|
Alcohol (drug)
Alcohol, sometimes referred to by the chemical name ''ethanol'', is a depressant drug that is the active ingredient in drinks such as beer, wine, and distilled spirits (hard liquor). It is one of the oldest and most commonly consumed recreational drugs, causing the characteristic effects of alcohol intoxication ("drunkenness"). Among other effects, alcohol produces happiness and euphoria, decreased anxiety, increased sociability, sedation, impairment of cognitive, memory, motor, and sensory function, and generalized depression of central nervous system (CNS) function. Ethanol is only one of several types of alcohol, but it is the only type of alcohol that is found in alcoholic beverages or commonly used for recreational purposes; other alcohols such as methanol and isopropyl alcohol are significantly more toxic. A mild, brief exposure to isopropanol, being only moderately more toxic than ethanol, is unlikely to cause any serious harm. Methanol, being profoundly more t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alcohol Enema
An alcohol enema, also known colloquially as butt-chugging or boofing, is the act of introducing alcohol into the rectum and colon via the anus, i.e., as an enema. This method of alcohol consumption can be dangerous and even deadly because it leads to faster intoxication than drinking since the alcohol is absorbed directly into the bloodstream and bypasses the body's ability to reject the toxin by vomiting. Administration Two reported techniques specific to alcohol enemas are by inserting into the rectum either an alcohol-soaked tampon or tubing connected to a funnel into which alcohol is poured, known as a beer bong. Enema bags of the sort used medically, e.g., to remedy constipation, are also employed. Effects and dangers Compared to drinking, alcohol intoxication begins far more quickly upon rectal consumption since the alcohol is absorbed directly into the bloodstream. The lower gastrointestinal tract lacks the alcohol dehydrogenase enzyme present in the stomach and live ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetaldehyde
Acetaldehyde (IUPAC systematic name ethanal) is an organic chemical compound with the formula CH3 CHO, sometimes abbreviated by chemists as MeCHO (Me = methyl). It is a colorless liquid or gas, boiling near room temperature. It is one of the most important aldehydes, occurring widely in nature and being produced on a large scale in industry. Acetaldehyde occurs naturally in coffee, bread, and ripe fruit, and is produced by plants. It is also produced by the partial oxidation of ethanol by the liver enzyme alcohol dehydrogenase and is a contributing cause of hangover after alcohol consumption. Pathways of exposure include air, water, land, or groundwater, as well as drink and smoke. Consumption of disulfiram inhibits acetaldehyde dehydrogenase, the enzyme responsible for the metabolism of acetaldehyde, thereby causing it to build up in the body. The International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) has listed acetaldehyde as a Group 1 carcinogen. Acetaldehyde is "one of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urine
Urine is a liquid by-product of metabolism in humans and in many other animals. Urine flows from the kidneys through the ureters to the urinary bladder. Urination results in urine being excreted from the body through the urethra. Cellular metabolism generates many by-products that are rich in nitrogen and must be cleared from the bloodstream, such as urea, uric acid, and creatinine. These by-products are expelled from the body during urination, which is the primary method for excreting water-soluble chemicals from the body. A urinalysis can detect nitrogenous wastes of the mammalian body. Urine plays an important role in the earth's nitrogen cycle. In balanced ecosystems, urine fertilizes the soil and thus helps plants to grow. Therefore, urine can be used as a fertilizer. Some animals use it to mark their territories. Historically, aged or fermented urine (known as lant) was also used for gunpowder production, household cleaning, tanning of leather an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
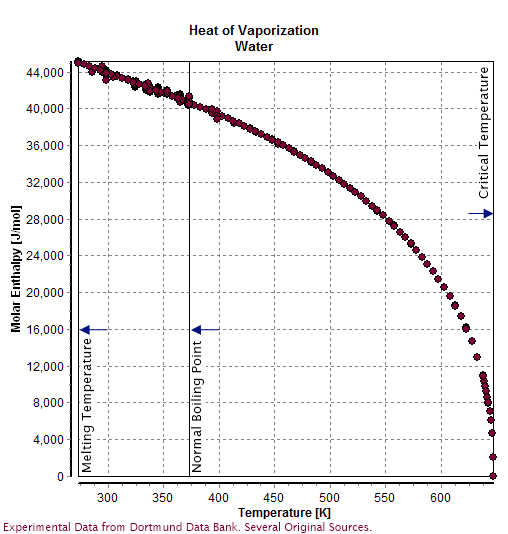
Water
Water (chemical formula ) is an inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms (in which it acts as a solvent). It is vital for all known forms of life, despite not providing food, energy or organic micronutrients. Its chemical formula, H2O, indicates that each of its molecules contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms, connected by covalent bonds. The hydrogen atoms are attached to the oxygen atom at an angle of 104.45°. "Water" is also the name of the liquid state of H2O at standard temperature and pressure. A number of natural states of water exist. It forms precipitation in the form of rain and aerosols in the form of fog. Clouds consist of suspended droplets of water and ice, its solid state. When finely divided, crystalline ice may precipitate in the form of snow. The gaseous state of water is steam or water vap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Dioxide
Carbon dioxide ( chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is transparent to visible light but absorbs infrared radiation, acting as a greenhouse gas. It is a trace gas in Earth's atmosphere at 421 parts per million (ppm), or about 0.04% by volume (as of May 2022), having risen from pre-industrial levels of 280 ppm. Burning fossil fuels is the primary cause of these increased CO2 concentrations and also the primary cause of climate change.IPCC (2022Summary for policy makersiClimate Change 2022: Mitigation of Climate Change. Contribution of Working Group III to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA Carbon dioxide is soluble in water and is found in groundwater, lakes, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metabolism
Metabolism (, from el, μεταβολή ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cellular processes; the conversion of food to building blocks for proteins, lipids, nucleic acids, and some carbohydrates; and the elimination of metabolic wastes. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to the sum of all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transportation of substances into and between different cells, in which case the above described set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary (or intermediate) metabolism. Metabolic reactions may be categorized as '' catabolic'' – the ''breaking down'' of compounds (for example, of glucose to pyruv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zero-order Kinetics
In chemistry, the rate law or rate equation for a reaction is an equation that links the initial or forward reaction rate with the concentrations or pressures of the reactants and constant parameters (normally rate coefficients and partial reaction orders). For many reactions, the initial rate is given by a power law such as :v_0\; =\; k mathrmx mathrmy where and express the concentration of the species and usually in moles per liter (molarity, ). The exponents and are the partial ''orders of reaction'' for and and the ''overall'' reaction order is the sum of the exponents. These are often positive integers, but they may also be zero, fractional, or negative. The constant is the reaction rate constant or ''rate coefficient'' of the reaction. Its value may depend on conditions such as temperature, ionic strength, surface area of an adsorbent, or light irradiation. If the reaction goes to completion, the rate equation for the reaction rate v\; =\; k cex cey applies througho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fasting
Fasting is the abstention from eating and sometimes drinking. From a purely physiological context, "fasting" may refer to the metabolic status of a person who has not eaten overnight (see " Breakfast"), or to the metabolic state achieved after complete digestion and absorption of a meal. Metabolic changes in the fasting state begin after absorption of a meal (typically 3–5 hours after eating). A diagnostic fast refers to prolonged fasting from 1 to 100 hours (depending on age) conducted under observation to facilitate the investigation of a health complication, usually hypoglycemia. Many people may also fast as part of a medical procedure or a check-up, such as preceding a colonoscopy or surgery, or before certain medical tests. Intermittent fasting is a technique sometimes used for weight loss that incorporates regular fasting into a person's dietary schedule. Fasting may also be part of a religious ritual, often associated with specifically scheduled fast days, as dete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cmax (pharmacology)
Cmax is the maximum (or peak) serum concentration that a drug achieves in a specified compartment or test area of the body after the drug has been administered and before the administration of a second dose. It is a standard measurement in pharmacokinetics. Description Cmax is the opposite of Cmin, which is the minimum (or trough) concentration that a drug achieves after dosing. The related pharmacokinetic parameter tmax is the time at which the Cmax is observed. After an intravenous administration, Cmax and tmax are closely dependent on the experimental protocol, since the concentrations are always decreasing after the dose. But after oral administration, Cmax and tmax are dependent on the extent, and the rate of drug absorption and the disposition profile of the drug. They could be used to characterize the properties of different formulations in the same subject. Short term drug side effects are most likely to occur at or near the Cmax, whereas the therapeutic effect o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethyl Sulfate
Ethyl sulfate (IUPAC name: ethyl hydrogen sulfate), also known as sulfovinic acid, is an organic chemical compound used as an intermediate in the production of ethanol from ethylene. It is the ethyl ester of sulfuric acid. History This substance was studied contemporaneously with ether by German alchemist August Siegmund Frobenius in 1730, subsequently by French chemists Fourcroy in 1797 and Gay-Lussac in 1815. Swiss scientist Nicolas-Théodore de Saussure also studied it in 1807. In 1827, French chemist and pharmacist Félix-Polydore Boullay (1806-1835) along with Jean-Baptiste André Dumas noted the role of ethyl sulfate in the preparation of diethyl ether from sulfuric acid and ethanol. Further studies by the German chemist Eilhard Mitscherlich and the Swedish chemist Jöns Berzelius suggested sulfuric acid was acting as a catalyst, this eventually led to the discovery of sulfovinic acid as an intermediate in the process. The advent of electrochemistry by Italian physici ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethyl Glucuronide
Ethyl glucuronide (EtG) is a metabolite of ethanol which is formed in the body by glucuronidation following exposure to ethanol, usually from drinking alcoholic beverages. It is used as a biomarker to test for ethanol use and to monitor alcohol abstinence in situations where drinking is prohibited, such as by the military, in alcohol treatment programs, in professional monitoring programs (health professionals, attorneys, airline pilots in recovery from addictions), in schools, liver transplant clinics, or in recovering alcoholic patients. In addition to its use to monitor abstinence and detect drinking, EtG also has potential for monitoring the amount of alcohol use over time because it can be detected in hair and nails, though the effectiveness of this has not yet been proven. A disadvantage of the test is that because EtG can be detected in samples at very low levels, it can also be positive after exposure to alcohol from non-beverage sources, or incidental exposure, which can l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Properties Of Water
Water () is a polar inorganic compound that is at room temperature a tasteless and odorless liquid, which is nearly colorless apart from an inherent hint of blue. It is by far the most studied chemical compound and is described as the "universal solvent" and the "solvent of life". It is the most abundant substance on the surface of Earth and the only common substance to exist as a solid, liquid, and gas on Earth's surface. It is also the third most abundant molecule in the universe (behind molecular hydrogen and carbon monoxide). Water molecules form hydrogen bonds with each other and are strongly polar. This polarity allows it to dissociate ions in salts and bond to other polar substances such as alcohols and acids, thus dissolving them. Its hydrogen bonding causes its many unique properties, such as having a solid form less dense than its liquid form, a relatively high boiling point of 100 °C for its molar mass, and a high heat capacity. Water is amphoteric, meani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |