|
BMC Domain
In molecular biology the Bacterial Microcompartment (BMC) domain is a protein domain found in a variety of shell proteins, including CsoS1A, CsoS1B and CsoS1C of ''Thiobacillus neapolitanus'' (''Halothiobacillus neapolitanus'') and their orthologs from other bacteria. These shell proteins form the polyhedral structure of the carboxysome and related structures that plays a metabolic role in bacteria. The BMC domain consists of about 90 amino acid residues, characterized by β-α-β motif connected by a β-hairpin The beta hairpin (sometimes also called beta-ribbon or beta-beta unit) is a simple protein structural motif involving two beta strands that look like a hairpin. The motif consists of two strands that are adjacent in primary structure, oriented in .... The majority of the shell proteins consist of a single BMC domain in each subunit, forming a hexameric structure that assembles to form the flat facets of the polyhedral shell. To date, two shell proteins were found to consi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Biology
Molecular biology is a branch of biology that seeks to understand the molecule, molecular basis of biological activity in and between Cell (biology), cells, including biomolecule, biomolecular synthesis, modification, mechanisms, and interactions. Though cells and other microscopic structures had been observed in living organisms as early as the 18th century, a detailed understanding of the mechanisms and interactions governing their behavior did not emerge until the 20th century, when technologies used in physics and chemistry had advanced sufficiently to permit their application in the biological sciences. The term 'molecular biology' was first used in 1945 by the English physicist William Astbury, who described it as an approach focused on discerning the underpinnings of biological phenomena—i.e. uncovering the physical and chemical structures and properties of biological molecules, as well as their interactions with other molecules and how these interactions explain observ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Domain
In molecular biology, a protein domain is a region of a protein's Peptide, polypeptide chain that is self-stabilizing and that Protein folding, folds independently from the rest. Each domain forms a compact folded Protein tertiary structure, three-dimensional structure. Many proteins consist of several domains, and a domain may appear in a variety of different proteins. Molecular evolution uses domains as building blocks and these may be recombined in different arrangements to create proteins with different functions. In general, domains vary in length from between about 50 amino acids up to 250 amino acids in length. The shortest domains, such as zinc fingers, are stabilized by metal ions or Disulfide bond, disulfide bridges. Domains often form functional units, such as the calcium-binding EF-hand, EF hand domain of calmodulin. Because they are independently stable, domains can be "swapped" by genetic engineering between one protein and another to make chimera (protein), chimeric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homology (biology)
In biology, homology is similarity in anatomical structures or genes between organisms of different taxa due to shared ancestry, ''regardless'' of current functional differences. Evolutionary biology explains homologous structures as retained heredity from a common descent, common ancestor after having been subjected to adaptation (biology), adaptive modifications for different purposes as the result of natural selection. The term was first applied to biology in a non-evolutionary context by the anatomist Richard Owen in 1843. Homology was later explained by Charles Darwin's theory of evolution in 1859, but had been observed before this from Aristotle's biology onwards, and it was explicitly analysed by Pierre Belon in 1555. A common example of homologous structures is the forelimbs of vertebrates, where the bat wing development, wings of bats and origin of avian flight, birds, the arms of primates, the front flipper (anatomy), flippers of whales, and the forelegs of quadrupedalis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyhedron
In geometry, a polyhedron (: polyhedra or polyhedrons; ) is a three-dimensional figure with flat polygonal Face (geometry), faces, straight Edge (geometry), edges and sharp corners or Vertex (geometry), vertices. The term "polyhedron" may refer either to a solid figure or to its boundary surface (mathematics), surface. The terms solid polyhedron and polyhedral surface are commonly used to distinguish the two concepts. Also, the term ''polyhedron'' is often used to refer implicitly to the whole structure (mathematics), structure formed by a solid polyhedron, its polyhedral surface, its faces, its edges, and its vertices. There are many definitions of polyhedron. Nevertheless, the polyhedron is typically understood as a generalization of a two-dimensional polygon and a three-dimensional specialization of a polytope, a more general concept in any number of dimensions. Polyhedra have several general characteristics that include the number of faces, topological classification by Eule ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carboxysome
Carboxysomes are bacterial microcompartments (BMCs) consisting of polyhedral protein shells filled with the enzymes ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase ( RuBisCO)—the predominant enzyme in carbon fixation and the rate limiting enzyme in the Calvin cycle—and carbonic anhydrase. Carboxysomes are thought to have evolved as a consequence of the increase in oxygen concentration in the ancient atmosphere; this is because oxygen is a competing substrate to carbon dioxide in the RuBisCO reaction. To overcome the inefficiency of RuBisCO, carboxysomes concentrate carbon dioxide inside the shell by means of co-localized carbonic anhydrase activity, which produces carbon dioxide from the bicarbonate that diffuses into the carboxysome. The resulting concentration of carbon dioxide near RuBisCO decreases the proportion of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate oxygenation and thereby avoids costly photorespiratory reactions. The surrounding shell provides a barrier to carbon dio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amino Acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the 22 α-amino acids incorporated into proteins. Only these 22 appear in the genetic code of life. Amino acids can be classified according to the locations of the core structural functional groups ( alpha- , beta- , gamma- amino acids, etc.); other categories relate to polarity, ionization, and side-chain group type ( aliphatic, acyclic, aromatic, polar, etc.). In the form of proteins, amino-acid '' residues'' form the second-largest component (water being the largest) of human muscles and other tissues. Beyond their role as residues in proteins, amino acids participate in a number of processes such as neurotransmitter transport and biosynthesis. It is thought that they played a key role in enabling life on Earth and its emergence. Amino acids are formally named by the IUPAC- IUBMB Joint Commi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
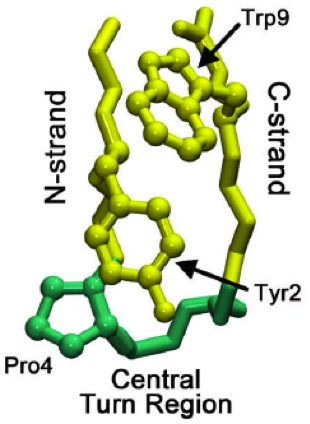
β-hairpin
The beta hairpin (sometimes also called beta-ribbon or beta-beta unit) is a simple protein structural motif involving two beta strands that look like a hairpin. The motif consists of two strands that are adjacent in primary structure, oriented in an antiparallel direction (the N-terminus of one sheet is adjacent to the C-terminus of the next), and linked by a short loop of two to five amino acids. Beta hairpins can occur in isolation or as part of a series of hydrogen bonded strands that collectively comprise a beta sheet. Researchers such as Francisco Blanco ''et al.'' have used protein NMR to show that beta-hairpins can be formed from isolated short peptides in aqueous solution, suggesting that hairpins could form nucleation sites for protein folding. Classification Beta hairpins were originally categorized solely by the number of amino acid residues in their loop sequences, such that they were named one-residue, two-residue, etc. This system, however, is somewhat ambiguous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |