infections caused by parasi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy, treatment and antibiotic prophylaxis, prevention of such infections. They may either bactericide, kill or bacteriostatic agent, inhibit the growth of bacteria. A limited number of antibiotics also possess antiprotozoal activity. Antibiotics are not effective against viruses such as the ones which cause the common cold or influenza. Drugs which inhibit growth of viruses are termed antiviral drugs or antivirals. Antibiotics are also not effective against fungi. Drugs which inhibit growth of fungi are called antifungal drugs. Sometimes, the term ''antibiotic''—literally "opposing life", from the Greek language, Greek roots ἀντι ''anti'', "against" and βίος ''bios'', "life"—is broadly used to refer to any substance used against ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasite
Parasitism is a Symbiosis, close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives (at least some of the time) on or inside another organism, the Host (biology), host, causing it some harm, and is Adaptation, adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson characterised parasites' way of feeding as "predators that eat prey in units of less than one". Parasites include single-celled protozoans such as the agents of malaria, sleeping sickness, and amoebic dysentery; animals such as hookworms, lice, mosquitoes, and vampire bats; fungi such as Armillaria mellea, honey fungus and the agents of ringworm; and plants such as mistletoe, dodder, and the Orobanchaceae, broomrapes. There are six major parasitic Behavioral ecology#Evolutionarily stable strategy, strategies of exploitation of animal hosts, namely parasitic castration, directly transmitted parasitism (by contact), wikt:trophic, trophicallytransmitted parasitism (by being eaten), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intravenous
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutrients for those who cannot, or will not—due to reduced mental states or otherwise—consume food or water per os, by mouth. It may also be used to administer pharmaceutical drug, medications or other medical therapy such as blood transfusion, blood products or electrolytes to correct electrolyte imbalances. Attempts at providing intravenous therapy have been recorded as early as the 1400s, but the practice did not become widespread until the 1900s after the development of techniques for safe, effective use. The intravenous route is the fastest way to deliver medications and fluid replacement throughout the body as they are introduced directly into the circulatory system and thus quickly distributed. For this reason, the intravenous route ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
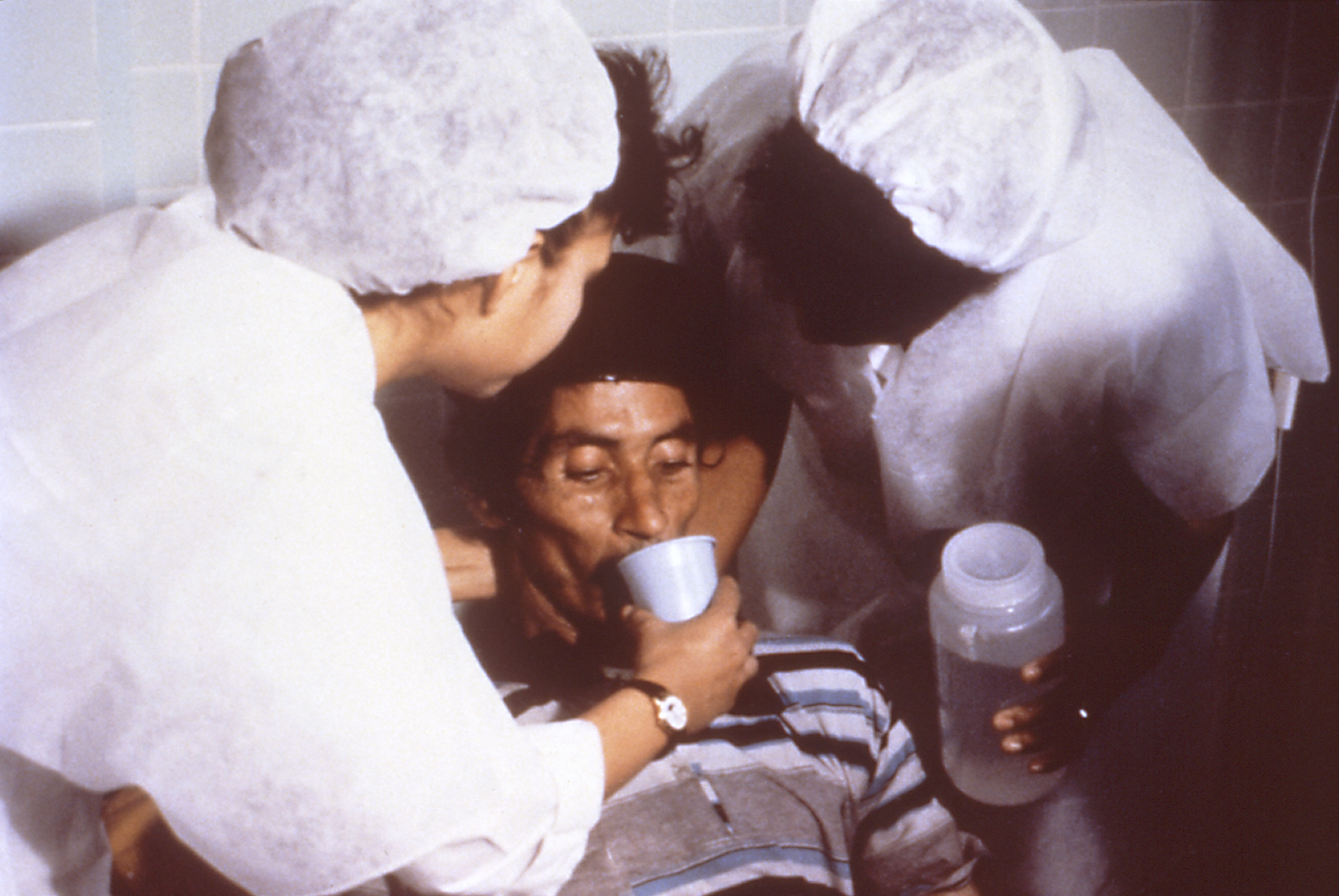
Oral Rehydration Therapy
Oral rehydration therapy (ORT) also officially known as Oral Rehydration Solution is a type of fluid replacement used to prevent and treat dehydration, especially due to diarrhea. It involves drinking water with modest amounts of sugar and salts, specifically sodium and potassium. Oral rehydration therapy can also be given by a nasogastric tube. Therapy can include the use of zinc supplements to reduce the duration of diarrhea in infants and children under the age of 5. Use of oral rehydration therapy has been estimated to decrease the risk of death from diarrhea by up to 93%. Side effects may include vomiting, high blood sodium, or high blood potassium. If vomiting occurs, it is recommended that use be paused for 10 minutes and then gradually restarted. The recommended formulation includes sodium chloride, sodium citrate, potassium chloride, and glucose. Glucose may be replaced by sucrose and sodium citrate may be replaced by sodium bicarbonate, if not available, althoug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
XLD Agar
Xylose lysine deoxycholate agar (XLD agar) is a wikt:selective, selective growth medium used in the isolation of ''Salmonella'' and ''Shigella'' species from clinical samples and from food. The agar was developed by Welton Taylor in 1965. It has a pH of approximately 7.4, leaving it with a bright pink or red appearance due to the indicator phenol red. Sugar Fermentation (biochemistry), fermentation lowers the pH and the phenol red indicator registers this by changing to yellow. Most gut bacteria, including ''Salmonella'', can ferment the sugar xylose to produce acid; ''Shigella'' colonies cannot do this and therefore remain red. After exhausting the xylose supply ''Salmonella'' colonies will decarboxylate lysine, increasing the pH once again to alkaline and mimicking the red ''Shigella'' colonies. Salmonellae metabolise thiosulfate to produce hydrogen sulfide, which leads to the formation of colonies with black centers and allows them to be differentiated from the similarly colour ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |