|
Babbage Building
The Babbage Building is a teaching building at the University of Plymouth for the university's School of Engineering, Computing and Mathematics and the School of Art, Design and Architecture. Background The Babbage Building, also known as the New Engineering and Design Facility, is a teaching building named after Charles Babbage, a mathematician, philosopher, inventor and mechanical engineer who originated the concept of a digital programmable computer. After renovations in 2021–2023, the building contains a number of fabrication and computing laboratories. History 1979-2019: Original building The Babbage Building was originally constructed in 1979 as an engineering facility for the University of Plymouth. Prior to being named the Babbage Building, it was called the General Teaching Block (abbreviated to GTB). 2019-2023: Renovation In 2019, a design competition was held for a renovation of the Babbage Building. Planning permission was granted for the works in Dec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Plymouth
The University of Plymouth is a public research university based predominantly in Plymouth, England, where the main campus is located, but the university has campuses and affiliated colleges across South West England. With students, it is the List of universities in the United Kingdom by enrollment, largest in the United Kingdom by total number of students (including the Open University). History 1862 – 2000 The university was originally founded as thPlymouth School of Navigation in 1862, before becoming a university college in 1920 and a polytechnic (United Kingdom), polytechnic institute in 1970, with its constituent bodies being Plymouth Polytechnic, Rolle College in Exmouth, the Exeter College of Art and Design (which were, before April 1989, run by Devon County Council) and Seale-Hayne College (which before April 1989 was an independent charity). It was renamed Polytechnic South West in 1989, a move that was unpopular with students as the name lacked identity. It was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feilden Clegg Bradley Studios
Feilden Clegg Bradley Studios (also known as FCBStudios) is a British architectural design firm, established in 1978, with offices in Bath, London and Manchester. The firm is known for its pioneering work in sustainable design and social design agenda. In 2008, Accordia, which was also designed by Alison Brooks Architects and Maccreanor Lavington, became the first housing development to win the Royal Institute of British Architects (RIBA) Stirling Prize. Background The company was formed in 1978 by architects Richard Feilden (1950–2005) and Peter Clegg, operating from small premises in Bath, Somerset. The company designed and constructed low-energy houses. Over the next two decades the company won awards for a number of school design projects and gained "a formidable reputation in the education sector". With over 100 staff the firm developed an "unusually democratic" way of operating. Feilden was accidentally killed by a falling tree in 2005 and the practice continued u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal BAM Group
Royal BAM Group nv () is a Dutch construction-services business with headquarters in Bunnik, Netherlands. Based on revenue it is the largest construction company in the Netherlands. History The company was founded by Adam van der Wal as a joiner's shop in 1869 in Groot-Ammers - a rural village in the Alblasserwaard region to the east of Rotterdam. At the end of the 19th century, Adam's son, Jan van der Wal, took over the business and worked as a construction contractor not only in the Alblasserwaard region but at further afield locations, including Vlaardingen and The Hague, where he soon opted to relocate to. Jan's son, Joop van der Wal, studied civil engineering in Delft prior to joining his father’s company in 1926. During 1927, the business was renamed ''Bataafsche Aanneming Maatschappij van Bouw- en Betonwerken'', in English, ''Batavian Construction Company for Construction and Concrete Projects plc''. ('BAM'); it transitioned from being a family-owned firm into a ‘naaml ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
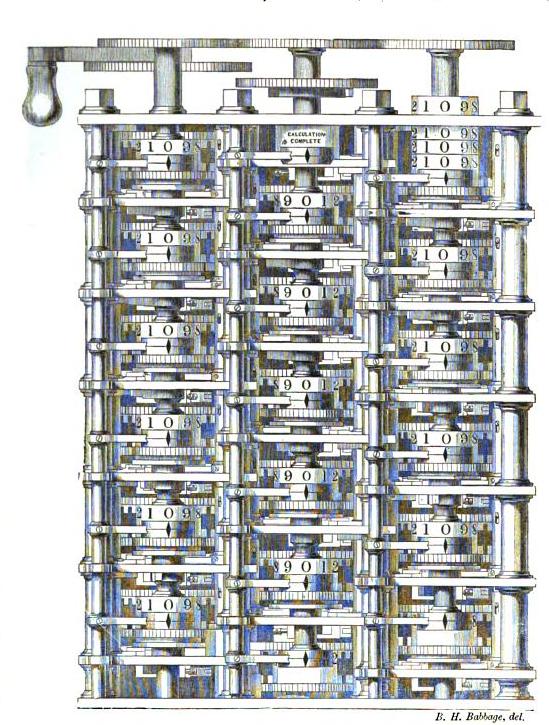
Charles Babbage
Charles Babbage (; 26 December 1791 – 18 October 1871) was an English polymath. A mathematician, philosopher, inventor and mechanical engineer, Babbage originated the concept of a digital programmable computer. Babbage is considered by some to be "List of pioneers in computer science, father of the computer". He is credited with inventing the first mechanical computer, the difference engine, that eventually led to more complex electronic designs, though all the essential ideas of modern computers are to be found in his analytical engine, programmed using a principle openly borrowed from the Jacquard loom. As part of his computer work, he also designed the first Printer (computing), computer printers. He had a broad range of interests in addition to his work on computers covered in his 1832 book ''Economy of Manufactures and Machinery''. He was an important figure in the social scene in London, and is credited with importing the "scientific soirée" from France with hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Center
A data center is a building, a dedicated space within a building, or a group of buildings used to house computer systems and associated components, such as telecommunications and storage systems. Since IT operations are crucial for business continuity, it generally includes redundant or backup components and infrastructure for power supply, data communication connections, environmental controls (e.g., air conditioning, fire suppression), and various security devices. A large data center is an industrial-scale operation using as much electricity as a medium town. Estimated global data center electricity consumption in 2022 was 240–340 TWh, or roughly 1–1.3% of global electricity demand. This excludes energy used for cryptocurrency mining, which was estimated to be around 110 TWh in 2022, or another 0.4% of global electricity demand. The IEA projects that data center electric use could double between 2022 and 2026. High demand for electricity from data centers, incl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Babbage Building (During Renovations)
The Babbage Building is a teaching building at the University of Plymouth for the university's School of Engineering, Computing and Mathematics and the School of Art, Design and Architecture. Background The Babbage Building, also known as the New Engineering and Design Facility, is a teaching building named after Charles Babbage, a mathematician, philosopher, inventor and mechanical engineer who originated the concept of a digital programmable computer. After renovations in 2021–2023, the building contains a number of fabrication and computing laboratories. History 1979-2019: Original building The Babbage Building was originally constructed in 1979 as an engineering facility for the University of Plymouth. Prior to being named the Babbage Building, it was called the General Teaching Block (abbreviated to GTB). 2019-2023: Renovation In 2019, a design competition was held for a renovation of the Babbage Building. Planning permission was granted for the works in Dec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Babbage Building During Renovation
Charles Babbage (; 26 December 1791 – 18 October 1871) was an English polymath. A mathematician, philosopher, inventor and mechanical engineer, Babbage originated the concept of a digital programmable computer. Babbage is considered by some to be "List of pioneers in computer science, father of the computer". He is credited with inventing the first mechanical computer, the difference engine, that eventually led to more complex electronic designs, though all the essential ideas of modern computers are to be found in his analytical engine, programmed using a principle openly borrowed from the Jacquard loom. As part of his computer work, he also designed the first Printer (computing), computer printers. He had a broad range of interests in addition to his work on computers covered in his 1832 book ''Economy of Manufactures and Machinery''. He was an important figure in the social scene in London, and is credited with importing the "scientific soirée" from France with hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |