|
Azulene
Azulene is an aromatic organic compound and an isomer of naphthalene. Naphthalene is colourless, whereas azulene is dark blue. The compound is named after its colour, as "azul" is Spanish for blue. Two terpenoids, vetivazulene (4,8-dimethyl-2-isopropylazulene) and guaiazulene (1,4-dimethyl-7-isopropylazulene), that feature the azulene skeleton are found in nature as constituents of pigments in mushrooms, guaiac wood oil, and some marine invertebrates. Azulene has a long history, dating back to the 15th century as the azure-blue chromophore obtained by steam distillation of German chamomile. The chromophore was discovered in yarrow and wormwood and named in 1863 by Septimus Piesse. Its structure was first reported by Lavoslav Ružička, followed by its organic synthesis in 1937 by Placidus Plattner. Structure and bonding left, The blue color of the mushroom '' Lactarius indigo'' is due to the azulene derivative (7-isopropenyl-4-methylazulen-1-yl)methyl stearate. Azulene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guaiazulene
Guaiazulene, also azulon or 1,4-dimethyl-7-isopropylazulene, is a dark blue crystalline hydrocarbon. A derivative of azulene, guaiazulene is a bicyclic sesquiterpene that is a constituent of some essential oils, mainly oil of guaiac and chamomile oil, which also serve as its commercial sources. Various soft corals also contain guaiazulene as a principal pigment. Its low melting point makes guaiazulene difficult to handle, in contrast to the crystalline nature of the parent azulene. The electronic structure (and colors) of guaiazulene and azulene are very similar. Applications Guaiazulene is an U.S. FDA-approved cosmetic color additive. It – or its 3-sulfonate – is a component of some skin care products together with other skin soothing compounds such as allantoin Allantoin is a chemical compound with formula C4H6N4O3. It is also called 5-ureidohydantoin or glyoxyldiureide. It is a diureide of glyoxylic acid. Allantoin is a major metabolic intermediate in most organisms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vetivazulene
Vetivazulene is an azulene derivate obtained from vetiver oil. It is a bicyclic sesquiterpene and an isomer In chemistry, isomers are molecules or polyatomic ions with identical molecular formula – that is, the same number of atoms of each element (chemistry), element – but distinct arrangements of atoms in space. ''Isomerism'' refers to the exi ... of guaiazulene. References Azulenes Sesquiterpenes {{hydrocarbon-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yarrow
''Achillea millefolium'', commonly known as yarrow () or common yarrow, is a flowering plant in the family Asteraceae. Growing to tall, it is characterized by small whitish flowers, a tall stem of fernlike leaves, and a pungent odor. The plant is Native species, native to temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere in Asia, Europe, and North America. It has been introduced as a feed for livestock in New Zealand and Australia. Used by some animals, the plant may have somewhat toxic properties, although historically it has been employed for medicinal purposes. Description ''Achillea millefolium'' is an erect, herbaceous, perennial plant that produces one to several stems in height, and has a spreading rhizomatous growth form. Cauline and more or less clasping, the leaves appear spirally and evenly along the stem, with the largest and most Petiole (botany), petiolate towards the base; they are long and fernlike, divided Pinnation, bipinnately or tripinnately. The infloresc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
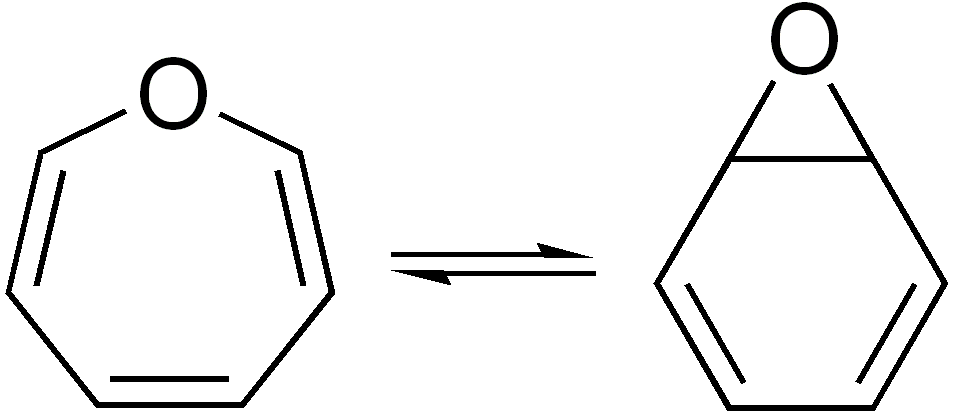
Valence Isomer
In organic chemistry, two molecules are valence isomers when they are constitutional isomers that can interconvert through pericyclic reactions. Benzene There are many valence isomers one can draw for the C6H6 formula benzene. Some were originally proposed for benzene itself before the actual structure of benzene was known. Others were later synthesized in lab. Some have been observed to isomerize to benzene, whereas others tend to undergo other reactions instead, or isomerize by ways other than pericyclic reactions. Image:Benzene-2D-flat.png, Benzene Image:Historic Benzene Formulae Dewar(1867) V.1.svg, Dewar benzene Image:Prisman2.svg, Prismane Image:Benzvalene.png, Benzvalene Image:Bicycloprop-2-enyl.svg, Bicyclopropenyl Cyclooctatetraene The valence isomers are not restricted to isomers of benzene. Valence isomers are also seen in the series (CH)8. Due to the larger number of units, the number of possible valence isomers is also greater and at least 21: Image:Cyclooc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclodecapentaene
Cyclodecapentaene or 0nnulene is an annulene with molecular formula C10H10. This organic compound is a conjugated 10 pi electron cyclic system and according to Huckel's rule it should display aromaticity. It is not aromatic, however, because various types of ring strain destabilize an all-planar geometry. Conformation, strain, and non-aromaticity Although not aromatic itself, 0nnulene can transition between different conformational isomers through aromatic or quasiaromatic excited states, such that its conformational isomerism is fixed only at extreme cryogenic temperatures. Understanding the composition and reactivity of these mixtures computationally has proven difficult, because a large number of conformations all minimize the energy locally. The all- ''cis'' isomer ( 1), a fully convex decagon, would have bond angles of 144°, which creates large amounts of angle strain relative t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entoloma Hochstetteri
''Entoloma hochstetteri'', also known as the blue pinkgill, sky-blue mushroom or similar names, is a species of mushroom that is native to New Zealand. The small mushroom is a distinctive all-blue colour, while the lamella (mycology), gills have a slight reddish tint from the spores. The blue colouring of the Sporocarp (fungi), fruit body is due to azulene pigments. Whether ''Entoloma hochstetteri'' is poisonous or not is unknown. This species was one of six native fungi featured in a set of fungal stamps issued in New Zealand in 2002. It is also featured on the New Zealand fifty-dollar note. With ''E. hochstetteris inclusion, this makes it the only banknote in the world which features a mushroom on it. In a 2018 poll, ''E. hochstetteri'' was ranked first by Manaaki Whenua – Landcare Research for its pick as New Zealand's national fungus. Naming The Māori language, Māori name for the mushroom is , because its colour is similar to the blue Wattle (anatomy), wattle of the k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
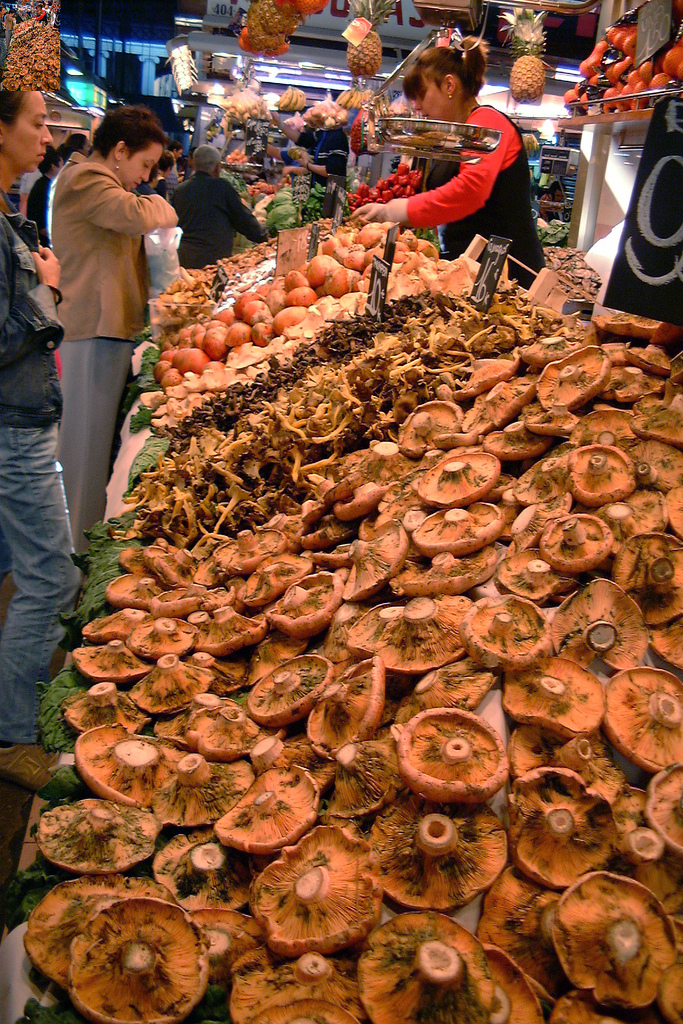
Lactarius Indigo 48568 Edit
''Lactarius'' is a genus of mushroom-producing, ectomycorrhizal fungi, containing several edible species. The species of the genus, commonly known as milk-caps, are characterized by the milky fluid ("latex") they exude when cut or damaged. Like the closely related genus ''Russula'', their flesh has a distinctive brittle consistency. It is a large genus with over 500 known species, mainly distributed in the Northern hemisphere. Recently, the genus ''Lactifluus'' has been separated from ''Lactarius'' based on molecular phylogenetic evidence. Systematics and taxonomy The genus ''Lactarius'' was described by Christian Hendrik Persoon in 1797 with '' L. piperatus'' as the original type species. In 2011, '' L. torminosus'' was accepted as the new type of the genus after the splitting-off of ''Lactifluus'' as separate genus. The name "''Lactarius''" is derived from the Latin ''lac'', "milk". Placement within Russulaceae Molecular phylogenetics uncovered that, while macromorphologic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naphthalene
Naphthalene is an organic compound with formula . It is the simplest polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon, and is a white Crystal, crystalline solid with a characteristic odor that is detectable at concentrations as low as 0.08 Parts-per notation, ppm by mass. As an Aromaticity, aromatic hydrocarbon, naphthalene's structure consists of a fused pair of benzene rings. It is the main ingredient of traditional mothballs. History In the early 1820s, two separate reports described a white solid with a pungent odor derived from the distillation of coal tar. In 1821, John Kidd (chemist), John Kidd cited these two disclosures and then described many of this substance's properties and the means of its production. He proposed the name ''naphthaline'', as it had been derived from a kind of naphtha (a broad term encompassing any volatile, flammable liquid hydrocarbon mixture, including coal tar). Naphthalene's chemical formula was determined by Michael Faraday in 1826. The structure of two f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Dipole Moment
In physics, a dipole () is an electromagnetic phenomenon which occurs in two ways: * An electric dipole deals with the separation of the positive and negative electric charges found in any electromagnetic system. A simple example of this system is a pair of charges of equal magnitude but opposite sign separated by some typically small distance. (A permanent electric dipole is called an electret.) * A magnetic dipole is the closed circulation of an electric current system. A simple example is a single loop of wire with constant current through it. A bar magnet is an example of a magnet with a permanent magnetic dipole moment. Dipoles, whether electric or magnetic, can be characterized by their dipole moment, a vector quantity. For the simple electric dipole, the electric dipole moment points from the negative charge towards the positive charge, and has a magnitude equal to the strength of each charge times the separation between the charges. (To be precise: for the definit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Debye
The debye ( , ; symbol: D) is a CGS unit (a non- SI metric unit) of electric dipole momentTwo equal and opposite charges separated by some distance constitute an electric dipole. This dipole possesses an electric dipole moment whose value is given as charge times length of separation. The dipole itself is a vector whose direction coincides with the position vector of the positive charge with respect to the negative charge: : p = ''q''r. named in honour of the physicist Peter J. W. Debye. It is defined as statcoulomb-centimetres.The statcoulomb is also known as the franklin or electrostatic unit of charge. : 1 statC = 1 Fr = 1 esu = 1 cm3/2⋅g1/2⋅s−1. Historically the debye was defined as the dipole moment resulting from two charges of opposite sign but an equal magnitude of 10−10 statcoulomb10−10 statcoulomb corresponds to approximately 0.2083 units of elementary charge. (generally called e.s.u. (electrostatic unit) in ol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Periphery
Periphery or peripheral may refer to: Music *Periphery (band), American progressive metal band * ''Periphery'' (album), released in 2010 by Periphery *"Periphery", a song from Fiona Apple's album '' The Idler Wheel...'' Gaming and entertainment *Periphery, a group of political entities in BattleTech, a wargaming franchise *'' The Peripheral'', a 2014 novel by William Gibson ** ''The Peripheral'' (TV series), a streaming series based on Gibson's novel Mathematics *Peripheral, an alternate mathematical term for boundary parallel in manifold theory *Peripheral cycle, a mathematical term in graph theory Computing *Peripheral, a device connected to a computer Political *Periphery countries, the least developed countries in world systems theory *Periphery (France), statistical area designating a commuter belt around an urban unit *Peripheries of Greece or ''administrative regions of Greece'' (Greek: , '), the country's first-level administrative divisions **Peripheral units ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |