|
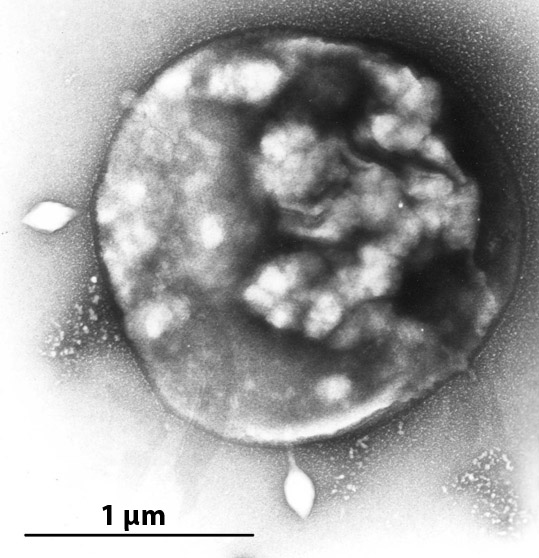
Azorudivirus
Stygiolobus rod-shaped virus (SRV), scientific name ''Azorudivirus SRV'', is an archaeal virus and the sole species in the genus ''Azorudivirus''. Its only known host is '' Stygiolobus'' archaea Archaea ( ) is a Domain (biology), domain of organisms. Traditionally, Archaea only included its Prokaryote, prokaryotic members, but this has since been found to be paraphyletic, as eukaryotes are known to have evolved from archaea. Even thou .... References Archaeal viruses Ligamenvirales {{virus-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeal Virus
An archaeal virus is a virus that infects and replicates in archaea, a domain of unicellular, prokaryotic organisms. Archaeal viruses, like their hosts, are found worldwide, including in extreme environments inhospitable to most life such as acidic hot springs, highly saline bodies of water, and at the bottom of the ocean. They have been also found in the human body. The first known archaeal virus was described in 1974 and since then, a large diversity of archaeal viruses have been discovered, many possessing unique characteristics not found in other viruses. Little is known about their biological processes, such as how they replicate, but they are believed to have many independent origins, some of which likely predate the last archaeal common ancestor (LACA). Much of the diversity observed in archaeal viruses is their morphology. Their complete bodies, called virions, come in many different forms, including being shaped like spindles or lemons, rods, bottles, droplets, and coi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stygiolobus
''Stygiolobus'' is a genus in the family Sulfolobaceae.See the NCBIbr>webpage on Stygiolobus Data extracted from the See also * List of Archaea genera This article lists the genera of the Archaea. The currently accepted taxonomy is based on the List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN) and National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). However, in the List provided bel ... References Further reading Scientific journals * * Scientific books * External links Archaea genera Thermoproteota {{archaea-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaea
Archaea ( ) is a Domain (biology), domain of organisms. Traditionally, Archaea only included its Prokaryote, prokaryotic members, but this has since been found to be paraphyletic, as eukaryotes are known to have evolved from archaea. Even though the domain Archaea Cladistics, cladistically includes eukaryotes, the term "archaea" (: archaeon , from the Greek "ἀρχαῖον", which means ancient) in English still generally refers specifically to prokaryotic members of Archaea. Archaea were initially Taxonomy (biology), classified as bacteria, receiving the name archaebacteria (, in the Archaebacteria Kingdom (biology), kingdom), but this term has fallen out of use. Archaeal cells have unique properties separating them from Bacteria and Eukaryote, Eukaryota. Archaea are further divided into multiple recognized phylum, phyla. Classification is difficult because most have not been Isolation (microbiology), isolated in a laboratory and have been detected only by their Gene, gene s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeal Viruses
An archaeal virus is a virus that infects and replicates in archaea, a domain of unicellular, prokaryotic organisms. Archaeal viruses, like their hosts, are found worldwide, including in extreme environments inhospitable to most life such as acidic hot springs, highly saline bodies of water, and at the bottom of the ocean. They have been also found in the human body. The first known archaeal virus was described in 1974 and since then, a large diversity of archaeal viruses have been discovered, many possessing unique characteristics not found in other viruses. Little is known about their biological processes, such as how they replicate, but they are believed to have many independent origins, some of which likely predate the last archaeal common ancestor (LACA). Much of the diversity observed in archaeal viruses is their morphology. Their complete bodies, called virions, come in many different forms, including being shaped like spindles or lemons, rods, bottles, droplets, and coil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |