|
BMW R69
The R69, R69S, and R69US are motorcycles, fitted with 594 cc Flat-twin, boxer twin engines, that were manufactured by BMW Motorrad, BMW in Munich, Germany. Production history From 1955 to 1969, 15,347 of these 594 cc shaft-drive, Flat-twin, opposed twin motorcycles were built. The R69 was produced from 1955 to 1960, the R69S was produced from 1960 to 1969, and the 42 hp R69US was produced from 1968 to 1969. These models were designed as relatively high powered, high compression sport bikes, although the Motorcycle fork#Earles, Earles fork R69 and R69S came with sidecar lugs installed on the frames. These lugs were deleted from the telescopic fork "US" models. The low compression BMW R60/2, R60/2, produced from 1955 to 1960, was designed primarily for sidecar use, though it was popularly used as a solo bike, along with the 30 hp R60US, which was produced between 1968 and 1969. The sport-oriented R69S, R69US, and R69 succeeded the plunger-framed 1951 to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BMW R68
The BMW R68 is a sport bike, sport version of the pre-1955 BMW Motorrad, BMW motorcycles. A total of 1,452 models were manufactured from 1952 to 1954,Preston making it one of BMW's rarest production motorcycles.Falloon pp: 8–13 History In October 1951, at the German International Motorcycle Show in Frankfurt, BMW displayed a new high performance model.Walker The machine had improved performance of compared to the low-compression R67/2, a racing-type magneto, bigger bore 26 mm Bing carburetors and improved twin leading-shoe front brake. It also came with a more modern sporty narrow front fender rather than the deeply valanced fender used on other BMW twins. BMW announced the R68 as "The first 100 mph motorcycle." It was shown as a road bike, capable of , with normal two low exhaust silencers, and an off-road version with a single high silencer. A separate pillion pad resembled a passenger saddle, but was provided for the rider to slide backward in order to crouch low ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
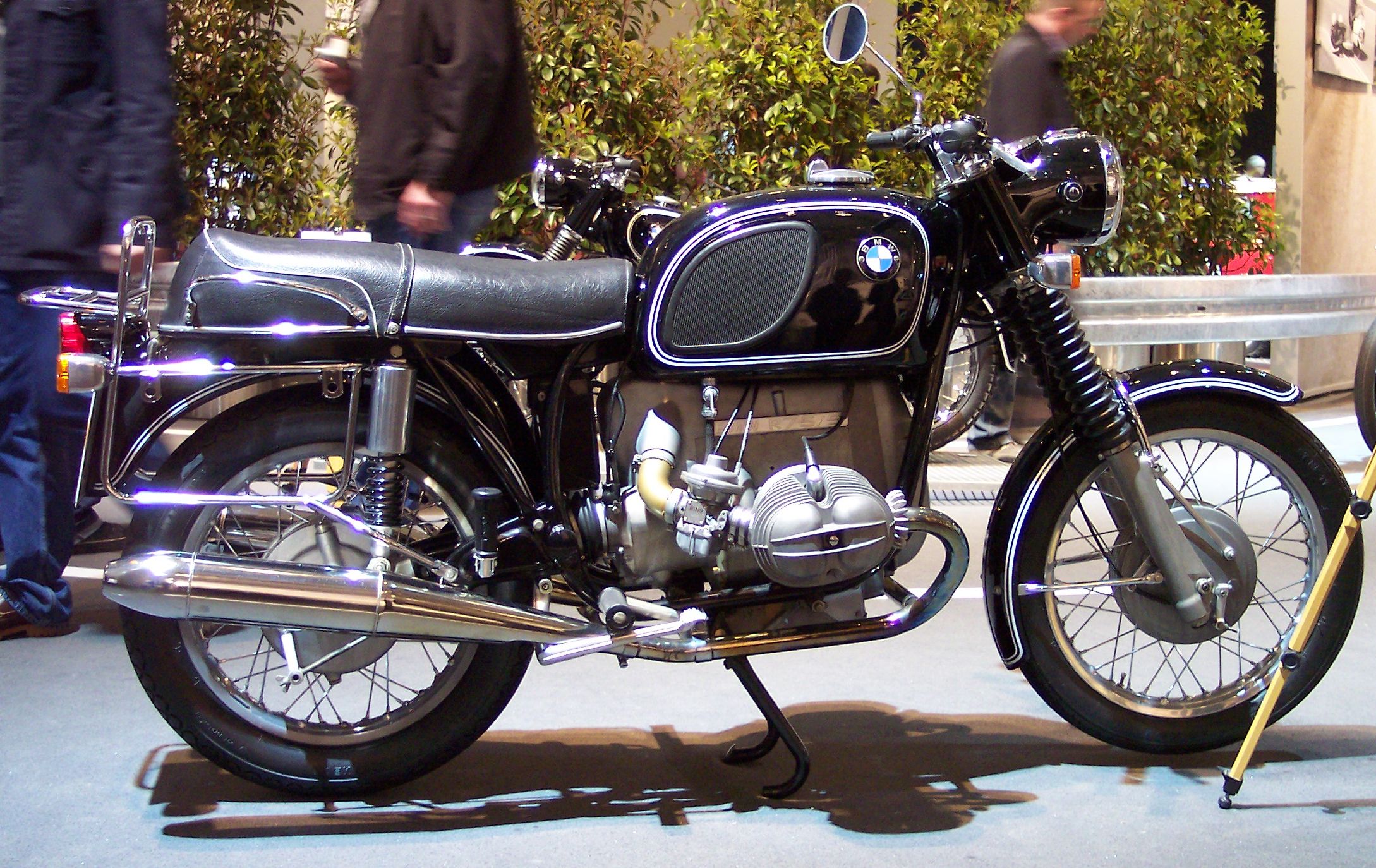
BMW /5 Motorcycles
''For the WWII-era motorcycle, see BMW R75'' The BMW R50/5, R60/5, and R75/5 form a range of boxer twin motorcycles manufactured in Berlin, Germany, by BMW for model years 1970-1973 and featuring electric starting and telescopic forks. History For the 1970 model year, BMW launched three new models having engine capacities of 500 cc (R50/5), 600 cc (R60/5), and 750 cc (R75/5). The R75/5 could reach 110 mph (177 km/h). Model year 1972 saw the introduction of the rectangular tank with chrome side panels. For the second half of the 1973 model year, BMW lengthened the rear swingarm 2 inch (5 cm), resulting in the “long-wheelbase” (LWB) models mainly to improve the stability of the motorcycles at higher speeds and when loaded up. It also enabled a larger battery, while retaining the kick starter. The /5 series was the first series to be manufactured completely in Berlin, as by 1969 all of Munich's production capacity was needed for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motorcycles Powered By Flat Engines
A motorcycle (motorbike, bike; uni (if one-wheeled); trike (if three-wheeled); quad (if four-wheeled)) is a lightweight private 1-to-2 passenger personal motor vehicle Steering, steered by a Motorcycle handlebar, handlebar from a saddle-style seat. Motorcycle designs vary greatly to suit a range of different purposes: Long-distance motorcycle riding, long-distance travel, Motorcycle commuting, commuting, cruising (driving), cruising, Motorcycle sport, sport (including Motorcycle racing, racing), and Off-roading, off-road riding. Motorcycling is riding a motorcycle and being involved in other related social activities such as joining a motorcycle club and attending motorcycle rally, motorcycle rallies. The 1885 Daimler Reitwagen made by Gottlieb Daimler and Wilhelm Maybach in Germany was the first internal combustion, petroleum-fueled motorcycle. In 1894, Hildebrand & Wolfmüller became the first series production motorcycle. Globally, motorcycles are comparable numerically t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BMW Motorcycles
''BMW Motorrad'' is the motorcycle brand and division of German automotive manufacturer, BMW. It has produced motorcycles since 1923, and achieved record sales for the fifth year in succession in 2015. With a total of 136,963 vehicles sold in 2015, BMW registered a growth of 10.9% in sales in comparison with 2014. In May 2011, the 2,000,000th motorcycle produced by BMW Motorrad was an R1200GS. History The company began as an aircraft engine manufacturer in the early 20th century and through World War I. BMW manufactured its first motorcycle in 1923, the R32, which featured a flat-twin boxer engine. BMW Motorrad still uses the flat-twin boxer configuration, but now manufactures motorcycles with a variety of engine configurations. Current production With the exception of the G310 series (which is produced at TVS' plant in Hosur, Tamil Nadu, India) and the C400 series (which is produced at Loncin's plant in Chongqing, China), all BMW Motorrad's motorcycle production takes p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Motorcycles Of The 1950s
This a listing of motorcycles of the 1950s, including those on sale, introduced, or otherwise relevant in this period. * AJS 18 (1949–1963)Total Bike Classics (accessed 2016-04-23) * AJS Model 31 * Ariel Leader * BMW R24 * BMW R25 * BMW R25/2 * BMW R25/3 * [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of BMW Motorcycles
BMW's motorcycle history began in 1921 when the company commenced manufacturing engines for other companies. BMW's own motorcycles—sold under the BMW Motorrad brand—began in 1923 with the BMW R 32, which was powered by a flat-twin engine (also called a "boxer-twin" engine). Production of motorcycles with flat-twin engines continues to this day, however BMW has also produced many models with other types of engines. Motorcycle history 1921–1938 At the end of World War I, the Treaty of Versailles demanded that BMW cease production of aircraft engines. To remain in business, the company began producing small industrial engines (along with farm equipment, household items and railway brakes). In 1920, BMW M2B15 flat-twin petrol engine was released. Despite being designed as a portable industrial engine, the M2B15 was also used by several motorcycle manufacturers, including for the 1920–1923 Victoria KR1 and the 1920–1922 Bayerische Flugzeugwerke (BFw) ''Helios'' motorcyc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daytona International Speedway
Daytona International Speedway is a race track in Daytona Beach, Florida, Daytona Beach, Florida, United States, about north of Orlando, Florida, Orlando. Since opening in 1959, it has been the home of the Daytona 500, the most prestigious race in NASCAR as well as its season opening event. The venue also hosts the 24 Hours of Daytona, one of three races that make up the Triple Crown of endurance racing. In addition to NASCAR and IMSA, the track also hosts races of Automobile Racing Club of America, ARCA, AMA Superbike, SCCA, and AMA Supercross. The track features multiple layouts including the primary high-speed tri-oval, a sports car course, a motorcycle course, and a karting and motorcycle flat-track. The track's infield includes the Lake Lloyd, which has hosted powerboat racing. The track was built in 1959 by NASCAR founder Bill France Sr., William "Bill" France Sr. to host racing that was held at the former Daytona Beach Road Course. His banked design permitted higher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kawasaki Z1
The Kawasaki Z1 is a four-cylinder, air-cooled, double-overhead camshaft, carbureted, chain-drive motorcycle introduced in 1972 by Kawasaki. Following the introduction of Honda's CB750 in 1968, the Z1 helped popularize the in-line, across-the-frame four-cylinder, a format that became known as the '' Universal Japanese Motorcycle'' or ''UJM.'' The Z1 was noted for being the first large-capacity Japanese four-cylinder motorcycle to use the double-overhead-camshaft system on a production motorcycle. When it was introduced, only the MV Agusta 750 S used this system; it was a very expensive limited-production machine, as opposed to the Kawasaki which was less than half the price. Marketed variously as the Z1-900, 900 Z1 or 900 S4 ("Super Four"), the Z1 was the first of Kawasaki's Z models. History The Kawasaki Z1 was developed under the project name "New York Steak". In the late 1960s Kawasaki, already an established manufacturer of two-stroke motorcycles, had begun prototyping ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LJK Setright
Leonard John Kensell Setright (10 August 1931 – 7 September 2005) was an English motoring journalist and author. Early life and education Setright was born in London to Australian parents; his father, Henry Roy Setright, was an engineer who invented the Setright ticket machine used on buses and trams. He died when Setright was 11 years old. Setright attended Palmers Green Grammar school before studying law at the University of London which he practised for a time but hated the profession. His National Service was served in the Royal Air Force as an air traffic controller. Writing career After writing for the engineering magazine ''Machine Age'' in the early 1960s, Setright became a motoring journalist and author, contributing to ''Car Magazine'' for more than 30 years and writing several books on cars and automotive engineering. Setright's writing style polarised readers as some considered it to be pompous and excessively esoteric, while others found his erudite style an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Final Drive Ratio
A gear train or gear set is a machine element of a mechanical system formed by mounting two or more gears on a frame such that the teeth of the gears engage. Gear teeth are designed to ensure the pitch circles of engaging gears roll on each other without slipping, providing a smooth transmission of rotation from one gear to the next. Features of gears and gear trains include: * The gear ratio of the pitch circles of mating gears defines the speed ratio and the mechanical advantage of the gear set. * A planetary gear train provides high gear reduction in a compact package. * It is possible to design gear teeth for gears that are non-circular, yet still transmit torque smoothly. * The speed ratios of chain and belt drives are computed in the same way as gear ratios. See bicycle gearing. The transmission of rotation between contacting toothed wheels can be traced back to the Antikythera mechanism of Greece and the south-pointing chariot of China. Illustrations by the Renaissance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autodrome De Linas-Montlhéry
A race track (racetrack, racing track or racing circuit) is a facility built for racing of vehicles, athletes, or animals (e.g. horse racing or greyhound racing). A race track also may feature grandstands or concourses. Race tracks are also used in the study of animal locomotion. A ''racetrack'' is a permanent facility or building. ''Racecourse'' is an alternate term for a horse racing track, found in countries such as the United Kingdom, India, Australia, Hong Kong, and the United Arab Emirates. Race tracks built for bicycles are known as ''velodromes''. ''Circuit'' is a common alternate term for race track, given the circuit configuration of most race tracks, allowing races to occur over several laps. Some race tracks may also be known as ''speedways'', or ''raceways''. A ''race course'', as opposed to a ''racecourse'', is a nonpermanent track for sports, particularly road running, water sports, road racing, or rallying. Many sports usually held on race tracks also can occur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cycle World
''Cycle World'' is a motorcycling magazine in the United States. It was founded in 1962 by Joe Parkhurst, who was inducted to the Motorcycle Hall of Fame as "the person responsible for bringing a new era of objective journalism" to the US. ''Cycle World'' was the largest motorcycling magazine in the world. The magazine is headquartered in Irvine, California. Regular contributors include Peter Egan and Nick Ienatsch. Previous or occasional contributors have included gonzo journalist and author Hunter S. Thompson, journalist and correspondent Henry N. Manney III, and professional riding coach Ken Hill. Parkhurst sold ''Cycle World'' to CBS in 1971. CBS executive Peter G. Diamandis and his associates bought CBS Magazines from CBS in 1987, forming Diamandis Communications, which was acquired by Hachette Magazines the following year, 1988. In 2011, Hachette sold the magazine to Hearst Corporation Hearst Corporation, Hearst Holdings Inc. and Hearst Communications Inc. comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |