BMD-1 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The BMD-1 is a Soviet airborne amphibious tracked
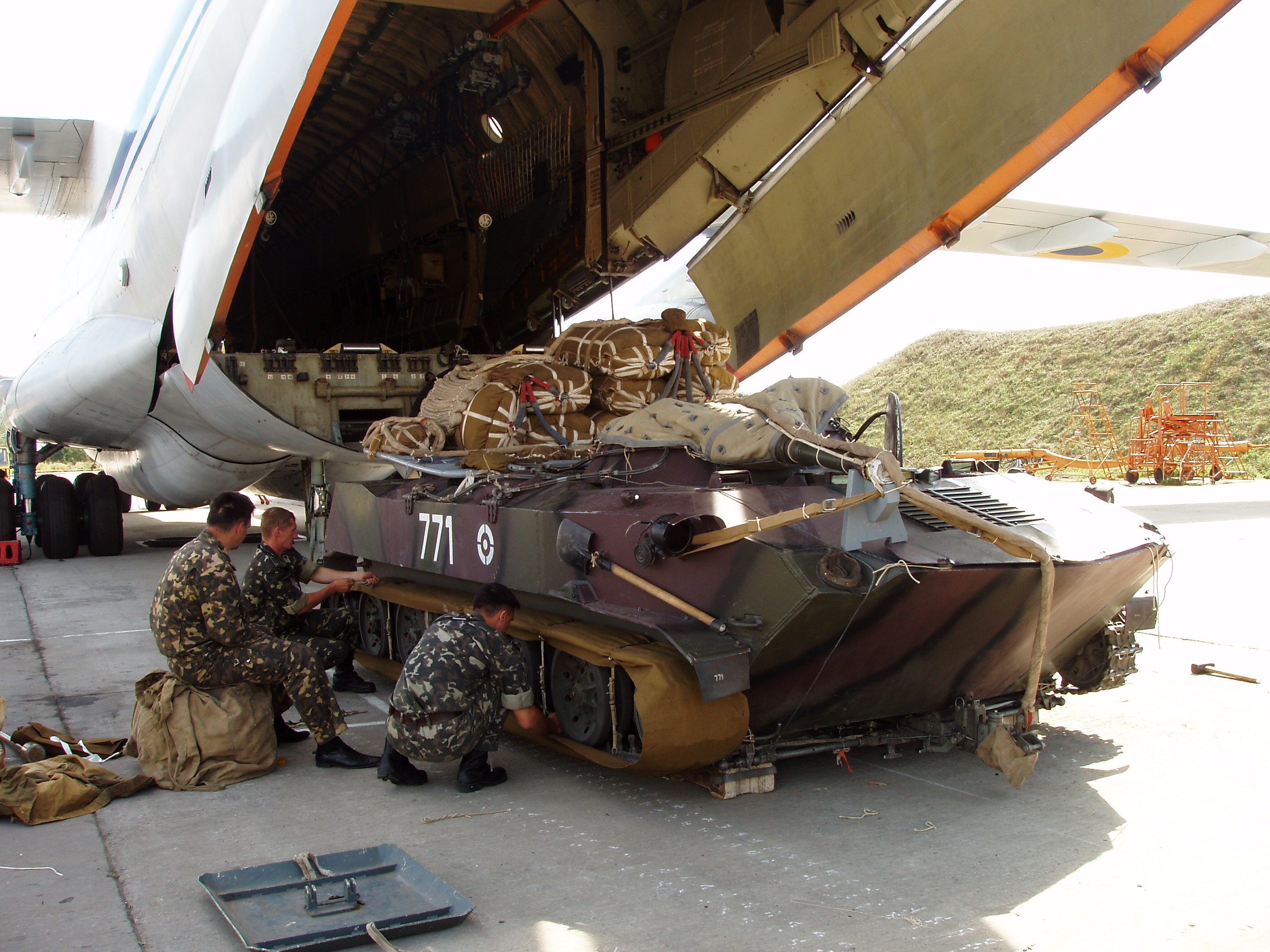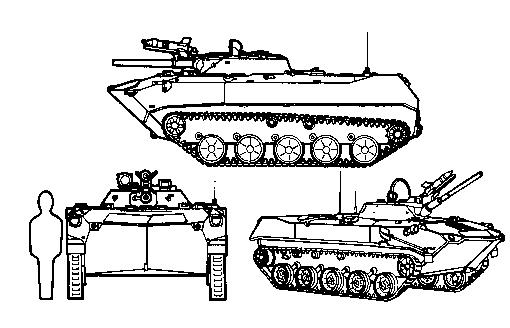
 The vehicle can be transported by
The vehicle can be transported by
. Pancerni.abajt.pl. Retrieved 20 September 2011. The intention was to drop the vehicle off without the crew. This proved to be very problematic since the crew frequently landed at a considerable distance from the vehicle and often had trouble finding it. Also, the vehicle itself could easily land in a location from which it couldn't be extracted (either because of a lack of suitable equipment or because of the location being virtually inaccessible). Several experiments were done in the 1970s in order to find a way to circumvent these limitations, including dropping the BMD with the two key crew members, the driver, and the gunner, seated inside the vehicle during the descent. The first such test took place on 23 January 1976 with Lieutenant-Colonel Leonid Shcherbakov and Major , and the concept was proved to be valid in a subsequent series of tests. A rocket parachute, the PRSM-915, was developed to ensure the vehicle's safe landing. To use the parachute, the BMD is first packed onto a special pallet before take-off. To drop the BMD, a

Warfare.ru. Retrieved 20 September 2011. 98th Guards Airborne Division from
Warfare.ru. Retrieved 20 September 2011. 81st tank repair plant from Armavir (
Warfare.ru. Retrieved 20 September 2011.
 * BMD – First production model.
** BMD-1 (Ob'yekt 915) – Final production model. It has a dome-shaped NBC filter intake on the right hand side of the center of the hull roof.
*** BMD-1K (K stands for komandirskaya – command) – Command variant fitted with R-126 and R-107 transceivers, two Clothes Rail antennas and a generator box. It's sometimes called BMD-K.
*** BMD-1P – BMD-1 modernization with its 9S428 ATGM launcher replaced by pintle-mounted 9P135M-1 ATGM launcher capable of firing 9M113 "Konkurs" (AT-5 Spandrel), 9M113M "Konkurs-M" (AT-5B Spandrel B), 9M111 "Fagot" (AT-4 Spigot) and 9M111-2 "Fagot" (AT-4B Spigot B) ATGMs. Entered service in 1977.
**** BMD-1PK (K stands for komandirskaya – command) – Command variant of BMD-1P. It is fitted with an additional R-123M radio set, a generator, the GPK-59 gyroscopic compass, the PRKhR radiation and chemical reconnaissance unit and two attachable tables. The machine gun mounted in the left corner of the bow of the hull has been eliminated as well as one of the seats. The crew consists of 6 men. The ammo load was reduced by one 9M113 "Konkurs" (AT-5 Spandrel) ATGM and 250 7.62 mm machine gun rounds.
*** BMD-1M – BMD-1 with smoke grenade launchers on the rear of the turret, improved ventilation and road wheels.
*** BMD-1 with its 73 mm 2A28 "Grom" main gun replaced by 30 mm autocannon.
*** BMD-1 with its 73 mm 2A28 "Grom" main gun replaced by 30 mm AGS-17 "Plamya"
* BMD – First production model.
** BMD-1 (Ob'yekt 915) – Final production model. It has a dome-shaped NBC filter intake on the right hand side of the center of the hull roof.
*** BMD-1K (K stands for komandirskaya – command) – Command variant fitted with R-126 and R-107 transceivers, two Clothes Rail antennas and a generator box. It's sometimes called BMD-K.
*** BMD-1P – BMD-1 modernization with its 9S428 ATGM launcher replaced by pintle-mounted 9P135M-1 ATGM launcher capable of firing 9M113 "Konkurs" (AT-5 Spandrel), 9M113M "Konkurs-M" (AT-5B Spandrel B), 9M111 "Fagot" (AT-4 Spigot) and 9M111-2 "Fagot" (AT-4B Spigot B) ATGMs. Entered service in 1977.
**** BMD-1PK (K stands for komandirskaya – command) – Command variant of BMD-1P. It is fitted with an additional R-123M radio set, a generator, the GPK-59 gyroscopic compass, the PRKhR radiation and chemical reconnaissance unit and two attachable tables. The machine gun mounted in the left corner of the bow of the hull has been eliminated as well as one of the seats. The crew consists of 6 men. The ammo load was reduced by one 9M113 "Konkurs" (AT-5 Spandrel) ATGM and 250 7.62 mm machine gun rounds.
*** BMD-1M – BMD-1 with smoke grenade launchers on the rear of the turret, improved ventilation and road wheels.
*** BMD-1 with its 73 mm 2A28 "Grom" main gun replaced by 30 mm autocannon.
*** BMD-1 with its 73 mm 2A28 "Grom" main gun replaced by 30 mm AGS-17 "Plamya"  * 2S2 Fialka (Object 924) – Prototype airborne self-propelled gun designed by I. V. Gabalov.
* 2S2 Fialka (Object 924) – Prototype airborne self-propelled gun designed by I. V. Gabalov.


Armstrade.sipri.org. Retrieved 20 September 2011. * * : 25 received from Soviet Union in 1981. *: Retired in favour of BMD-2. * *: An unspecified number inherited from the Soviet Union. 20 in service as recently as 2023, though serviceability was doubtful.
DishModels.ru: Walkaround of BMD-1 in Saratov
{{PostWWIISovietAFVS Tracked infantry fighting vehicles Fire support vehicles Infantry fighting vehicles of the Soviet Union Airborne fighting vehicles Infantry fighting vehicles of the Cold War Volgograd Tractor Plant products Military vehicles introduced in the 1960s
infantry fighting vehicle
An infantry fighting vehicle (IFV), also known as a mechanized infantry combat vehicle (MICV), is a type of armoured fighting vehicle and armoured personnel carrier used to carry infantry into battle and provide direct fire, direct-fire suppo ...
(IFV), which was introduced in 1969 and first seen by the West in 1970. BMD stands for ''Boyevaya Mashina Desanta'' (Боевая Машина Десанта, which literally translates to "Airborne Combat Vehicle"). It can be dropped by parachute and although it is of similar shape to the BMP-1
The BMP-1 is a Soviet Union, Soviet Amphibious vehicle, amphibious tracked infantry fighting vehicle that has been in service from 1966 to the present. BMP stands for ''Boyevaya Mashina Pyekhoty 1'' (), meaning "infantry fighting vehicle, 1st ...
it is smaller, at just over half the weight. The BMD-1 was used as an IFV by the Soviet Airborne Forces
The Soviet Airborne Forces or VDV (from ''Vozdushno- desantnye voyska SSSR'', Russian: Воздушно-десантные войска СССР, ВДВ; Air-landing Forces) was a separate troops branch of the Soviet Armed Forces. First formed b ...
(VDV). An improved variant of the BMD-1 was developed, the BMD-2
The BMD-2 is a Soviet airborne forces, airborne infantry fighting vehicle, introduced in 1985. It is a variant of BMD-1 with a new turret and changes to the hull. BMD stands for ''Boyevaya Mashina Desanta'' (Боевая Машина Десант� ...
. The BMD-1 also provided a basis for the BTR-D
The BTR-D is a Soviet airborne multi-purpose tracked armoured personnel carrier. It was introduced in 1974 and first seen by the West in 1979 during the Soviet–Afghan War. BTR-D stands for ''Bronetransportyor Desanta'' (БТР-Д, Бронет ...
airborne multi-purpose tracked APC.
Development
In the wake of theCuban Missile Crisis
The Cuban Missile Crisis, also known as the October Crisis () in Cuba, or the Caribbean Crisis (), was a 13-day confrontation between the governments of the United States and the Soviet Union, when American deployments of Nuclear weapons d ...
, the army was instructed to consider putting more emphasis on means to project power outside of the normal sphere of Soviet
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
influence. As a result, there was a major effort to develop the VDV as a rapid deployment force. Soviet studies of airborne operations had shown that lightly armed paratroops were unable to deal with armoured forces. Also, in the early 1960s, the BMP-1 infantry fighting vehicle was being developed. Before the BMP-1 entered service in 1966, the Soviet Army high command decided to equip the newly created airborne divisions with similar vehicles.
The use of Antonov An-12
The Antonov An-12 ( Russian: Антонов Ан-12; NATO reporting name: Cub) is a four-engined turboprop transport aircraft designed in the Soviet Union. It is the military version of the Antonov An-10 and has many variants. For more than thr ...
aircraft during the BMD development limited the transport to only light armored vehicles for an airborne drop, each weighing less than seven tons. Because the existing BMP-1 weighed 13 tonnes, it was effectively ruled out of being considered for the VDV service.
The task of designing the BMD fell to the Volgograd Tractor Factory
The Volgograd Tractor Plant (, ''Volgogradski traktorni zavod'', or , ''VgTZ''), formerly the ''Dzerzhinskiy'' Tractor Factory or the Stalingrad Tractor Plant, is a heavy equipment factory located in Volgograd, Russia. It was once one of the larg ...
, which had produced an unsuccessful competitor to the Ob'yekt 764 that eventually became the BMP-1 – the Ob'yekt 914. The BMD design, Ob'yekt 915, was basically a trimmed-down version of the Ob'yekt 914 – smaller, lighter aluminium armour, while retaining the 73mm 2A28 "Grom" low-pressure smoothbore short-recoil semi-automatic gun. The compromise made is the extremely cramped crew compartment.
Development started in 1965 and trials began in 1967. A limited production began in 1968. After operational trials, it was commissioned on 14 April 1969 and serial production started in 1970, although the vehicle weighed 500 kg more than what the requirements stated (7.5 tonnes and 13.3 tonnes when loaded with equipment).
Starting from 1977 a new modernized vehicle received a designation BMD-1P following adoption of the new 9P135M-1 ATGM launcher instead of 9S428 ATGM launcher, firing the 9M113 Konkurs
The 9M113 ''Konkurs'' (; ; NATO reporting name AT-5 ''Spandrel'') is a Soviet SACLOS wire-guided anti-tank missile.
A development of the 9K111 Fagot with greater firepower, the 9M113 Konkurs can use the same launchers and is very similar vis ...
(AT-5 Spandrel) and 9M111M Fagot or 9M111-2 (standard load: two 9M113 and one 9M111M missiles). Most of older BMD-1s were subsequently modernized this way.
In 1983, based on the combat experience in Afghanistan, a decision was made to produce a new variant of the BMD with a weapon capable of engaging targets such as those faced by the airborne troops in that conflict. This resulted in "Ob'yekt 916", which later became the BMD-2
The BMD-2 is a Soviet airborne forces, airborne infantry fighting vehicle, introduced in 1985. It is a variant of BMD-1 with a new turret and changes to the hull. BMD stands for ''Boyevaya Mashina Desanta'' (Боевая Машина Десант� ...
.
A lengthened BMD-1 chassis served as the basis for the BTR-D
The BTR-D is a Soviet airborne multi-purpose tracked armoured personnel carrier. It was introduced in 1974 and first seen by the West in 1979 during the Soviet–Afghan War. BTR-D stands for ''Bronetransportyor Desanta'' (БТР-Д, Бронет ...
airborne multi-purpose tracked APC, which itself served as a basis for many specialized airborne vehicles.
Description

Overview
The BMD-1 can be thought of as a BMP intended for airborne troops. The vehicle therefore must be lighter and smaller in order to meet airdrop weight requirements (the BMD-1 is secured to a pallet and parachute-dropped from cargo planes). The BMD-1 has an unconventional layout for an IFV. From the front to the back of the vehicle, the compartments are located in the following formation: steering, fighting, troop, and engine. This is because the BMD-1 is based on Ob'yekt 914, which in turn is based on thePT-76
The PT-76 is a Soviet Union, Soviet amphibious vehicle, amphibious light tank that was introduced in the early 1950s and soon became the standard reconnaissance tank of the Soviet Army and the other Warsaw Pact armed forces. It was widely exporte ...
amphibious light tank (refer to for details). This meant that transported troops had to mount and dismount the vehicle via the roof hatches, which made them an easy target on the battlefield when these actions were performed.
Crew
The crew consists of four soldiers: driver, commander, gunner, and bow machine gunner, two of which (commander and machine gunner) are included in the number of soldiers carried. The driver's station is located centrally in the front of the vehicle and has a hatch that is opened by raising it and rotating it to the right. The driver is provided with three periscope vision blocks, which allow him to view the outer environment when his hatch is closed. The center one can be replaced with a night vision device for use in the night and bad visibility conditions or with an extended periscope for swimming with the trim vane erected. The commander's station is on the driver's left. It is provided with a hatch, one periscope vision block, an outer environment observation device, and anR-123
R-123 "Magnolia" (Р-123 «Магнолия») is a Soviet military HF/ VHF radio transceiver designed for use in tanks and other armoured vehicles. The device was made in the Ryazan radio plant.
Deployment
The R-123 set was commonly used in c ...
radio set for communications. He also fires the left bow machine gun. The right one is operated by a bow machine gun gunner, who sits to the right of the driver. The gunner's station is located on the left side of the turret, like in the BMP-1, and has the same equipment (see Gunner's station section in the BMP-1 article for details).
Turret
The BMD-1 has the same turret as the BMP-1.Armament
The vehicle is armed with a 73 mm2A28 Grom
The 2A28 Grom also known as KBP 2A28 Grom, is the main armament of the Soviet-designed BMP-1 and BMD-1 infantry fighting vehicles. It is a 73 mm low pressure smoothbore semi-automatic gun with a wedge breech block. Development of the 2A28 G ...
gun and a 7.62 mm PKT coaxial tank machine gun. Mounted on the mantlet is the 9S428 ATGM launcher capable of firing 9M14 Malyutka
The 9M14 Malyutka (; "Little one", NATO reporting name: AT-3 Sagger) is a manual command to line of sight (MCLOS) wire-guided anti-tank guided missile (ATGM) system developed in the Soviet Union. It was the first man-portable anti-tank guided mi ...
(NATO: AT-3A Sagger A) and 9M14M Malyutka-M (NATO: AT-3B Sagger B) ATGMs (for which the vehicle carries two ATGMs in the turret). There are also two 7.62 mm PKT machine guns in fixed mounts, one in each corner of the bow.
Mobility
Maneuverability
The vehicle is powered by a 5D-20 6-cylinder 4-stroke V-shaped liquid-cooled 15.9-liter diesel engine, which develops 270 hp (201 kW) at 2,600 revolutions per minute. The engine drives a manual gearbox with five forward and one reverse gear. The BMD-1 has a maximum road speed of 80 kilometers per hour, reduced to around 45 kilometers per hour off-road and 10 kilometers per hour while swimming. The BMD-1 can climb vertical obstacles, cross trenches, and 30% side slopes. It can climb 60% gradients. The BMD-1 has a ground pressure of 0.57 kg/cm2. The 230 mm wide track is driven at the rear and passes over five small evenly spaced road wheels suspended on independent torsion bars. On each side, there is an idler wheel at the front, a rear drive sprocket, and four track-return rollers. The independent suspension combines a hydraulic system for altering the ground clearance and maintaining the track tension with pneumatic springs, which enables the ground clearance to be altered from 100 mm to 450 mm. The alternative ground clearance allows easier transportation in an airplane.Amphibious ability
The BMD-1 is fully amphibious, it can swim after switching on the two electric bilge pumps, erecting the two-piece trim vane which improves the vehicle's stability and displacement in water and prevents the water from flooding the bow of the tank, and switching the driver's periscope for a swimming periscope that enables the driver to see over the trim vane. When not in use the trim vane is placed in its laying position in the front of the bow under the barrel of the main gun and serves as additional armour. There is also a manual bilge pump for emergency use. The bilge pumps keep the vehicle afloat even if it is hit, damaged or leaks. In water, it is propelled by two hydro jets, one on each side of the hull, with the entrance under the hull and exits at the rear of the hull. The rear exits have lids that can be fully or partially closed, redirecting the water stream to the forward-directed exits at the sides of the hull, thus enabling the vehicle to turn or float reverse, for example, to go left, the left water jet is closed, reducing thrust on that side and redirecting some or all of the water flow to the forward facing nozzle. To go right, the right water-jet is covered. The closure of the nozzles is proportionate to the control input. To make a 180° turn the left water-jet can direct water to the rear nozzle and the right water-jet to the front nozzle, creating forward thrust on one side and reverse thrust on the other, or the vehicle can reverse by closing both nozzles and directing all water flow out the forward nozzles (seePT-76
The PT-76 is a Soviet Union, Soviet amphibious vehicle, amphibious light tank that was introduced in the early 1950s and soon became the standard reconnaissance tank of the Soviet Army and the other Warsaw Pact armed forces. It was widely exporte ...
for full explanation of the water jet system).
Air-drop techniques
 The vehicle can be transported by
The vehicle can be transported by An-12
The Antonov An-12 (Russian language, Russian: Антонов Ан-12; NATO reporting name: Cub) is a four-engined turboprop Cargo aircraft, transport aircraft designed in the Soviet Union. It is the military version of the Antonov An-10 and has ...
, An-22, Il-76
The Ilyushin Il-76 (; NATO reporting name: Candid) is a multi-purpose, fixed-wing, four-engine turbofan strategic airlifter designed by the Soviet Union's Ilyushin design bureau as a commercial freighter in 1967, to replace the Antonov An-12. ...
, An-124 airplanes and Mi-6
The Secret Intelligence Service (SIS), commonly known as MI6 ( Military Intelligence, Section 6), is the foreign intelligence service of the United Kingdom, tasked mainly with the covert overseas collection and analysis of human intelligence ...
and Mi-26
The Mil Mi-26 (, NATO reporting name: Halo) is a Soviet Union, Soviet/Russian heavy Military transport helicopter, transport helicopter. Its product code is ''Izdeliye 90''. Operated by both military and civilian operators, it is the largest ...
helicopters.
The BMD was originally dropped under the MKS-350-9 multi-canopy parachute
A parachute is a device designed to slow an object's descent through an atmosphere by creating Drag (physics), drag or aerodynamic Lift (force), lift. It is primarily used to safely support people exiting aircraft at height, but also serves va ...
with a descending speed between 15 m/s and 20 m/s.Pancerni.net BMD-2 2. Pancerni.abajt.pl. Retrieved 20 September 2011. The intention was to drop the vehicle off without the crew. This proved to be very problematic since the crew frequently landed at a considerable distance from the vehicle and often had trouble finding it. Also, the vehicle itself could easily land in a location from which it couldn't be extracted (either because of a lack of suitable equipment or because of the location being virtually inaccessible). Several experiments were done in the 1970s in order to find a way to circumvent these limitations, including dropping the BMD with the two key crew members, the driver, and the gunner, seated inside the vehicle during the descent. The first such test took place on 23 January 1976 with Lieutenant-Colonel Leonid Shcherbakov and Major , and the concept was proved to be valid in a subsequent series of tests. A rocket parachute, the PRSM-915, was developed to ensure the vehicle's safe landing. To use the parachute, the BMD is first packed onto a special pallet before take-off. To drop the BMD, a
drogue
A drogue or storm drogue is a device trailed behind a boat on a long line attached to the stern. A drogue is used to slow the boat down in a storm and to prevent the hull (watercraft), hull from becoming side-on to the water waves, waves. A boa ...
chute is released that initially drags the BMD out of the Il-76 transport plane. Once clear of the plane a single large main chute opens. The deployment of the main chute triggers the deployment of four long rods which hang beneath the pallet. As soon as the rods touch the ground retrorocket
A retrorocket (short for ''retrograde rocket'') is a rocket engine providing thrust opposing the motion of a vehicle, thereby causing it to decelerate. They have mostly been used in spacecraft, with more limited use in short-runway aircraft land ...
fires, slowing the BMD to a descending speed between 6 m/s and 7 m/s and giving it a relatively soft landing.. This system entered service in 1975 and allows a BMD to be relatively safely parachuted with both the driver and the gunner.
Armour protection
The BMD-1's armour is made of ABT-101 an alloy composed of 91% Aluminum, 6% Zinc, and 3% Magnesium. The BMD-2 on the other hand is composed of ABT-102, which is 94% Aluminum, 4% Zinc, and 2% Magnesium. Armour thickness is 23 mm at 42° on the front of the turret, 19 mm at 36° on the sides of the turret, 13 mm at 30° on the rear of the turret, 6 mm on the top of the turret, 15 mm on the front of the hull and 10 mm on the rest of the hull. The hull's front armour has two sections: upper and lower. The upper section is angled at 78° while the lower one is angled at 50°. It is resistant to small arms fire and shrapnel.Troop compartment
Many compromises had to be made to the design in order to save the necessary weight, not least to crew comfort. The BMD-1 has an extremely cramped interior space, which is much smaller than that found in the BMP-1 and BMP-2 IFVs. It can carry five infantrymen, comprising the vehicle's commander, bow machine gunner, and three soldiers seated behind a turret. Nevertheless, it is equipped with periscope vision blocks on the sides and rear of the vehicle. There are only three firing ports, one on each side of the hull and one in the rear. As standard, the vehicle carries the following weapons inside the troop compartment: anRPG-7
The RPG-7 is a portable, reusable, unguided, shoulder-launched, anti-tank, rocket launcher. The RPG-7 and its predecessor, the RPG-2, were designed by the Soviet Union, and are now manufactured by the Russian company Bazalt. The weapon has t ...
or RPG-16 shoulder-launched anti-tank rocket-propelled grenade launcher, which is to be operated by two soldiers, RPKS light machine gun, and five AKMS assault rifles. It also carries portable launchers for 9M14M Malyutka missiles (9M111/9M113 missiles in BMD-1P).
Equipment
The vehicle has electric and manual bilge pumps, Gpk-S9 gyro-compass, engine pre-heater, TDA smoke-generating equipment, FTP-100M NBC system, R-123 transceiver, R-124 intercom and a centralizedmethyl bromide
Bromomethane, commonly known as methyl bromide, is an organobromine compound with chemical formula, formula Carbon, CHydrogen, H3Bromine, Br. This colorless, odorless, nonflammable gas is Bromine cycle, produced both industrially and biologically ...
fire extinguishing system, the same as the one fitted to other former Soviet armoured vehicles.
Service history
The BMD-1 entered serial production in 1968. It was produced byVolgograd Tractor Plant
The Volgograd Tractor Plant (, ''Volgogradski traktorni zavod'', or , ''VgTZ''), formerly the ''Dzerzhinskiy'' Tractor Factory or the Stalingrad Tractor Plant, is a heavy equipment factory located in Volgograd, Russia. It was once one of the larg ...
. Two airborne regiments of each airborne division were equipped with BMD-1 IFVs. Overall, each division operated 220 BMD-1 IFVs. It was displayed publicly for the first time during the Dvina exercise in the USSR in 1970. The BMD-1 was showcased for the second time during the Moscow Red Square parade in November 1973. Western governments originally classified the BMD-1 as a light tank before its true nature was known. Because of its small crew, the introduction of the BMD led to a reduction in the number of soldiers in an airborne battalion, from 610 to 316 men. The firepower of the BMD also meant that some of the battalion's integral fire support could be done away with. In 1973, the BMD-1 completely replaced the ASU-57
The ASU-57 was a small, lightly constructed Soviet Union, Soviet assault gun specifically designed for use by Soviet Airborne Forces, Soviet airborne divisions. From 1960 onwards, it was gradually phased out in favour of the ASU-85.
Development ...
airborne assault guns in the Soviet airborne forces, increasing the firepower and maneuverability of the airborne division. Since 1977 a number of Soviet BMD-1 IFVs underwent a modernization to the BMD-1P standard.

Ogaden War
In 1978, a force of 70Cuban Army
The Cuban Revolutionary Army () serve as the ground forces of Cuba. Formed in 1868 during the Ten Years' War, it was originally known as the Cuban Constitutional Army. Following the Cuban Revolution, the revolutionary military forces was recon ...
BMD-1s and ASU-57s fighting on behalf of the Ethiopian government was airlifted by Mi-6 helicopters behind the lines of Somali forces holding the town of Jijiiga. This attack formed a pincer with a conventional Cuban armored push and routed the Somali forces in Ogaden
Ogaden (pronounced and often spelled ''Ogadēn''; , ) is one of the historical names used for the modern Somali Region. It is also natively referred to as Soomaali Galbeed (). The region forms the eastern portion of Ethiopia and borders Somalia ...
.
Soviet–Afghan War
It was widely used by airborne units during Soviet–Afghan War. During the initialSoviet invasion of Afghanistan
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until it dissolved in 1991. During its existence, it was the largest country by are ...
in 1979, BMD-1s of the Soviet 103rd Guards Airborne Division and 345th Separate Parachute Regiment were air landed by Il-76 transports into Kabul
Kabul is the capital and largest city of Afghanistan. Located in the eastern half of the country, it is also a municipality, forming part of the Kabul Province. The city is divided for administration into #Districts, 22 municipal districts. A ...
airport and Bagram Airfield
Bagram Airfield-BAF, also known as Bagram Air Base , is located southeast of Charikar in the Parwan Province of Afghanistan. It is under the Ministry of Defense (Afghanistan), Afghan Ministry of Defense. Sitting on the site of the ancient town ...
, enabling the rapid seizure of critical cities and facilities throughout Afghanistan. The 56th Air Assault Brigade executed a similar capture of Kunduz
Kunduz (; ; ) is a city in northern Afghanistan and the capital of Kunduz Province. The city has an estimated population of about 268,893 as of 2015, making it about the List of cities in Afghanistan, seventh largest city of Afghanistan, and the ...
. For the remainder of the Soviet occupation of Afghanistan through 1989, airborne forces under the 40th Army used BMD-1s as infantry fighting vehicles for transportation and fire support in operations against the mujahideen
''Mujahideen'', or ''Mujahidin'' (), is the plural form of ''mujahid'' (), an Arabic term that broadly refers to people who engage in ''jihad'' (), interpreted in a jurisprudence of Islam as the fight on behalf of God, religion or the commun ...
.
BMD-1 IFVs were not suited for fighting in the hot mountain regions of Afghanistan, as they were originally developed to provide airborne units with an IFV to give them a chance in engagements with enemy armour and allow them to operate in Nuclear-Biological-Chemical (NBC) warfare conditions. In Afghanistan, the main enemies were not AFVs but land mines and ambushes prepared by skillful Afghan Mujahideen armed with light anti-tank weapons, which meant that the BMD-1's anti-tank firepower was useless. Many BMD-1 IFVs and light APCs fell victim to Mujahideen attacks and antitank landmines. The Soviet Army lost 1,317 APCs and IFVs of all types during nine years of war in Afghanistan.
Iraq
Iraqi BMD-1s were deployed during the 2003 invasion of Iraq.Former Yugoslavia
BMD-1 and BMD-1PK IFVs are used by the Russian airborne units inKFOR KFOR may refer to:
* KFOR (AM), a radio station (1240 AM) licensed to Lincoln, Nebraska, United States,
* KFOR-TV, a television station (channel 4 analog/27 digital) licensed to Oklahoma City, Oklahoma, United States,
* KFOR-TV (Nebraska), a defun ...
. BMD-1 IFVs were used by Russian airborne units in SFOR.
2008 Georgia–Russia War
During theRusso-Georgian War
The August 2008 Russo-Georgian War, also known as the Russian invasion of Georgia,Occasionally, the war is also referred to by other names, such as the Five-Day War and August War. was a war waged against Georgia by the Russian Federation and the ...
, BMD-1s of the 104th Airborne Assault Regiment of the 76th Guards Air Assault Division advanced into South Ossetia
South Ossetia, officially the Republic of South Ossetia or the State of Alania, is a landlocked country in the South Caucasus with International recognition of Abkhazia and South Ossetia, partial diplomatic recognition. It has an offici ...
and successfully engaged Georgian Army troops and vehicles. However, the BMD's visual and sighting equipment was criticized as being primitive.
2014 Russo-Ukrainian War
During theRusso-Ukrainian War
The Russo-Ukrainian War began in February 2014 and is ongoing. Following Ukraine's Revolution of Dignity, Russia Russian occupation of Crimea, occupied and Annexation of Crimea by the Russian Federation, annexed Crimea from Ukraine. It then ...
in 2014 in Eastern Ukraine
Eastern Ukraine or East Ukraine (; ) is primarily the territory of Ukraine east of the Dnipro (or Dnieper) river, particularly Kharkiv, Luhansk and Donetsk oblasts (provinces). Dnipropetrovsk and Zaporizhzhia oblasts are often also regarded as ...
, BMD-1s were used both by mechanized units of the Ukrainian Army
The Ukrainian Ground Forces (SVZSU, ), also referred to as the Ukrainian army, is a land force, and one of the eight Military branch, branches of the Armed Forces of Ukraine. It was formed from Ukrainian units of the Soviet Army after Declaratio ...
and in smaller numbers by the separatists of the Donetsk People's Republic
The Donetsk People's Republic (DPR; , ) is Russian-occupied territories of Ukraine, occupied territory in Ukraine that the Russian Federation has claimed to annex and declared as a Republics of Russia, republic of Russia, comprising parts o ...
. It was claimed that a BMD-1 was one of the six armored vehicles in Separatist forces defending Sloviansk when it was besieged.
Present service
As of now, BMD-1 and vehicles based on it are used by the following units of Russian Airborne Troops or are stationed in following bases (this list does not include BTR-D APCs and BTR-D variants): 76th Guards Air Assault Division (CDO) fromPskov
Pskov ( rus, Псков, a=Ru-Псков.oga, p=psˈkof; see also Names of Pskov in different languages, names in other languages) is a types of inhabited localities in Russia, city in northwestern Russia and the administrative center of Pskov O ...
, which is part of Leningrad Military District (210 BMD vehicles as of 2000), the subunits of this division include 104th airborne regiment from Pskov (51 BMD-1) and 234th airborne regiment from Pskov (98 BMD-1).VDVWarfare.ru. Retrieved 20 September 2011. 98th Guards Airborne Division from
Ivanovo
Ivanovo (, ) is a types of inhabited localities in Russia, city in Russia and the administrative center and largest city of Ivanovo Oblast, located northeast of Moscow and approximately from Yaroslavl, Vladimir, Russia, Vladimir and Kostroma. ...
(220 BMD vehicles as of 2000), the subunits of this division include 217th Guards Airborne Regiment from Ivanovo (109 BMD-1) and 331st airborne regiment from Kostroma
Kostroma (, ) is a historic city and the administrative center of Kostroma Oblast, Russia. A part of the Golden Ring of Russian cities, it is located at the confluence of the rivers Volga and Kostroma. In the 2021 census, the population is 267, ...
(102 BMD-1).
106th Guards Airborne Division from Tula, which is a part of the Moscow Military District (306 BMD as of 2000), the subunits of this division include 51st airborne regiment from Tula (93 BMD-1) and 137th airborne regiment from Ryazan
Ryazan (, ; also Riazan) is the largest types of inhabited localities in Russia, city and administrative center of Ryazan Oblast, Russia. The city is located on the banks of the Oka River in Central Russia, southeast of Moscow. As of the 2010 C ...
(10 BMD-1).
7th Guards Airborne Mountain Division CDO from Novorossyysk (190 BMD and BMP vehicles as of 2000), the subunits of this division include 108th Guards Air Assault Regiment from Novorossyysk (70 BMD-1) and 743rd commandos battalion from Novorossyysk (6 BMD-1).
31st Separate Airborne Brigade from Ul'yanovsk
Ulyanovsk,, , known as Simbirsk until 1924, is a types of inhabited localities in Russia, city and the administrative center of Ulyanovsk Oblast, Russia, located on the Volga River east of Moscow. Ulyanovsk has been the only Russian UNESCO Ci ...
, which is a part of the Volga-Ural Military District (26 BMD-1 as of 2000).
Ryazan Higher Airborne Command School (51 BMD-1).
99th Internal Troops division from Rostov
Rostov-on-Don is a port city and the administrative centre of Rostov Oblast and the Southern Federal District of Russia. It lies in the southeastern part of the East European Plain on the Don River, from the Sea of Azov, directly north of t ...
, Persianovka, which is a part of the North Caucasus Military District (4 BMD-1 and 33 BMD-1 IFVs in the Cherkmen regiment).North Caucasus Military DistrictWarfare.ru. Retrieved 20 September 2011. 81st tank repair plant from Armavir (
Krasnodar
Krasnodar, formerly Yekaterinodar (until 1920), is the largest city and the administrative centre of Krasnodar Krai, Russia. The city stands on the Kuban River in southern Russia, with a population of 1,154,885 residents, and up to 1.263 millio ...
) (1 BMD-1).General StaffWarfare.ru. Retrieved 20 September 2011.
Replacement
The Russian military was considering replacing the BMD series altogether with the GAZ-3937. This very lightweight wheeled armoured personnel carrier that incorporates plastic andcarbon fibre
Carbon fiber-reinforced polymers (American English), carbon-fibre-reinforced polymers ( Commonwealth English), carbon-fiber-reinforced plastics, carbon-fiber reinforced-thermoplastic (CFRP, CRP, CFRTP), also known as carbon fiber, carbon comp ...
in its construction, as well as aluminum. The GAZ-3937 can be air-dropped like the BMD, but is considerably lighter and less expensive to manufacture. Since the GAZ-3937 lacks the armor protection, cross-country mobility, and heavy armament of the BMD series, and is armed only with a 7.62 mm PKM machine gun in front of the commander's hatch, the BMD-4 (an upgraded BMD-3) has been selected for the future use of the Russian airborne and naval infantry. The BMD-4 uses the same 100 mm main gun with 30 mm autocannon and 7.62 mm medium machine gun turret on an improved, larger hull raising overall weight to the 15-ton class. The waterjet swim propulsion systems of the BMD-3/4 are strong enough to enable ship-to-shore transport, resulting in Russian naval infantry use.
Variants
Former USSR
automatic grenade launcher
An automatic grenade launcher (AGL) or grenade machine gun is a grenade launcher that is capable of fully automatic fire, and is typically loaded with either an Belt (firearm), ammunition belt or Magazine (firearm), magazine.
These weapons are oft ...
.
*** BMD-1 converted into a mortar carrier.
*** BMD-1 with turret mounted 2B9 Vasilek mortar.
*** BMD-1 converted into a self-propelled multiple rocket launcher. The armament was removed and replaced by a vision device. Fitted on top of the turret is a small box-type launcher for 12×80 mm rockets.
*** BMD-2
The BMD-2 is a Soviet airborne forces, airborne infantry fighting vehicle, introduced in 1985. It is a variant of BMD-1 with a new turret and changes to the hull. BMD stands for ''Boyevaya Mashina Desanta'' (Боевая Машина Десант� ...
(Object 916) – BMD-1 variant with a new one-man turret armed with stabilized 30 mm 2A42 multi-purpose autocannon and 7.62 mm PKT coaxial tank machine gun (mounted on the right hand side of the main gun). The vehicle carries 300 rounds for the main gun (180 AP and 120 HE) and 2,940 rounds for the machine gun. The gun has a maximum elevation of 75° and can be used to fire at air targets. The turret is also armed with pintle-mounted 9P135M launcher, on the right hand side of the roof of the turret, with semi-automatic control capable of firing SACLOS guided 9M113 "Konkurs" (AT-5 Spandrel) and 9M113M "Konkurs-M" (AT-5B Spandrel B) ATGMs. The new turret seats the gunner on the left hand side of the main gun. On top of the turret there's one single piece circular hatch opening to the front. Located in front of the said hatch is the gunner's sight which is the same one as the one used in BMP-2
The BMP-2 (''Boyevaya Mashina Pekhoty'', , literally "combat machine/vehicle f theinfantry") is an amphibious infantry fighting vehicle introduced in the 1980s in the Soviet Union, following on from the BMP-1 of the 1960s.
Development his ...
. Another gunner's sight is located on the left hand side of the main gun and moves in vertical planes along with it. It is a high angle of fire sight used when the gunner is aiming at air targets. The vehicle also has additional periscopes that provide it with vision on the sides. A white searchlight is mounted in front of the turret. The amount of bow mounted tank machine guns decreased from two to one. The right hand side bow mounted machine gun was preserved. NATO gave it the designation BMD M1981/1.
*** BTR-D
The BTR-D is a Soviet airborne multi-purpose tracked armoured personnel carrier. It was introduced in 1974 and first seen by the West in 1979 during the Soviet–Afghan War. BTR-D stands for ''Bronetransportyor Desanta'' (БТР-Д, Бронет ...
(Object 925) (''bronyetransportyor'') – Lengthened variant (with 6 rather than 5 road wheels), slightly up-armoured at the front. The BTR-D has no turret, but is armed with two bow-mounted machine guns PKB and can be fitted with pintle-mounted automatic grenade launchers (AGS-17, AGS-30 or AGS-57) and/or machine guns (PKM, 6P41, "Utyos" or "Kord"). Entered service in 1974 and can carry 10 passengers. Combat weight: 8.5 tons.
Belarus
* BMD-1 fitted with 2A42 Cobra overhead mount modular one-man turret.Russia
* BMD-1 modernization fitted with TKB-799 "Kliver" one-man weapons station developed by Tula Instrument Engineering Design Bureau (KBP). It is armed with a missile pod, a 30 mm 2A72 multipurpose autocannon (it can be used against both ground targets and air targets) and a 7.62 mm PKTM coaxial general purpose machine gun. The missile pod is mounted on the right side of the weapons station and normally holds four 9M133 Kornet (AT-14 Spriggan) or 9M133F "Kornet" ATGMs with laser jam-resistant fire control system but these can be removed and replaced by a pod of 9K38 Igla (SA-18 Grouse) surface-to-air missiles. It carries 300 rounds for the main gun, 2000 rounds for PKTM machine gun and 4 ATGMs. It also has a modern computerized fire control system with two-plane stabilizer, 1K13-2 telescopic sight with distance measurement/thermal/laser channels and ballistic calculator with external sensors.Operators


Current operators
*: 10 as of 2024; in service with Armenian army and border guards. *: 20 in service as of 2024. * : Some may remain in reserve storage. *: 44 BMD-1 as of 2024. *: 8 BMD-1 in service as of 2024. *: 120 BMD-1 in service as of 2024.Former operators
*: 10 received from Soviet Union in 1988. * * : 35 received from Soviet Union in 1977.SIPRI Arms Transfers DatabaseArmstrade.sipri.org. Retrieved 20 September 2011. * * : 25 received from Soviet Union in 1981. *: Retired in favour of BMD-2. * *: An unspecified number inherited from the Soviet Union. 20 in service as recently as 2023, though serviceability was doubtful.
See also
* BMP Development *BMD-2
The BMD-2 is a Soviet airborne forces, airborne infantry fighting vehicle, introduced in 1985. It is a variant of BMD-1 with a new turret and changes to the hull. BMD stands for ''Boyevaya Mashina Desanta'' (Боевая Машина Десант� ...
* BMD-3
* BTR-D
The BTR-D is a Soviet airborne multi-purpose tracked armoured personnel carrier. It was introduced in 1974 and first seen by the West in 1979 during the Soviet–Afghan War. BTR-D stands for ''Bronetransportyor Desanta'' (БТР-Д, Бронет ...
* BMP-1
The BMP-1 is a Soviet Union, Soviet Amphibious vehicle, amphibious tracked infantry fighting vehicle that has been in service from 1966 to the present. BMP stands for ''Boyevaya Mashina Pyekhoty 1'' (), meaning "infantry fighting vehicle, 1st ...
* BMP-2
The BMP-2 (''Boyevaya Mashina Pekhoty'', , literally "combat machine/vehicle f theinfantry") is an amphibious infantry fighting vehicle introduced in the 1980s in the Soviet Union, following on from the BMP-1 of the 1960s.
Development his ...
* BMP-3
* List of AFVs
*
*
References
* Hull, A.W., Markov, D.R., Zaloga, S.J. (1999). ''Soviet/Russian Armor and Artillery Design Practices 1945 to Present''. Darlington Productions. . * *External links
DishModels.ru: Walkaround of BMD-1 in Saratov
{{PostWWIISovietAFVS Tracked infantry fighting vehicles Fire support vehicles Infantry fighting vehicles of the Soviet Union Airborne fighting vehicles Infantry fighting vehicles of the Cold War Volgograd Tractor Plant products Military vehicles introduced in the 1960s