|
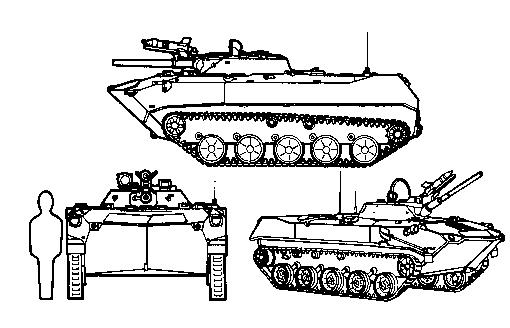
BMD-3
The BMD-3 (''Boyevaya Mashina Desanta '', ) is a light infantry fighting vehicle originating in the Soviet Union that is fully amphibious and air-droppable with crew inside. It is intended to be used by airborne and air assault units. It is not an upgraded BMD-1 but a completely redesigned vehicle with a hydropneumatic suspension, new hull, a more powerful 2V-06-2 diesel engine and fitted with the complete turret of the BMP-2. Development Even before the start of the BMD-2's production, a new model of airborne infantry fighting vehicle was already envisaged by the Soviet military planners. This new type would first replace the BMD-1, and later the BMD-2. Two configurations were considered: one using the same armament as the future BMP-3, and another equipped with the BMP-2's turret. The latter option was chosen, because it would allow for a lighter vehicle (12.5 tonnes, compared to 18 tonnes for the other one). Six ''Object 950'' prototypes were built in 1985 and 1986. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BMD-4
The BMD-4 () is an amphibious infantry fighting vehicle (IFV) originating from post-Cold War Russia. Originally designated as the BMD-3M, the chassis of the BMD-4 is the same as that of the BMD-3 because it was developed on the same basis. This armored fighting vehicle is one of the lightest in its class, possessing a substantial amount of firepower. The vehicle was designed to transport Russian Airborne Troops (VDV), increasing its mobility, armament, and protection on the battlefield. Many aspects of the vehicle, such as the ergonomics and positioning of the passengers, remain relatively unchanged. Primary differences between the BMD-4 and its predecessors lie in its armament. The vehicle is fitted with the Bakhcha-U turret, which consists of a 100 mm 2A70 low-pressure rifled gun, a 30 mm 2A72 coaxial autocannon, and a 7.62 mm PKT coaxial machine gun. The 2A70 rifled cannon is capable of firing high explosive fragmentation rounds and laser-guided anti-tank mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2S25 Sprut-SD
The 2S25 Sprut-SD (Russian language, Russian: 2С25 «Спрут-СД»; 2S25 "Octopus-SD") is a tank destroyer, self-propelled anti-tank gun developed and to be manufactured by the Volgograd Tractor Plant to meet the requirements of the Russian Airborne Troops, VDV. In mid-2001, the Volgograd tractor plant revealed that the development of the 2S25 had lasted several years. The Sprut-SD is designed to defeat tanks, hard-skinned material and enemy manpower by airborne and amphibious landing forces, as well as by specially designated units of ground forces. Its main armament, the 125 mm 2A75, is capable of firing APFSDS, HE-Frag, HEAT and ATGM ammunition. This allows the 2S25 firepower to be as powerful as a main battle tank and as maneuverable and amphibious as airborne infantry combat vehicles. The 2S25 can be used by units of ground forces and naval infantry as a light amphibious tank. the only operators of the 2S25 are the Russian airborne troops with 24 of these vehicles in s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BMP-3
The BMP-3 is a Soviet and Russian infantry fighting vehicle, successor to the BMP-1 and BMP-2. The abbreviation BMP stands for ''Boevaya Mashina Pekhoty'' (, literally "infantry combat vehicle"). Production history The design of the BMP-3 ('' Obyekt'' 688M) can be traced back to the ''Obyekt'' 685 light tank prototype with an 2A48-1 100 mm gun from 1975.Zaloga, Steven J., Hull, Andrew W. and Markov, David R. (1999). ''Soviet/Russian Armor and Artillery Design Practices: 1945 to Present''. Darlington Productions. The prototype did not enter series production, but the chassis, with a new engine, was used for the next-generation infantry combat vehicle ''Obyekt'' 688 from A. Blagonravov's design bureau. The Ob. 688's original weapon configuration consisting of an externally mounted Shipunov 2A42 30 mm autocannon, a 7.62 mm PKT machine gun and twin ''9M113 Konkurs'' ATGM launcher was rejected; instead, the new 2K23 armament system was selected. The resulting BMP-3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BMD-1
The BMD-1 is a Soviet airborne amphibious tracked infantry fighting vehicle (IFV), which was introduced in 1969 and first seen by the West in 1970. BMD stands for ''Boyevaya Mashina Desanta'' (Боевая Машина Десанта, which literally translates to "Airborne Combat Vehicle"). It can be dropped by parachute and although it is of similar shape to the BMP-1 it is smaller, at just over half the weight. The BMD-1 was used as an IFV by the Soviet Airborne Forces (VDV). An improved variant of the BMD-1 was developed, the BMD-2. The BMD-1 also provided a basis for the BTR-D airborne multi-purpose tracked APC. Development In the wake of the Cuban Missile Crisis, the army was instructed to consider putting more emphasis on means to project power outside of the normal sphere of Soviet influence. As a result, there was a major effort to develop the VDV as a rapid deployment force. Soviet studies of airborne operations had shown that lightly armed paratroops were unable to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ZBD-03
The ZBD-03 or Type 03 (industrial designation WZ506) is a Chinese airborne infantry fighting vehicle. It features a light-weight chassis and hydropneumatic suspension for airborne operations. Early prototypes received the designation ZLC-2000. Development The ZBD-03 was designed to replace the BMD-3 and was in service as part of the People's Liberation Army Air Force. The vehicle was designed to be air-dropped from medium-sized aircraft such as the Xi'an Y-20 if necessary. Available variants include the infantry fighting vehicle (IFV), armored recovery vehicle (ARV), and anti-tank guided missiles ( ATGMs). Design The ZBD-03 features indigenously designed chassis and internal subsystems, which possess a distinctive layout different from Russian designs. However, some part of the vehicle might contain Russian technologies used on BMD-3. Mobility The vehicle can be airdropped from Y-20 transport aircraft. The vehicle also retains the Russian parachute system for airdrop operations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BMD-2
The BMD-2 is a Soviet airborne forces, airborne infantry fighting vehicle, introduced in 1985. It is a variant of BMD-1 with a new turret and changes to the hull. BMD stands for ''Boyevaya Mashina Desanta'' (Боевая Машина Десанта, which literally translates to "Airborne Combat Vehicle"). It was developed as a replacement for the BMD-1 but did not supersede it entirely in Soviet service. Its NATO designation is BMD M1981/1. Development When the Soviet–Afghan War broke out, the Soviet forces operated BMP-1 IFVs and BMD-1 airborne IFVs. They were both armed with a 73 mm 2A28 Grom low-pressure smoothbore short-recoil semi-automatic gun, a 9S428 ATGM launcher capable of firing the 9M14 Malyutka, the 9M14M Malyutka-M and the 9M14P Malyutka-P ATGMs and a coaxial 7.62 mm PKT machine gun. This armament was effective against soft targets such as unarmoured vehicles, infantry, and lightly fortified positions, but was not effective in the anti-tank role, and suf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Airborne Troops
The Russian Airborne Forces () is the airborne separate combat arm of the Russian Armed Forces. It is a rapid response force and strategic reserve that is under the President of Russia, reporting directly to the Chief of the General Staff, and is organized into airborne and air assault units. It was formed in 1992 from divisions of the Soviet Airborne Forces that came under Russian control following the dissolution of the Soviet Union. Troops of the Russian Airborne Forces have traditionally worn a blue beret and blue-striped '' telnyashka'' undershirt and are called ''desant'' (Russian: Десант), from the French ''Descente''. The Russian Airborne Forces utilizes a range of specialist airborne warfare vehicles and are fully mechanized. Traditionally they have had a larger complement of heavy weaponry than most contemporary airborne forces. Mission According to an order of the Ministry of Defense of the Russian Federation in 1997, the Airborne Forces form the strategic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2A42
The Shipunov 2A42 is a Soviet/Russian 30 mm autocannon. It is built by the Tulamashzavod Joint Stock Company and named after . Design The 30 mm 2A42 autocannon was developed as a replacement for 2A28 Grom and has a dual feed. One is for HE-T and the other for AP-T rounds. The gunner can select one of two rates of full automatic fire, low at 200 to 300 rds/min and high at 550 to 800 rds/min. According to the manufacturer, effective range when engaging ground targets such as light armoured vehicles is while soft-skinned targets can be engaged out to . Air targets can be engaged flying at low altitudes of up to at subsonic speeds, and up to a slant range of . In addition to being installed in a two-person turret on the BMP-2 mechanised infantry combat vehicle, this gun is also fitted in the BMD-2 airborne combat vehicle, BMD-3 airborne combat vehicle and BTR-90 (or GAZ-5923) (8 × 8) armoured personnel carrier. A small number of these have now entered service. More rec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volgograd Tractor Factory
The Volgograd Tractor Plant (, ''Volgogradski traktorni zavod'', or , ''VgTZ''), formerly the ''Dzerzhinskiy'' Tractor Factory or the Stalingrad Tractor Plant, is a heavy equipment factory located in Volgograd, Russia. It was once one of the largest tractor manufacturing enterprises in the USSR. It was a site of fierce fighting during World War II's Battle of Stalingrad. During its lifetime, VgTZ has supplied more than 2.5 million tractors to the farming industry, making a huge contribution to the mechanization of agriculture. VgTZ tractors operate in 32 countries throughout Southeast Asia, Africa, Europe, North America, and Latin America. Also used for the production of military vehicles, VgTZ is inextricably linked with the history of Soviet tank building. The plant continues to operate on a small scale, but much of it is now derelict or has been demolished. History Until 1961, the plant was called the Stalingrad Tractor Plant named for F. Dzerzhinsky (, ''Stalingradski tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BMP-1
The BMP-1 is a Soviet Union, Soviet Amphibious vehicle, amphibious tracked infantry fighting vehicle that has been in service from 1966 to the present. BMP stands for ''Boyevaya Mashina Pyekhoty 1'' (), meaning "infantry fighting vehicle, 1st serial model". The BMP-1 was the first mass-produced infantry fighting vehicle (IFV) of the Soviet Union. It was called the M-1967, BMP and BMP-76PB by NATO before its correct designation was known. The Soviet military leadership saw any future wars as being conducted with nuclear, chemical and biological weapons. A new design, like the BMP, combining the properties of an armoured personnel carrier (APC) and a light tank would allow infantry to operate from the relative safety of its armoured, radiation-shielded interior in contaminated areas and to fight alongside it in uncontaminated areas. It would increase infantry squad mobility, provide fire support to them, and also be able to fight alongside main battle tanks. The BMP-1 was first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of AFVs
This is a list of lists of armoured fighting vehicles. __NOTOC__ By period * List of armoured fighting vehicles of World War I * List of interwar armoured fighting vehicles * List of military vehicles of World War II * List of armoured fighting vehicles of World War II * List of modern armoured fighting vehicles * List of main battle tanks by generation By country * List of armoured fighting vehicles by country * List of Sd.Kfz. designations (Germany from 1939) * Tanks of Japan (Japan up to present) * List of Polish armoured fighting vehicles * List of tanks of the Soviet Union * List of armoured fighting vehicles of Ukraine * List of tanks of the United Kingdom (United Kingdom up to 1945) * List of FV series military vehicles (United Kingdom after 1945) * List of "M" series military vehicles (United States) By type * List of armoured trains * List of artillery, including self-propelled guns * List of main battle tanks by country * List of experimental tanks by countr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PKT Machine Gun
The PK (, transliterated as ''Pulemyot Kalashnikova'', or "Kalashnikov's machine gun"), is a belt-fed general-purpose machine gun, chambered for the 7.62×54mmR rimmed cartridge. The modernized and most commonly known variant, known as the PKM, features several enhancements over the original PK design. Designed in the Soviet Union and currently in production in Russia, the original PK machine gun was introduced in 1961 and the improved PKM variant was introduced in 1969. The PKM was designed to replace the SGM and RP-46 machine guns that were previously in Soviet service. The weapon remains in use as a front-line infantry and vehicle-mounted weapon with Russia's armed forces and has also been exported extensively and produced in several other countries under license. History The Main Artillery Directorate of the Soviet Union (GRAU) adopted specification requirements for a new 7.62 mm general-purpose company and battalion-level machine gun that was to be chambered for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |