|
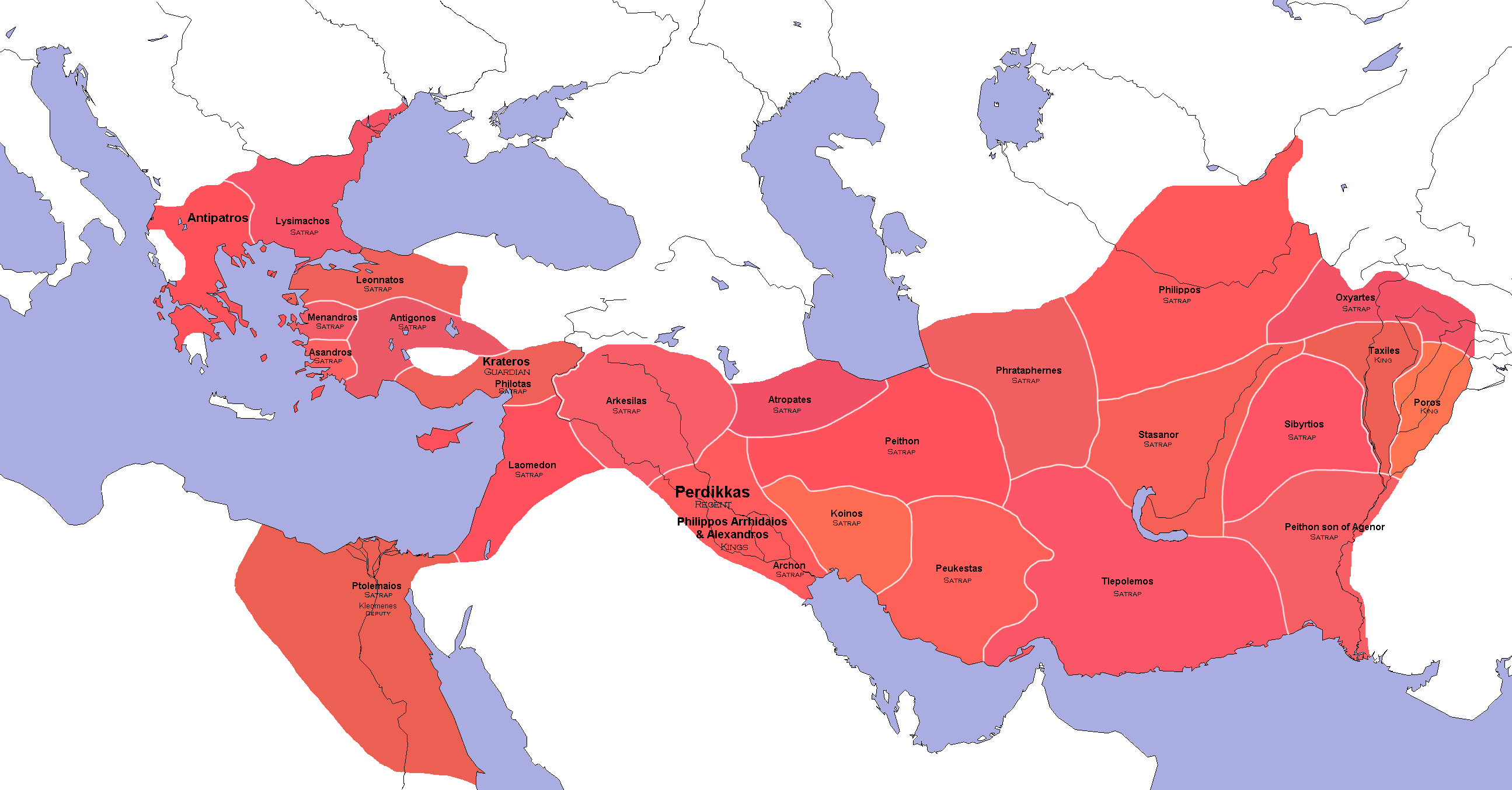
Babylonian War
The Babylonian War was a conflict fought between 311–309 BC between Antigonus I Monophthalmus and Seleucus I Nicator, ending in a victory for Seleucus. This conflict ended any possibility of restoration of the former empire of Alexander the Great, a result confirmed in the Battle of Ipsus. The battle also marked the birth of the Seleucid Empire by giving Seleucus control over the eastern satrapies of Alexander's former territory. Preliminaries After the death of Alexander the Great on 11 June 323 BC, his empire disintegrated. Officers who were trying to save it were defeated during the First War of the Diadochi. During the Second War of the Diadochi, the power of Antigonus I Monophthalmus, who had created a state of his own in Anatolia and Syria, was growing; this caused alarm among the other generals, but in the Third War of the Diadochi, Antigonus managed to keep Ptolemy I Soter of Egypt and Cassander of Macedon in check. In December 311 BC, the warring parties concluded the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wars Of The Diadochi
The Wars of the Diadochi (, Romanization of Greek, romanized: ', ''War of the Crown Princes'') or Wars of Alexander's Successors were a series of conflicts fought between the generals of Alexander the Great, known as the Diadochi, over who would rule his Macedonia (ancient kingdom)#Empire, empire following his death. The fighting occurred between 322 and 281 BC. Background Alexander the Great died on June 10, 323 BC, leaving behind an empire that stretched from Macedon and the rest of Hellenistic Greece, Greece in Europe to the Indus valley in South Asia. The empire had no clear successor, with the Argead dynasty, Argead family, at this point, consisting of Alexander's mentally disabled half-brother, Philip III of Macedon, Arrhidaeus; his unborn son Alexander IV of Macedon, Alexander IV; his reputed illegitimate son Heracles, son of Alexander, Heracles; his mother Olympias; his sister Cleopatra of Macedon, Cleopatra; and his half-sisters Thessalonike of Macedon, Thessalonike and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ptolemaic Kingdom
The Ptolemaic Kingdom (; , ) or Ptolemaic Empire was an ancient Greek polity based in Ancient Egypt, Egypt during the Hellenistic period. It was founded in 305 BC by the Ancient Macedonians, Macedonian Greek general Ptolemy I Soter, a Diadochi, companion of Alexander the Great, and ruled by the Ptolemaic dynasty until the death of Cleopatra VII in 30 BC. Reigning for nearly three centuries, the Ptolemies were the longest and final Dynasties of ancient Egypt, dynasty of ancient Egypt, heralding a distinct era of Hellenistic religion, religious and cultural syncretism between Greek and Egyptian culture. Alexander the Great conquered Thirty-first Dynasty of Egypt, Persian-controlled Egypt in 332 BC during Wars of Alexander the Great, his campaigns against the Achaemenid Empire. Death of Alexander the Great, Alexander's death in 323 BC was followed by the Empire of Alexander the Great, rapid unraveling of the Macedonian Empire amid competing claims by the ''diadochi'', his closest fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecbatana
Ecbatana () was an ancient city, the capital of the Median kingdom, and the first capital in History of Iran, Iranian history. It later became the summer capital of the Achaemenid Empire, Achaemenid and Parthian Empire, Parthian empires.Nardo, Don. "Ecbatana." ''The Greenhaven Encyclopedia of Ancient Mesopotamia'', edited by Robert B. Kebric, Greenhaven Press, 2007, pp. 97-98. ''Gale In Context: World History'', link.gale.com/apps/doc/CX3205100129/WHIC?u=wylrc_uwyoming&sid=summon&xid=e9682d3c. Accessed 20 Nov. 2022. It was also an important city during the Seleucid Empire, Seleucid and Sasanian Empire, Sasanian empires. It is believed that Ecbatana is located in the Zagros Mountains, the east of central Mesopotamia, on Hagmatana Hill (Tappe-ye Hagmatāna). Ecbatana's strategic location and resources probably made it a popular site even before the 1st millennium BC. Along with Athens in Greece, Rome in Italy and Susa in Iran, Ecbatana is one of the few ancient cities in the world th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zagros
The Zagros Mountains are a mountain range in Iran, northern Iraq, and southeastern Turkey. The mountain range has a total length of . The Zagros range begins in northwestern Iran and roughly follows Iran's western border while covering much of southeastern Turkey and northeastern Iraq. From this border region, the range continues southeast to the waters of the Persian Gulf. It spans the southern parts of the Armenian highlands, and the whole length of the western and southwestern Iranian plateau, ending at the Strait of Hormuz. The highest point is Mount Dena, at . Geology The Zagros fold and thrust belt was mainly formed by the continental collision, collision of two tectonic plates, the Eurasian Plate and the Arabian Plate. This collision mainly happened during the Miocene (about 25–5 mya or million years ago) and folded the entirety of the rocks that had been deposited from the Paleozoic (541–242 mya) to the Cenozoic (66 mya – present) in the passive continental ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tigris
The Tigris ( ; see #Etymology, below) is the eastern of the two great rivers that define Mesopotamia, the other being the Euphrates. The river flows south from the mountains of the Armenian Highlands through the Syrian Desert, Syrian and Arabian Deserts, before merging with the Euphrates and reaching to the Persian Gulf. The Tigris passes through historical cities like Mosul, Tikrit, Samarra, and Baghdad. It is also home to archaeological sites and ancient religious communities, including the Mandaeans, who use it for Masbuta, baptism. In ancient times, the Tigris nurtured the Assyria, Assyrian Empire, with remnants like the relief of Tiglath-Pileser I, King Tiglath-Pileser. Today, the Tigris faces modern threats from geopolitical instability, dam projects, poor water management, and climate change, leading to concerns about its sustainability. Efforts to protect and preserve the river's legacy are ongoing, with local archaeologists and activists working to safeguard its future ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicanor (satrap)
Nicanor (; ''Nīkā́nōr'') was a Macedonian officer of distinction who served as satrap of Media under Antigonus (possibly Nicanor of Stageira, who served under Alexander the Great). In 321 BCE, at the division of the provinces, after the death of the regent Perdiccas, he gained the position of satrap of Cappadocia. He attached himself to the party of Antigonus I Monophthalmus, whom he accompanied in the war against Eumenes. After the Battle of Gabiene, the mutinous Argyraspids agreed to surrender their general into Antigonus's hands; it was Nicanor who was selected to receive the prisoner from them. After the defeat of Peithon and his associates around 314 BCE, Antigonus appointed Nicanor as satrap of Media and the adjoining provinces, commonly termed the " Upper Satrapies", which he continued to hold until 311 BCE when Seleucus made himself master of Babylon, and started the Babylonian War. Nicanor now assembled a large force and marched against the invader, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aria (satrapy)
Aria ( ''Ar(e)ía'', آريا; Latin ''Aria'', representing Old Persian. 𐏃𐎼𐎡𐎺 ''Haraiva'', Avestan 𐬵𐬀𐬭𐬋𐬌𐬬𐬀 ''Harōiva'') was an Achaemenid region centered on the city of Herat in present-day western Afghanistan. In classical sources, Aria has been several times confused with the greater region of ancient Ariana, of which Aria formed a part. Geography Aria was an Old Persian satrapy, which enclosed chiefly the valley of the Hari River (Greek , this being eponymous to the whole land according to Arrian) and which in antiquity was considered as particularly fertile and, above all, rich in wine. The region of Aria was separated by mountain ranges from the Paropamisadae in the east, Parthia in the west and Margiana and Hyrcania in the north, while a desert separated it from Carmania and Drangiana in the south. It is described in a very detailed manner by Ptolemy and Strabo and corresponds, according to that, almost to the Herat Province of today's A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euphrates
The Euphrates ( ; see #Etymology, below) is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of West Asia. Tigris–Euphrates river system, Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia (). Originating in Turkey, the Euphrates flows through Syria and Iraq to join the Tigris in the Shatt al-Arab in Iraq, which empties into the Persian Gulf. The Euphrates is the List of longest rivers of Asia, fifteenth-longest river in Asia and the longest in West Asia, at about , with a drainage area of that covers six countries. Etymology The term ''Euphrates'' derives from the Koine Greek, Greek ''Euphrátēs'' (), adapted from , itself from . The Elamite name is ultimately derived from cuneiform 𒌓𒄒𒉣; read as ''Buranun'' in Sumerian language, Sumerian and ''Purattu'' in Akkadian language, Akkadian; many cuneiform signs have a Sumerian pronunciation and an Akkadian pronunciation, taken from a Sumerian word and an Akkadian word that mean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seleucid Era
The Seleucid era ("SE") or (literally "year of the Greeks" or "Greek year"), sometimes denoted "AG," was a Calendar era, system of numbering years in use by the Seleucid Empire and other countries among the ancient Hellenistic period, Hellenistic civilizations, and later by the Parthians. It is sometimes referred to as "the dominion of the Seleucidæ," or the Year of Alexander. The era dates from Seleucus I Nicator's reconquest of Babylon in 312/11 BC after his exile in Ptolemaic Kingdom, Ptolemaic Egypt, considered by Seleucus and his court to mark the founding of the Seleucid Empire. According to Jewish tradition, it was during the sixth year of Alexander the Great's reign (lege: possibly Alexander the Great's infant son, Alexander IV of Macedon) that they began to make use of this counting. Versions Two different variations of the Seleucid years existed, one where the year started in spring and another where it starts in autumn: # The natives of the empire used the Babylonian c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Babylon
Babylon ( ) was an ancient city located on the lower Euphrates river in southern Mesopotamia, within modern-day Hillah, Iraq, about south of modern-day Baghdad. Babylon functioned as the main cultural and political centre of the Akkadian-speaking region of Babylonia. Its rulers established two important empires in antiquity, the 19th–16th century BC Old Babylonian Empire, and the 7th–6th century BC Neo-Babylonian Empire. Babylon was also used as a regional capital of other empires, such as the Achaemenid Empire. Babylon was one of the most important urban centres of the ancient Near East, until its decline during the Hellenistic period. Nearby ancient sites are Kish, Borsippa, Dilbat, and Kutha. The earliest known mention of Babylon as a small town appears on a clay tablet from the reign of Shar-Kali-Sharri (2217–2193 BC), of the Akkadian Empire. Babylon was merely a religious and cultural centre at this point and neither an independent state nor a large city, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harran
Harran is a municipality and Districts of Turkey, district of Şanlıurfa Province, Turkey. Its area is 904 km2, and its population is 96,072 (2022). It is approximately southeast of Urfa and from the Syrian border crossing at Akçakale. Harran was founded at some point between the 25th and 20th centuries BC, possibly as a merchant colony by Sumerian traders from Ur. Over the course of its early history, Harran rapidly grew into a major Mesopotamian cultural, commercial and religious center. It was made a religiously and politically influential city through its association with the moon-god Sin (mythology), Sin; many prominent Mesopotamian rulers consulted with and renovated the moon-temple of Ekhulkhul in Harran. Harran came under Assyrian rule under Adad-nirari I ( BC) and became a provincial capital often second in importance only to the Assyrian capital of Assur itself. During the collapse of the Assyrian Empire, Harran briefly served as the final capital of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diodorus Siculus
Diodorus Siculus or Diodorus of Sicily (; 1st century BC) was an ancient Greece, ancient Greek historian from Sicily. He is known for writing the monumental Universal history (genre), universal history ''Bibliotheca historica'', in forty books, fifteen of which survive intact, between 60 and 30 BC. The history is arranged in three parts. The first covers mythic history up to the destruction of Troy, arranged geographically, describing regions around the world from Egypt, India and Arabia to Europe. The second covers the time from the Trojan War to the death of Alexander the Great. The third covers the period to about 60 BC. ''Bibliotheca'', meaning 'library', acknowledges that he was drawing on the work of many other authors. Life According to his own work, he was born in Agira, Agyrium in Sicily (now called Agira). With one exception, classical antiquity, antiquity affords no further information about his life and doings beyond his written works. Only Jerome, in his ''Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |