|
Aztec Cuisine
Aztec cuisine is the cuisine of the former Aztec Empire and the Nahua peoples of the Valley of Mexico prior to European contact in 1519. The most important staple was corn (maize), a crop that was so important to Aztec society that it played a central part in their culture. Just like wheat in much of Europe or rice in most of East Asia, it was the food without which a meal was not a meal. It came in varieties that differed in color, texture, size and prestige, and was eaten as corn tortillas, tamales or ''ātōlli'', maize gruel. The other constants of Aztec food were salt and chili peppers and the basic definition of Aztec fasting was to abstain from these two. The other major foods were beans, squash and New World varieties of the grains amaranth (or pigweed), and chia. The combination of maize and these basic foods would have provided the average diet. Aztec cuisine was a very well-rounded diet without any significant deficiencies in vitamins or minerals. The cooking of m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aztec Shared Meal
The Aztecs ( ) were a Mesoamerican civilization that flourished in central Mexico in the post-classic period from 1300 to 1521. The Aztec people included different ethnic groups of central Mexico, particularly those groups who spoke the Nahuatl language and who dominated large parts of Mesoamerica from the 14th to the 16th centuries. Aztec culture was organized into city-states (''altepetl''), some of which joined to form alliances, political confederations, or empires. The Aztec Empire was a confederation of three city-states established in 1427: Tenochtitlan, the capital city of the Mexica or Tenochca, Tetzcoco, and Tlacopan, previously part of the Tepanec empire, whose dominant power was Azcapotzalco. Although the term Aztecs is often narrowly restricted to the Mexica of Tenochtitlan, it is also broadly used to refer to Nahua polities or peoples of central Mexico in the prehispanic era, as well as the Spanish colonial era (1521–1821). The definitions of Aztec and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amaranth
''Amaranthus'' is a cosmopolitan distribution, cosmopolitan group of more than 50 species which make up the genus of annual plant, annual or short-lived perennial plants collectively known as amaranths. Some names include "prostrate pigweed" and "Amaranthus caudatus, love lies bleeding". Some amaranth species are cultivated as leaf vegetables, pseudocereals, and ornamental plants. Catkin-like cymes of densely-packed flowers grow in summer or fall. Amaranth varies in flower, leaf, and stem color with a range of striking Plant pigments, pigments from the spectrum of maroon to crimson and can grow longitudinally from tall with a cylindrical, Succulent plant, succulent, fibrous stem that is hollow with grooves and bracteoles when mature. There are approximately 75 species in the genus, 10 of which are dioecious and native to North America, and the remaining 65 are monoecious species that are endemic to every continent (except Antarctica) from tropical lowlands to the Himalayas. Mem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acocil
The ''acocil'' (''Cambarellus montezumae'') is a species of crayfish in the family Cambaridae. It is endemic to Mexico, where it is known from Jalisco and Puebla. The name ''acocil'' comes from the Nahuatl ', meaning "crooked one of the water" or "squirms in the water". It is a traditional foodstuff of the Pre-Columbian Mexicans, who boiled or baked the animal, and ate it in tacos. This is a common species in its range, becoming abundant in some areas. It can be found in a number of aquatic habitat types, including artificial habitats such as canals. It is found in areas with aquatic vegetation, and it often buries itself among the roots. It can tolerate a relatively wide range of temperatures, pH, and oxygen concentrations. It is considered to be a least-concern species by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) because it is adaptable, its populations are stable, and it faces no major threats. Minor threats include the introduction of common carp The commo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crayfish As Food
Crayfish are eaten all over the world. Like other edible large crustaceans, like lobsters, only a portion of the body of a crayfish is eaten. In most prepared dishes, such as soups, bisques and étouffées, only the tail section is served. At crawfish boils or other meals where the entire body of the crayfish is presented, other parts, such as the claw meat, may be eaten. Claws of larger boiled crayfish are often pulled apart to access the meat, as seasoning and flavor can collect in the fat of the boiled interior. Regional cuisines Australia Australia is home to genus ''Cherax'' which is distinct from European, Asian and North and South American species. Two of the Australian edible crayfish are the common yabby ('' C. destructor'') and the red claw ('' C. quadricarinatus''). The common yabby is closest in size to the North American species, but is not considered to be commercially viable outside Australia because of its relatively slow growth and small size. The "red claw" c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
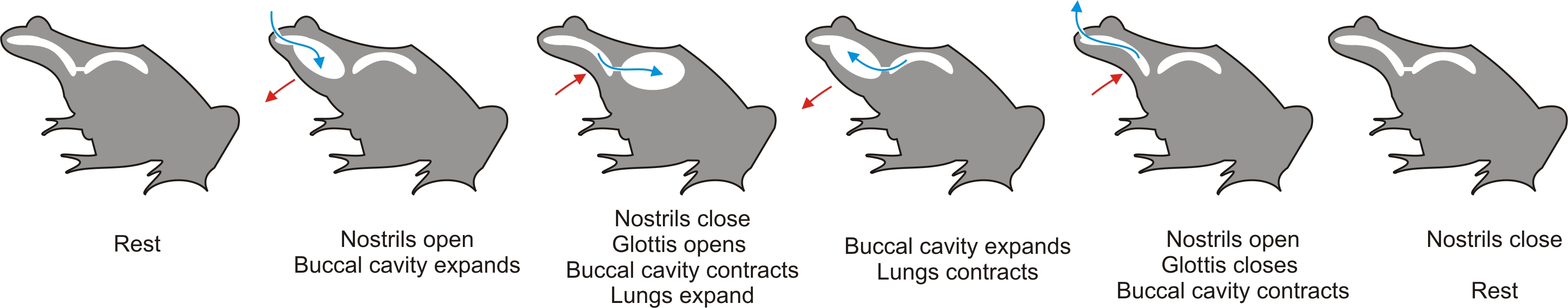
Axolotl
The axolotl (; from ) (''Ambystoma mexicanum'') is a neoteny, paedomorphic salamander, one that Sexual maturity, matures without undergoing metamorphosis into the terrestrial adult form; adults remain Aquatic animal, fully aquatic with obvious external gills. This trait is somewhat unusual among amphibians, though this trait is not unique to axolotls, and this is apparent as they may be confused with the Tadpole, larval stage or Ambystoma#Species, other neotenic adult mole salamanders (''Ambystoma spp.''), such as the occasionally paedomorphic tiger salamander (''Ambystoma tigrinum, A. tigrinum'') widespread in North America; or with mudpuppies (''Necturus spp.''), which bear a superficial resemblance but are from a different Family (biology), family of salamanders. Axolotls originally inhabited a system of interconnected wetlands and lakes in the Mexican highlands; they were known to inhabit the smaller lakes of Lake Xochimilco, Xochimilco and Lake Chalco, Chalco, and are al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Green Iguana
The green iguana (''Iguana iguana''), also known as the American iguana or the common green iguana, is a large, arboreal, mostly Herbivory, herbivorous species of lizard of the genus ''Iguana''. Usually, this animal is simply called the iguana. The green iguana ranges over a large geographic area; it is native from southern Brazil and Paraguay as far north as Mexico. A herbivore, it has adapted significantly with regard to locomotion and osmoregulation as a result of its diet. It grows to in length from head to tail, although a few specimens have grown more than with bodyweights upward of . Commonly found in captivity as a pet due to its calm disposition and bright colors, it can be very demanding to care for properly. Space requirements and the need for special lighting and heat can prove challenging to the hobbyist. Taxonomy The species was first officially described by Swedish botanist Carl Linnaeus in 1758. Since then, numerous subspecies have been identified, but later ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pocket Gopher
Pocket gophers, commonly referred to simply as gophers, are burrowing rodents of the family Geomyidae. The roughly 41 speciesSearch results for "Geomyidae" on thASM Mammal Diversity Database are all endemic to North and Central America. They are commonly known for their extensive tunneling activities and their ability to destroy farms and gardens. The name "pocket gopher" on its own may refer to any of a number of genera within the family Geomyidae. These are the "true" gophers, but several ground squirrels in the distantly related family Sciuridae are often called "gophers", as well. The origin of the word "gopher" is uncertain; the French , meaning waffle, has been suggested, on account of the gopher tunnels resembling the honeycomb-like pattern of holes in a waffle; another suggestion is that the word is of Muskogean origin. Description Pocket gophers weigh around , and are about in body length, with a tail long. A few species reach weights approaching . Within any p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
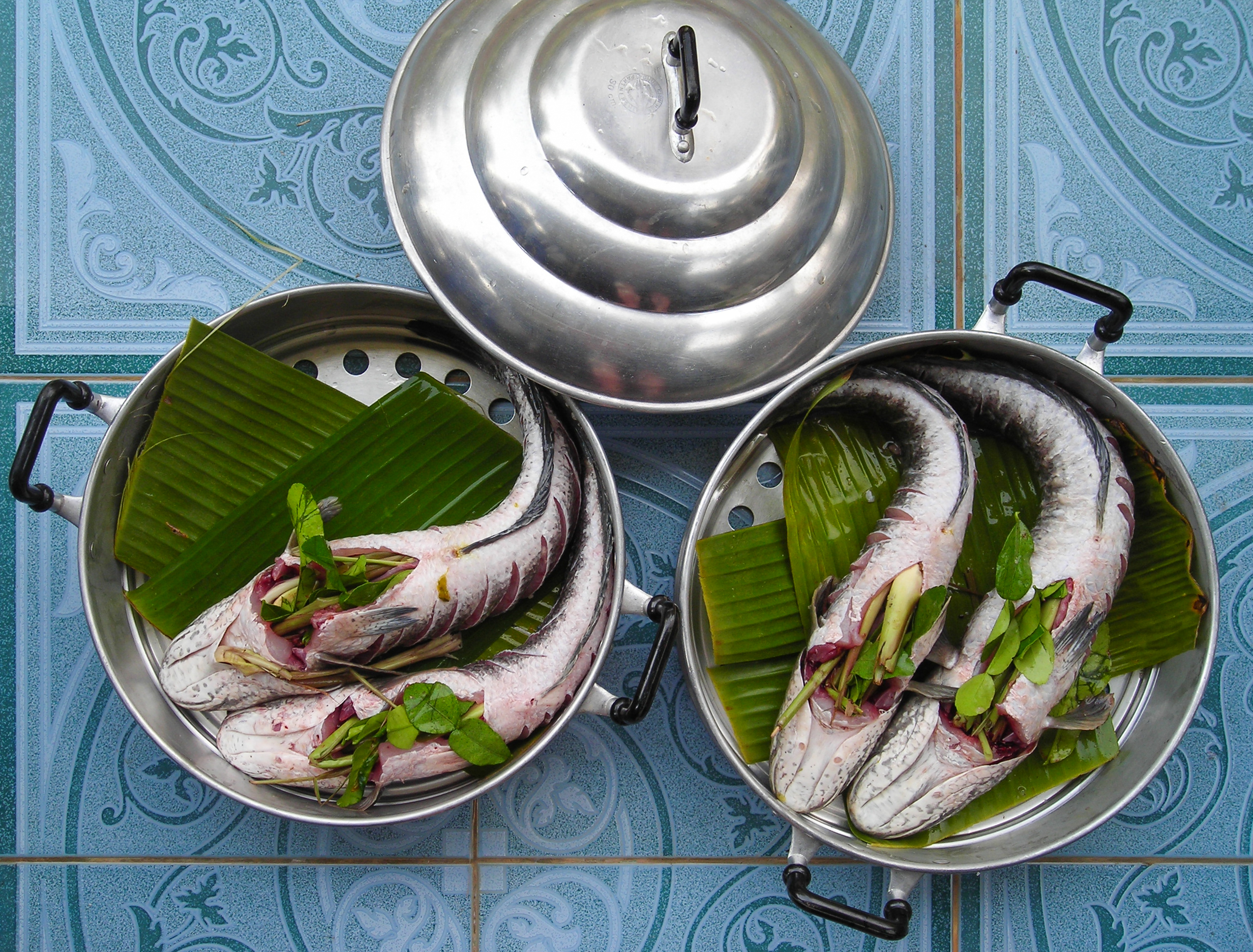
Fish As Food
Many species of fish are caught by humans and consumed as food in virtually all regions around the world. Their meat has been an important dietary source of protein and other nutrients in the human diet. The English language does not have a special culinary name for food prepared from fish like with other animals (as with '' pig'' vs. ''pork''), or as in other languages (such as Spanish '' pez'' vs. '' pescado''). In culinary and fishery contexts, ''fish'' may include so-called shellfish such as molluscs, crustaceans, and echinoderms; but, more expansively, ''seafood'' covers both fish and other marine life used as food. Since 1961, the average annual increase in global apparent food fish consumption (3.2 percent) has outpaced population growth (1.6 percent) and exceeded the increase in consumption of meat from all terrestrial animals except poultry (4.9 percent), both combined (2.8 percent) and individually (bovine, ovine, porcine, et cetera). In ''per capita'' terms, f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cacao Bean
The cocoa bean, also known as cocoa () or cacao (), is the dried and fully fermented seed of ''Theobroma cacao'', the cacao tree, from which cocoa solids (a mixture of nonfat substances) and cocoa butter (the fat) can be extracted. Cacao trees are native to the Amazon rainforest. They are the basis of chocolate and Mesoamerican foods including tejate, an indigenous Mexican drink. The cacao tree was first domesticated at least 5,300 years ago by the Mayo-Chinchipe culture in South America before it was introduced in Mesoamerica. Cacao was consumed by pre-Hispanic cultures in spiritual ceremonies, and its beans were a common currency in Mesoamerica. The cacao tree grows in a limited geographical zone; today, West Africa produces nearly 81% of the world's crop. The three main varieties of cocoa plants are Forastero, Criollo, and Trinitario, with Forastero being the most widely used. In 2024, global cocoa bean production reached 5.8 million tonnes, with Ivory Coast leading at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cacti
A cactus (: cacti, cactuses, or less commonly, cactus) is a member of the plant family Cactaceae (), a family of the order Caryophyllales comprising about 127 genera with some 1,750 known species. The word ''cactus'' derives, through Latin, from the Ancient Greek word (''káktos''), a name originally used by Theophrastus for a spiny plant whose identity is now not certain. Cacti occur in a wide range of shapes and sizes. They are native to the Americas, ranging from Patagonia in the south to parts of western Canada in the north, with the exception of '' Rhipsalis baccifera'', which is also found in Africa and Sri Lanka. Cacti are adapted to live in very dry environments, including the Atacama Desert, one of the driest places on Earth. Because of this, cacti show many adaptations to conserve water. For example, almost all cacti are succulents, meaning they have thickened, fleshy parts adapted to store water. Unlike many other succulents, the stem is the only part of most cacti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Century Plant
''Agave americana'', commonly known as the century plant, maguey, or American aloe, is a flowering plant species belonging to the family Asparagaceae. It is native to Mexico and the United States, specifically Texas. This plant is widely cultivated worldwide for its ornamental value and has become naturalized in various regions, including Southern California, the West Indies, South America, the Mediterranean Basin, Africa, the Canary Islands, India, China, Thailand, and Australia. Despite being called "American aloe" in common parlance, ''Agave americana'' is not a member of the same family as ''Aloe'', although it falls under the same order, Asparagales. Description The common name "century plant" stems from its monocarpic nature of flowering only once at the end of its long life. After flowering, the plant dies but produces adventitious shoots from the base, allowing its growth to continue. Although it is called the century plant, it typically lives only 10 to 30 years. It h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulque
Pulque (; ), occasionally known as octli or agave wine, is an alcoholic beverage made from the fermented sap of the maguey (agave) plant. It is traditional in central Mexico, where it has been produced for millennia. It has the color of milk, a rather viscous consistency and a sour yeast-like taste. The drink's history extends far back into the Mesoamerican period, when it was considered sacred, and its use was limited to certain classes of people. After the Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire, the drink became secular and its consumption rose. The consumption of pulque reached its peak in the late 19th century. In the 20th century, the drink fell into decline, mostly because of competition from beer, which became more prevalent with the arrival of European immigrants, but pulque remains popular in many parts of Central Mexico, however, and there have been some efforts to revive the drink's popularity elsewhere through tourism. Similar drinks exist elsewhere in Latin Ameri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |